Sports Medicine Flashcards
Older golfer falls onto butt walking on the green and has lower back pain. Common type of injury?
What to do if this was a young patient?
Lower thoracic spine compression fracture
If this is a young patient, do metabolic bone workup as this should only happen in older patients

Most common cause?

Anterior-inferior glenohumeral ligament tear
(Shoulder dislocation = 80-90% anterior due to AIGHL tear)
Presentation in adult?
Kid?

Adult = lower back pain + neuro sx (pain down leg)
Kids = pain in thigh/hamstring area OR back pain
(This is a ruptured lumbar disc)
This test is positive in a patient who would experience worsening pain when?

At night
(Drop arm test = supraspinatus tear)
What would you expect to see on imaging of young male weight lifter complaining of lower back pain without neuro sx?
Stres fracture or pars in lumbar spine

This Xray of 60 yo male. What additional PE should you do?

Rotator cuff tests
(Elderly pt with shoulder dislocation is at risk for rotator cuff tear)
This type of injury most commonly occurs at what level?

C5
(Stinger’s syndrome = traction injury = brachial plexus stretched away from side of tingling/warmth)
How would you fix this?

Extend to get it back in place
(PIP joint dislocation)
This pt who underwent this surgery is most likely what kind of athlete?

Overhead athlete (baseball player, tennis, track/field)
(This is repair of the biceps tendon ripped from the glenoid labrum = SLAP tear)
Such a fracture would be expected in a young patient if:

Caused by strong sartorius contraction during sports
(Pelvic avulsion fracture of ASIS)
This lesion predisposes to:

Arthritis of the hip because it wears on cartilage with hip flexion
(Pincer lesion - note bony mass on os coxae adjacent to acetabulum)
What PE finding?

Limited elbow flexion and forearm supination
(Distal biceps tendon rupture)
How did this pt jack himself up?

Fell on tip of shoulder
(AC joint separation)
How would this present?

Pain at base of 4th metatarsal
(Pseudo-Jones fracture = base of 5th metatarsal)
If this test is positive, what would you expect to see on CT?

Bone bruises (LFC, LTP)
(This is a positive pivot test = ACL tear)
Sx?

Popping/locking of knee + edema
(OCD of knee)
Demographic?

10-15 yo boy gymnast or weight lifter
(OCD capitellum)
Demographic?

20-30 yo
(Achilles tendon rupture)
Young drunk pt punches wall and complains of pain in his hand. What do you expect to see on Xray?
Boxer’s fracture (4th/5th digit)
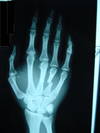
This type of injury commonly occurs at what level?

C5-6
(C spine subluxation)
A young soccer player presents with this finding. Cause?

Strong rectus femoris contraction causing fracture of AIIS
(Pelvic avulsion fracture)
Typical patient who will present with this finding?

Football player who uses head for tackling
(This is spear tackler’s spine - note loss of cervical lordosis compared to this normal cervical spine)

Most likely cause?

Jam finger (like on basketball)
(Mallet finger; unable to extend)
What precipitated this lesion?

Change in activity ~3 weeks prior
(Dreaded black line = tibial stress fracture)
Tx?

Immobilize and Xray in 3 weeks due to risk of secondary arthritis
(Scaphoid fracture)
Dx?

PIP joint dislocation
Dx?

Stress fracture of pars
(Lumbar spine)
5 yo falls from a tree with outstretched arm and has this finding. What would you counsel the parents about?

Pt needs immediate PT to avoid stiffening of elbow
(Elbow dislocation)
5 yo falls from a tree with outstretched arm and has this finding on Xray. You should counsel the parents about what?

Pt is at increased risk of recurrence
(Shoulder dislocation in young pt = increased risk of recurrence)
Complication?

Popliteal artery and/or peroneal nerve injury = must treat immediately
(Knee dislocation = 3+ ligaments torn)
This lesion results in what PE findings?

Inability to flex the DIP joint, pain in flexor tendon
(Jersey finger)
Cause?

Fall on flexed knee or direct tibial blow (dashboard injury)
This patient presents with pain in the indicated area. Xray is normal. First step in management?

Immobilize
(Snuff box pain + normal Xray = scaphoid fracture; you will Xray in 3 weeks to make sure it’s healed; risk of secondary arthritis)
Dx?

Lisfranc injury
(Injury at tarsal-metatarsal junction)
Dx?

IT fracture in kid from strong hamstrings contraction
(Pelvic avulsion fracture)
Tx?

None if older pt - mostly cosmetic
(Proximal biceps tendon rupture)
This type of movement might cause what injury?

Low ankle sprain = lateral ligament injury
Commonly seen in what kind of athletes?

Runners and baseball players
(Tibial stress fracture)
This movement could cause what type of injury?

Turf toe
(Extreme dorsiflexion of big toe)
Dx?

Psuedoparalysis of rotator cuff
Dx?

Posterior shoulder dislocation
(Light bulb sign)
Most sensitive test for ACL tear?
Lachman test

What type of athletes commonly present with this upon physical exam?

Swimmers, javelin throwers, pitchers
(Positive empty can test = supraspinatus tear)
Tx?

Figure 8 harness
(Clavicular harness)

Dx?

Type III AC joint separation
(Full AC ligament and coracoclavicular ligament tears = complete separation of acromion and clavicle)
Dx?

Common sports metacarpal fracture (3rd digit)
Inability to extend DIP joint
Mallet finger

Inability to flex DIP joint
Jersey finger

Dx?

Cam lesion
(Bony mass on femoral neck; type of femoroacetabulur impingement)
Management?

Fix immediately because it won’t fix by itself
(Patellar tendon rupture = notice displaced patella)
Dx?

ACL tear
Dx?

Jones fracture
(Metaphyseal of 5th metatarsal)
Dx?

Lisfranc injury
(Injury at tarsal-metatarsal junction)


