Skull Flashcards
In anatomical position, what is the plane that is at the level of the bottom of the orbit and the opening of the external auditory meatus?
orbitomeatal plane
Identify the portion of the cranium that is blacked out and its general functions.
List the (2) parts that make up this cranial segment and the (8) bones it is composed of.

Neurocranium
Consists of dome shaped Calvaria (skullcap) and basicranium
Cranial bones:
- Frontal
- Parietal (2)
- Temporal (2)
- Occipital
- Sphenoid
- Ethmoid
Identify the portion of the cranium that is blacked out.
What is this structure formed by and what is its function?
Name the (14) bones that make up this structure

viscerocranium
Formed from the skeleton of the pharyngeal arches. Functions related to respiration, mastication/jaw apparatus.
Facial bones:
- Maxillae (2)
- Zygomatic (2)
- Nasal (2)
- Lacrimal (2)
- Inferior nasal conchae (2)
- Palantine (2)
- Vomer
- Mandible
Describe the composition of the bone formign the calvaria.
outler layer of dense bone, spongy bone sandwitched between the dense cortical bone
spongy bone = diploe (large communicating venous channels)
What is the name for fibrous interlocking joints of the skull?
sutures (synarthroses)
What is the name for cranial bones connected by cartiledge during childhood?
synchrondroses
Which layer of cranial bone is most susceptible to fracture?
The inner layer of compact bone is distinctly thinner and more prone to injury. It can fracture with outer lamina still in tact.
What type of calvaria fracture results in a fragment of bone being depressed inward, compressing and/or injurign the brain?
depressed fracture
What type of calvarial fracture results in the bone breaking into several pieces?
comminuted fractures
What type of calvarial fracture occurs at the point of impact, but fracture lines often radiate away in two or more directions?
linear fractures (most common)
What type of calvarial fracture results in a fracture on the opposite side of the trauma?
contrecoup fracture
What is the name of landmarks that are used radiographically to make cranial meausrments and document abnormal variations?
craniometric points
What is the name of the craniometric point indicated by the picure. Describe its location with relation to sutures.

Nasion: the point on cranium where frontonasal adn internasal sutures meet
What is the name of the craniometric point indicated by the picure. Describe its location with relation to other structures.

Glabella: smooth prminence most marked in males; on frontal bones superior to root of nose between eyebrows
What is the name of the craniometric point indicated by the picure. Describe its location with relation to other structures.

Bregma: the point on calvaria at junction of coronal and sagittal sutures
What is the name of the craniometric point indicated by the picure. Describe its location with relation to other structures.
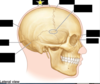
Vertex: the superior point of the neurocranium, in middle with cranium oriented in an anatomical plane
What is the name of the craniometric point indicated by the picure. Describe its location with relation to other structures.

Lambda: the pont of calvaria at junction of lambdoid adn sagittal sutures
What is the name of the craniometric point indicated by the picure. Describe its location with relation to other structures.

Pterion: a line/suture junction of greater wing of spenoid, squamous temporal, frontal and parietal bones (H)
What is the name of the craniometric point indicated by the picure. Describe its location with relation to other structures.

Asterion: star-shaped; located at junction of three sutures:
- parietomastoid
- occipitomastoid
- lambdoid
What is the name of the craniometric point indicated by the picure. Describe its qualifying characteristic.

Inion: most prominent point of external occipital protuberance
Why can a fracture at the pterion be life-threatening?
It overlies the anterior branches of the middle meningeal vessels, which runs in the grooves on the interal aspect of the lateral wall of the cranium. A rupture of these bones could rupture the meningeal artery, resultign in an epidural hemtoma.
What is the name for “soft spots” on the head present in neonates?
frontanelles
Name this fontanelle and describe its location.

Anterior: junctin of parietal adn frontal bones
Name this fontanelle and describe its location.

Posterior: junction of parietal and occipital bones

































