Spinal Cord (Back and Spinal Cord Part 1) Flashcards
cell body
contains nucleus and metabolic machineray of cell (trophic)
Dendrites
(receptive) form extension into tissues that may synapse on to one or many other neurons
Axon
Conductive
also called the “nerve fiber” = a long cytoplasmic process that can transmit nerve impulses over a long distance wihtout diminution of the amplitude of the signal
Terminal branches of axon
transmissive, make contact with other neurons at synpases
Ganglia
Groups of neuron cell bodies that lie in peripheral to the CNS in vertebrates
Pseudounipolar neurons

- somatic sensory neuron in the peripheral nervous system.
- somas in dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord
- have a single, long axon that splits into two branches
- “peripheral branch” which goes to the skin, joints, and muscles
- “central branch” which goes to the spinal cord
- fibers of the dorsal root ganglion project into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and synapse with neurons of the dorsal horn.
- axons of dorsal ganglion neurons are also known as afferents nerves.
- 1 axon, no true dendrite
- pseudounipolar neurons that detect changes in the internal and external environment and inform the CNS of the changes; cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in spinal (dorsal root) ganglia in spinal nerves or sensory ganglia of cranial nerves; enter the posterior gray horns of the CNS via posterior roots of the spinal cord or sensory nerves of the cranial nerves
exits cell body and travels through posterior root; enter spinal cord at posterior horn (or brainstem for cranial nerves) where they deliver their action potentials
multipolar neurons
has multiple dendrites and a single axon
- includes:
- most neurons
- most CNS neurons (Interneurons)
- all motorneurons
- Cell bodies in the anterior horn of the spinal cord
- axons form the anterior root.

multipolar vs pseudounipolar neuron

gray matter
H”-shaped gray matter core of spinal cord
- made up of neuronal cell bodies
- organized into anterior horn (motor cell bodies) and posterior horn (sensory cell bodies)
- thoracolumbar region {T1-L/L3) also features a lateral horn
- contains preganglionic sympathetic cell bodies organized into an intermediolateral cell column.

white matter
periphery of spinal cord
- made up of nerve fibers (axons).
- organized into specific ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) tracts.
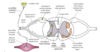


Spinal nerves carry autonomic and somatic motor nerve fibers: (2)
Spinal nerves carry sensory nerve fibers (2)
- carry autonomic and somatic motor (general visceral efferent [GVE] and general somatic efferent [GSE])
- sensory (general visceral afferent [GVA] and general somatic afferent [GSA]) nerve fibers.

Thirty-one paired spinal nerves exit the vertebral column through
Thirty-one paired spinal nerves exit the vertebral column through the intervertebral foramina or sacral foramina at each vertebral level (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal).
Anterior motor root carries
- General Somatic Efferent (GSE): motor to skeletal muscles (somatic)
- General Visceral Efferent (GVE): motor to viscera (visceral)
Carries motor (efferent) from anterior horn -> spinal nerve ->

Posterior sensory root carries:
- Sensory (affarent) from posterior horn -> spinal ganglion -> spinal nerve
- General Sensory Afferent (GSA): discriminative touch, proprioception, and pain and temperature from the skin, joints, and muscles (somatic)
- General Visceral Afferent (GVA): sensation from the viscera (visceral)

Anterior and posterior rootlets:
- arise from the spinal cord laterally, representing motor and sensory fibers, respectively
- Rootlets converge to form nerve roots, which contain autonomic and somatic motor (anterior root) or sensory (posterior root) components.

Anterior vs. posterior rami
Once the spinal nerve has exited the vertebral column, it splits into an anterior and a posterior ramus.
- Anterior rami provide motor and sensory innervation to the skin, muscles, vasculature, and joints of the trunk and extremities
- posterior rami innervate intrinsic back muscles, associated vasculature, and overlying skin.

ganglion
ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the periphery to the CNS.
Efferent
Motor
Soma in gray matter, axon extends along ventral root to eventually a spinal nerve
-multipolar neuron
(2 kinds: Voluntary (PNS) or autonomic (ANS))

Affarent
Sensory
Pseudounipolar neuron
Soma in middle at dorsal root ganglion
(2 kinds: visceral or somatic)

Dorsal root/Ventral root carry
Each only carry one type of modality
- dorsal root = sensory (affarent)
- ventral root - efferent (motor)
Spinal nerve
where mixed rami (dorsal and ventral) mix


