Skin Discoloration Flashcards
A baby with blue hands and feet
What is the most likely diagnosis?
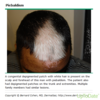
Acrocyanosis- a physiologic condition caused by increased tone of peripheral arterioles, usually in response to chilling
What is the most likely diagnosis?

Cutis Marmorata
a normal response to chilling- it can be a sign of sepsis in an unwell appearing child who has never exhibited CM before
What is the most likely diagnosis?
is this condition present at birth?
what is present in the pustules?
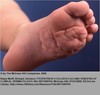
Transient Neonatal Pustular Melanosis
this is present at birth- but the vesicopustules or ruptured pustules disappear within 24-48 hours leaving pigmented macules with a scale.
The pustules are filled with neutrophils
pinpoint clear vesicles that suddently erupt over large areas- frequently in newborns
What is the most likely diagnosis?
How do we differentiate this from TNPM?
Miliaria crystallina occurs when the baby is overly warm mostly on the trunk
It can occur in the first few days to monts of life dt immature sweat ducts
this rarely presents on day 1 (TNPM is present at birth)
a flat, grey to bluish-black macule most often found on the lumbosacral area or buttocks
What is the most likely diagnosis?
is there an increased risk of malignancy?
Mongolian Spots are most common in black and Asian infants
there is NO risk of malignancy
A pale pink macules or poorly circumscribed patch that is completely flat- it becomes more apparent during crying, holding her breath, or physical exertion that blanches when pressed
What is the most likely diagnosis?
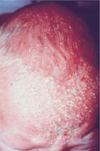
Salmon Patch (nevus simplex)
this is the most common vascular lesion of infancy and is present at birth.
50% on the posterior persist.
Some have a matching patch on the forehead
Macular, sharply circumscibed, pink to purple, and usually unilateral. This lesion does not blanch.
The lesion is present at birth and remains throughout life
What is the most likely diagnosis?
what is the etiology
what are complications?
Port wine Stain (nevus flammeus)
is often present in the head and neck region and can cause hypertrophy of underlying structure dt mature dilated dermal capillaries
Consider sturge-weber if it is located on the face or Klippel-Trenaunay-Wever if located on the extremities
What is Sturge-Weber Syndrome
What are other s/s of this condition?
Port-wine stain over the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve
Intracranial calcifications, seizure disorder, hemiparesis (contralateral), glaucoma, mental retardation, developmental delay
What is Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber Syndrome
A port-wine stain on an extremity associated with significant local overgrowth of soft tisue and bone
rapidly growing and raised (protrude from the surface of the skin) lesion. The lesion does not blanch and is usually not noticed within the first few days of life

Superficial HI i.e. “strawberry” capillary hemangiomas
usually found in the head and neck regions
Proliferative phase 9-12 months
Most of these (80%) resolve on their own by 6-10 yo.
remember: port wine= flat supeficial HI= raised
Kassaback-Merritt Syndrome
Kasabach-Merritt Syndrome is a rapidly enlarging hemangioma causing:
activation of the clotting system
coagulopathy
Thrombocytopenia
hemolytic anemai
the babies look VERY sick bc they are in shock.
Tx: excision, interferon, steroids, local radiation, or laser photocoagulation
What are some complicaitons of Superficial HI based on location?
beard
Near eye
Tip of nose
Lumbosacral
Beard= Airway compromise
Near Eye= Strabismus (lazy eye), Amblyopia, Astigmatism
Tip of Nose= altered growth of the septum
Lumbosacral= Get and MRI, tethered cord, spinal dysraphism, imperforate anus, renal anomalies, sacral anomalies
Common in adolescence and young adulthood
numerous small, circular, white, scaling papules/patches on teh upper trunk
lesions are hypopigmented
What is the most likely diagnosis?
How do we diagnose this?

Tinea Versicolor Malassezia furfur overgrowth
the hypopigmented areas of infection will have a faint yellow-green fluorescence under a Wood’s lamp
KOH of scraped scales has“spaghetti and meatballs” appearance
What is shown in the bottom picture?
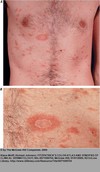
Herald Patch
Oval, slightly raised plaque or patch, salmon-red, fine collarette scale at the periphery
Fine scaling papules and plaques with marginal collarette that are dull pink or tawny. They are scattered with characteristic distribution following the lines of cleavage in a “Christmas tree” pattern
These lesions are usually confined to the trunk
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Seasonal DIstribution?
Pityriasis Rosea
a/w viral infections but true cause is unknown
Spring and Winter
Bening and self limited usually remits spontaneously in 6-12 weeks and is not contagious