Solid State Chemistry Flashcards
(95 cards)
What is a solid?
A group of atoms interconnected by arrays of strong, directional chemical bonds. It’s as if they’re “super molecules.”
When this external mechanical force is applied to a solid, it will not flow.
stress
What is a crystal?
A solid whose structure is highly ordered and symmetrical over macroscopic distances
What is Haüy’s Law?
Stated by René-Just Haüy, when one cleaves a crystal, one will observe constant interfacial angles. Haüy concluded the outward symmetry implies a highly regular internal structure and the existence of a smallest crystal unit cell.
What is a symmetry element?
An potential action such as reflection or rotation that, if the new image is symmetric with the original, will perfectly superimpose that new image over the original image.
What is a crystal lattice?
A 3-D array of a network of all the points in a crystal in the same environment and of the same orientation
What is the cubic system?
A crystal lattice comprising cubic unit cells. It is the lattice of highest possible symmetry.
What is a unit cell?
The smallest space-filling body in volume that contains all structural information about its crystal
What is the shape of a unit cell in a crystal?
Parallelepiped
What are the cell constants?
The 3 edge lengths (a, b, c) and the 3 angles (α, β, γ) unique to each different kind of unit cell
What are the minimum essential symmetry and conditions on unit cell edges and angles for a hexagonal crystal system?
1X 6-fold rotation a=b, α=β=90°, γ=120°
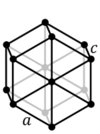
What are the minimum essential symmetry and conditions on unit cell edges and angles for a cubic crystal system?
4X independent 3-fold rotation axes (each 70.53° from each other) a=b=c, α=β=γ=90°
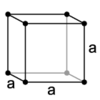
What are the minimum essential symmetry and conditions on unit cell edges and angles for a tetragonal crystal system?
1X 4-fold rotation a=b, α=β=γ=90°
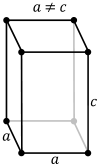
What are the minimum essential symmetry and conditions on edges and angles for a trigonal crystal system?
1X 3-fold rotation a=b=c, α=β=γ≠90°
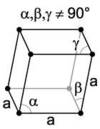
What are the minimum essential symmetry and conditions on unit cell edges and angles for an orthorhombic crystal system?
3X mutually perpendicular 2-fold rotations α=β=γ=90°
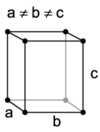
What are the minimum essential symmetry and conditions on unit cell edges and angles for a monoclinic crystal system?
1X 2-fold rotation α=γ=90°
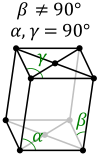
What are the minimum essential symmetry and conditions on unit cell edges and angles for a triclinic crystal system?
None, None

When would you use a nonprimitive unit cell over a primitive cell?
When the primitive cell lacks enough symmetry elements to be a unit cell
What are the 3 types of nonprimitive unit cells used to describe crystals?
1) body-centered
2) face-centered
3) side-centered
What is constructive interference?
When waves in phase encounter each other, reinforcing each other and thus amplifying the resulting wave. This occurs when the waves’ paths differ in length by a whole number of wavelengths. The amplitudes are additive.
What is destructive interference?
When waves out of phase encounter each other and combine to cancel each other out, producing a wave with an overall amplitude lesser than the originals’ average. The amplitudes are subtractive.
What is the Bragg law?
nλ = 2d sinθ
This law confirms if the waves in question are indeed diffracting on the crystal in question.

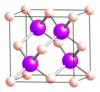
What is the simple cubic lattice?
The simplest form of crystal lattice in which the lattice points form perfect cubes with only 1 lattice point: 1 in the center. Po is the only element known to crystallize into a simple cubic lattice. Each unit cell contains 1 Po atom, separated from its neighboring Po atom by 3.35 Å.

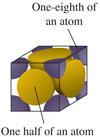
What is the body-centered cubic (bcc) structure?
A cubic unit cell form with 2 lattice points: 1 in the center and 1/8 on each corner. All alkali metals crystallize into the bcc structure.