Special Species Exam I Material Flashcards
What is the causative agent of “wet tail” in hamsters?

Lawsonia intracellularis
This is a chinchilla penis.
What’s the arrow pointing to?

fur ring
- Fur surrounding base of penis can accumulate and form a constricting ring
- Clinical Signs: stranguria, excessive grooming of prepuce –> paraphimosis or inflammation of penis (possible emergency).
- Treatment: sedate and remove, 50% dextrose and lube to reduce swelling and replace penis
This leukocyte is unique to the guinea pig. What is it called?

Kurloff Cell
- Origin is controversial
- Highest concentration in pregnant females
- Thought to play a role in creating a physiological barrier between fetus/mother
What animals transmit monkey pox?
Gambian Giant Rat and Prairie Dogs

How is rabbit tularemia transmitted?

Deer tick, brown dog tick, Lone star tick
Also biting flies, or contact with contaminated animals and material, poorly cooked meat, aerosol transmission (*possible biological warfare)
This viral disease in ferrets produces profuse, mucoid, green slime diarrhea; lethargy, dehydration, and anorexia:
Epizootic Catarrhal Enteritis (ECE)
- Epizootic catarrhal enteritis (enteric coronavirus)
- Older animals susceptible, young are carriers
- Profuse, mucoid, green slime diarrhea; lethargy, dehydration, anorexia
- Mortality low with treatment
- Antibiotics for secondary infection
Oh snap! What’s going on with these rabbit feet?

pododermatitis
- “Sore hocks”, avascular necrosis of plantar surface of rear feet
- Predisposing factors: obesity, lack of exercise, housing (wire, metal grate, concrete, carpet), breed (Rex)
- Txt: relieve pressure on affected area
- Non-abrasive, dry surface such as rubber, towels, newspaper, antibiotics, analgesics
Name the treatments that are generally effective with ‘snuffles’ in rabbits:
Generally responsive to chloramphenicol, novabiocin, oxytetracycline, penicillin G, fluroquinolones, TMS
Choose antibiotic with rabbit GI flora in mind
T/F: Mast cell tumors in ferrets commonly metastasize
False
- Mast cell tumors and basal tumors are only common in the skin of ferrets, and don’t typically metastasize.*
- They can be itchy, bleed, and appear ulcerated; can be removed surgically if needed - prognosis is good*
T/F: Ferrets that survive the respiratory phase of canine distemper typically succumb to the neurologic stage within several weeks
True

T/F: Bacillus, Bacteroides, small numbers of E. Coli, protozoa, yeasts, and Clostridium are all normal flora of the rabbit cecum
True

T/F: Rabbits produce “night stools” or cecotropes, which look somewhat like diarrhea but actually a good source of B vitamins, VFAs and amino acids.
True

What is the most common cutaneous tumor of guinea pigs?
Trichofolliculoma
Benign, on dorsum, round and hairless

What is the treatment protocol for rabbit spirochetosis (“rabbit syphylis”)?

long acting penicillin
Procaine+ Benzathine Pen G or Combi-pen, give 2 SQ doses 4 days apart
-
Spirochetosis - “Rabbit Syphilis” (aka Vent Disease)
- Treponema canuculi venereal from doe to kit during parturition.
- Dz of young rabbits à scabs on nose and vent.
- Dx: Biopsy, PCR, treatment response
- Tx: Long acting penicillin injection – Procaine + Benzathine Pen G or Combi-pen, give 2 SQ doses 4 days apart
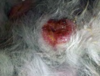
This urogenital disease in guinea pigs is the result of negative energy balance & fat metabolism during the last two weeks of gestation:
pregnancy toxemia
- CS: anorexia, lethargy, dyspnea, death
- Treatment: nutritional support – critical care diet
- Prognosis guarded
How does myxomatosis manifest in Sylvilagus species of rabbits?
In Sylvilagus species, manifests as a benign tumor at site of viral entry (typically ear base)
- Rabbit Myxomatosis (rabbit pox) – very deadly to rabbits, transmitted through arthropods
- Australia introduced this to the rabbit population to cull them “rabbit bioweapon”
- CS: lethargy, fever, anorexia, skin hemorrhages. Swelling around eyes and ear base
- In Sylvilagus species, manifests as a benign tumor at site of viral entry (typically ear base)
- Dx: CS, histopath of infected tissue and virus isolation
Canine distemper can be fatal in ferrets. What is the general treatment protocol?

no treatment
There is no treatment, so must vaccinate at 6, 10, 14 weeks old and annually
On histopathology, eosinophilic viral inclusion bodies (intracytoplasmic and intranuclear) were found in the bladder of a ferret. What is the most likely diagnosis?

canine distemper
Clinical signs: anorexia, pyrexia, chin dermatitis, photophobia, nasal or ocular discharge, brown crusts of face
T/F: Uterine adenocarcinoma is the most common neoplasia in rabbits, however it metastasizes slowly and can be cured with ovariohysterectomy
True

This occurs in prairie dogs when the root of an incisor enlarges to the point that the nasal passages become blocked, causing difficulty breathing:
odontoma

Name the mite in hamsters and gerbils that is zoonotic:
Liponyssoides sanguineus
- (house mouse mite)*
- Not common, but can bite humans and transmit Rickettsia akari (rickettsial pox)*

These neoplasias in ferrets originate from original notochord:
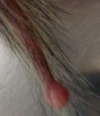
Ferret Chordomas
- Originate from original notocord
- Round, smooth, firm masses that develop on the tail tip
- Slow growing, but can metastasize
- Txt: surgical removal (tail amputation)
What is the etiological agent associated with Tyzzer’s Disease?
Clostridium piliforme
-
Tyzzers (gerbils, hamsters, mice)
-
Tyzzer’s disease – Clostridium piliforme
- “pick-up sticks” on pathology
- Clinical signs – death, dehydration, unkempt, diarrhea, etc.
- Diagnosis – often at necropsy with necrotic hepatic foci and intestinal lesions
- Predetermining factors – over crowding, poor sanitation, over heating, parasites, poor diet
- Treatment – supportive
-
Tyzzer’s disease – Clostridium piliforme

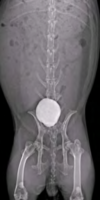
How do you diagnose urinary tract calculi in rabbits?
radiographs or ultrasound
-
Urinary Tract Calculi:
- Calculi and large amounts of calcium carbonate (urine sludge)
- Signs: calciuria with anorexia, dysuria, stranguria, hunched posture, perineal staining with calcium carbonate precipitate, reluctance to move
- DDx: bladder sludge without calculi, infectious cystitis
- Dx: radiographs or US
- Tx: SQ fluid diuresis, flush bladder (anesthesia) until urine is clear, or cystotomy with culture and stone analysis.
- May commonly recur: increase fluid consumption, change diet to decrease alfalfa (high in Ca2+)
Name four neoplasias seen in Hedgehogs:

- Mast cell tumor (MCT)
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- Neurofibroma
- Fibrous histiocytoma
What is B virus and what does it cause in humans?
Cercopithecine herpesvirus 1
- Causes fatal encephalomyelitits in humans; Mild or no signs in monkey*
- (Sir-co-pith-a-seen)*
T/F: E. coli makes up a large percentage of guinea pig gut flora
False
Guinea pig gut flora: Gram [+] bacteria with anaerobic Lactobacillus spp., coliforms, yeast, and few clostridia
T/F: Aggressive surgical debridement may be necessary in the case of dental abscess in a rabbit, including removal of affected teeth and the capsule of the abscess.
True

Describe the treatment combination for Helicobacter gastritis in ferrets:
antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, mucosal protectants, H2 antagonists
- Metronidazole + amoxicillin or clarithromycin
- Sucralfate
- Pepto-Bismol
- Famotidine or ranitidine
What is the major concern associated with tail holds in gerbils and rats?
degloving injuries

What is the most common cancer in rabbits?
uterine adenocarcinoma
- 30-80% of intact does over 3 years of age
- Most common cancer in rabbits
- Prevention and treatment: OHE prior to 6 months of age
- Spay procedure similar to dog or cat, but must ligate uterine arteries and uterine horns
Why can’t rabbits vomit?
well-developed cardiac sphincter
T/F: Mites can cause guinea pigs to seizure
True
-
Trixicarus caviae
- Sarcoptid mite causes intense pruritis sometimes to the extent of seizure
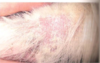
What is the most common etiology associated with otitis media/interna in ferrets?
Pasteurella multocida
- Diagnosis: radiology
- Treatment
- Enrofloxacin systemic and topical (Baytril or gentamicin) or chloramphenicol
- Flush ears with saline (under anesthesia)
T/F: Leupron is the drug of choice for medical treatment of insulinoma in ferrets
False
Leupron is the drug of choice for medical treatment of adrenal gland disease in ferrets
Name the cutaneous neoplasias in ferrets with metastatic capacity:
fibrosarcoma, sebaceous gland adenoma
What is the most common mammary tumor in rats and mice?
Fibroadenoma (80-90%)
“Camilla” a 4 1/2 year old spayed female ferret presents for bilateral hair loss of 1 month duration. PE reveals swollen vulva and palpable spleen
- CBC reveals: HGB 10.1, HCT 31%
- Chem reveals: AST 37 U/L, albumin 3.1 g/dL, globulin 2.5 g/dL, creatinine 0.2 mg/dL, glucose 100 mg/dL
- Ultrasound revealed: right adrenal gland difficult to find. Left adrenal gland enlarged. Adrenal panel pending.
What are your treatment options?
Leuprolide acetate or surgery (adrenalectomy)
What are the etiologic agents associated with cervical lymphadenitis in guinea pigs?
Streptococcus zooepidemicus and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
- Cervical lymphadenitis - “lumps”
- Streptococcus zooepidemicus Lancefield’s group C or Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
- Cervical lymph node swelling with thick purulent exudate
- May become systemic with lesions affecting the heart, lungs, kidneys, skin
- Bite wounds, abrasions in mouth from food
- Tx: surgical excision; antibiotics
- Lancing and draining is not as effective
- Yersinia is ZOONOTIC so remove prior to rupture
What are the top two locations used for venipuncture in hedgehogs?

lateral saphenous (below stifle) and cephalic
Jugular, cranial vena cava, and femoral can also be used –jugular under fat
What is the normal respiratory rate in the rabbit?
30-60 bpm
Where are cecotrophs formed in rabbits?
proximal colon and cecum
- Contains microorganisms, amino acids, VFAs and vitamins with gel coat to protect from stomach acid (so protein and vitamin absorption can occur in small intestine)
- Low fiber diet increases cecal retention time → hypomotility and reduced cecotrophs
- High protein = decreased cecotroph consumption
- High carb = excessive Clostridium spiroforme and E. coli, excessive VFA fermentation (gas and toxins produced disrupt motility, nutrient production, absorption.
- Overweight rabbits high protein/low fiber diet present for fecal matting with cecotrophes adhered to perineum
What is the normal temperature in sugar gliders?
97.2˚F
- Normal respiratory rate = 16-40 bpm
- Normal heart rate = 200-300 bpm
How would you medically treat insulinoma in a ferret?

prednisone
blocks peripheral uptake of glucose and increases hepatic gluconeogenesis

Lil Wayne cut open a rabbit and was amazed by what he found.
What is Lil Wayne pointing to?

sacculus rotundus
- The distal end of the rabbit ileum has a sacculus rotundus (spherical thick-walled enlargement, aka cecal tonsil)*
- Good job, Lil Wayne.*

What stain is used on histopathology to confirm diagnosis of Helicobacter in ferrets?
Warthin-Starry
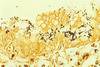
Paramyxovirus of rats and mice causing respiratory dyspnea:
Sendai virus
- Respiratory distress
- Treatment: supportive and resolves in about a week
- May exacerbate Mycoplasma pulmonis infection
- Hamsters as well
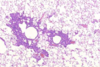
This ferret disease resembles FIP and causes pyogranulomatous inflammation in the peritoneum, liver, kidneys, pancreas, etc.
Ferret Systemic Coronavirus

T/F: Rabbits are unable to vomit, and the GI transit time can be 2-3 days, which makes fasting prior to surgery unnecessary.
True

What is the recommended IP injection volume in a mouse? What about a rat?
- Mouse: <0.5 mL
- Rat: <2 mL
T/F: Rabbits are obligate nasal breathers
True
- Dyspnea, open-mouthed breathing, agonal breathing = very stressed rabbit
- Consider anxiolytics and OXYGEN, minimal handling, analgesia, nebulization
What agent is responsible for rabbit tularemia?
Francisella tularensis
- Francisella tularensis – wild rabbits in N. America, highly virulent for humans & domestic rabbits
-
Transmission: Deer tick, brown dog tick, Lone star tick
- Also biting flies, or contact with contaminated animals and material, poorly cooked meat, aerosol transmission (*possible biological warfare)
- Signs: fever, lethargy, anorexia, septicemia, possibly death.
- Skin lesions in people, but rare in animals
- REPORTABLE
How do you diagnose insulinoma in ferrets?

blood glucose levels <70mg/dL
- Insulinoma
- β-cell tumor of the pancreas leads to hypersecretion of insulin
- CS: decreased activity, weight loss, difficult arousal from sleep, hypothermia, ptyalism, dullness, tremors, collapse. Owner may call about head pressing or standing in a corner
- Dx: blood glucose levels <70mg/dL
- Tx: prednisone – blocks peripheral uptake of glucose and increases hepatic gluconeogenesis
- Sx: nodulectomy or partial pancreatectomy
This diet in mice commonly leads to vitamin deficiency or obesity:
seed diet
This is an immune-mediated disorder in ferrets characterized by hyper- gammaglobulinemia:

Aleutian Disease
- Transmitted ferret-ferret or mink-ferret through Aerosolization of virus particles or direct contact with urine, feces, saliva, or blood
- CS: chronic weight loss, cachexia, malaise, melena, posterior paresis. Can progress to multiple organ failure and sudden death
- Dx: CS and hypergammaglobulinemia on electrophoresis (>20% of total protein)
- Tx – none
T/F: Female ferrets develop estrogen toxicity and bone marrow suppression if they are not bred
True