Skin Cancer, malignant tumors of the skin Flashcards
(36 cards)
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer (NMSC) risk factors:
what is the most common cause of BCC?
Other than UV radiation, what are other factors?
- Occurs more frequently in fair skinned individuals in geographic areas with higher UV exposure
- UV radiation is the most common cause of BCC
- Also occur after ionizing radiation, arsenic or polycyclic hydrocarbon exposure
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)

Of the subtypes, which one is the most common?
- Most common malignancy in the US
- An estimated 2.8 million are diagnosed annually in the US
- BCCs are rarely fatal, but can be highly disfiguring if allowed to grow.
Subtypes:
•Superficial (15%)
•Nodular (75%)**
–Micronodular
–Pigmented (6%)
- Infiltrative (5%)
- Sclerosing/ Morpheaform (3%)

Superficial basal cell carcinoma:

Superficial cell carcinoma

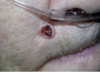
Nodular Basal Cell carcinoma

Raised papule or nodule with a central crater. In some cases, sides of crater are surfaces by telangiectatis vessels (from Goljan)
Basal cell carcinoma

Desmoplastic BCC

Pigmented BCC

BCC

What are the genetic defects in BCC?
Loss of function of _____ gene, which normally blocks _______.
What is a treatment drug that inhibits smoothened?

- The majority of BCCs have a loss of function of PTCH1 gene which normally acts to block smoothened (SMO) a transmembrane protein.
- **Vismodegib, an inhibitor of smoothened, was approved January 2012 for the treatment of advanced BCC

Actinic Keratosis

Intraepidermal neoplasia
It is a precursor for what type of cancer?
- AKs are the most common precancer affecting more than 58 million Americans
- Approximately 65 percent of all *squamous cell carcinomas and 36 percent of all basal cell carcinomas arise in lesions that previously were diagnosed as AKs
How do you treat it?
•Cryosurgery
–->Liquid nitrogen (boiling point of -196 C)
- Topical 5-fluoruracil
- Topical Imiquimod
- Topical Diclofenac
- Photodynamic therapy
- Sun protection
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Much more commonly in what kind of patients?
When SCC can begins within scars, skin ulcers or other areas of chronic injury and an SCC in these situations is called a _________.

- Second most common cutaneous malignancy.
- Occur much more commonly in immunosuppressed pts, especially organ transplant pts
- Risk factors: UV damage, thermal injury, radiation, HPV, burn scars (Marjolin’s ulcer) and chronic injury (i.e. EB)

SCC subtypes


SCC

SCC

Keratoacanthoma

Growth usually occurs rapidly, over _______.
Characterized by a crater with a ________ plug.
- Distribution- primarily sun-exposed skin
- Rapid growth over 6-8 weeks
- Size- 1-3 cm
•Crateriform endophytic and exophytic nodule with central keratin plug
•Complications- deep invasion without regression in 10-20%

Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Common in which part of the face?

- Hyperkeratotic papule with variable size and thickness
- Typically found on chronically sun damaged skin
- Metastasis occurs in 0.3-5%, but is more common in SCC of the lip (10-30%)
**Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin, and also usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer.

Skin cancer and transplant patients:
**Patients who have received an organ transplant have a higher risk than normal for developing skin cancers, in some cases up to 65 times the risk, compared with non-transplant patients.
In particular, transplant recipients have a significantly increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinomas. SCC is more likely to spread (metastatic SCC) in organ transplant recipients, and may lead to the death of the patient (from internet).
Which skin cancer is more likely to develop in the recipient of a transplant?
Which T cells are important in assessing the risk of developing a skin cancer for a transplant recipient?
- SCC = 65 fold risk
- BCC = 10 fold risk
- Melanoma = 3.4 fold risk (lowest)
- Kaposi’s sarcoma = **84 fold risk
What are some risk factors?
•Age, Skin type, UV radiation
- Genetic Factors
- HPV (in 65-90% of SCC)
•Level of immunosuppression:
–CD4 count
–Medications
–*Heart > Kidney > Liver

What are some common treatments for Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer?

- Topical 5-fluoruracil
- Topical Imiquimod
- Cryosurgery
- Electrodessication and Curettage
- Excision
- Mohs micrographic surgery
- Radiation
Malignant melanoma

A = Asymmetry
B = Border irregularity
C = Color variegation
D = Diameter greater than 6 mm
E= Evolution (or change)
Melanoma may arise within a previously existing nevus or dysplastic nevus, but approximately 70% of the time, they arise de novo. Superficial spreading melanomas typically show the ABCD’s of melanoma (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variegation and Diameter greater than 6mm). Many people as look at E for evolution or change. A new tool used in diagnosing melanoma is looking for the “Ugly Duckling”, or the mole(s) that look different from their neighboring moles.

Malignant melanoma

Relative risk
Melanoma facts

Melanoma Statistics

Melanoma

Malignant melanoma
Clinical features:
Affects what age groups?
•Affects all age groups
–**53 years = median
•Distribution
–-> Blacks-acral** (Acral melanoma is a type of skin cancer that occurs on fingers, palms, soles, and nail beds) and **mucosa
–Men- back
–Women- legs (torso in females age 15-29, perhaps due to tanning).
Malignant melanomas

Variants:
Which one is the most common type?
- **Superficial spreading—–>70%
- Nodular—–>15-30%
- Lentigo maligna melanoma—–> 5%
- Acral lentiginous——> 2-10%
What is Breslow’s depth?
Lesions with less than ______ have an excellent prognosis with infrequent metastasis.
Melanomas thicker than ____ mm have a poor prognosis with a 5-year survival of 50%.
The most important indicator of prognosis for all subtypes of melanoma is the Breslow depth, which is the maximal thickness of tumor invasion as measured by an ocular micrometer, from the top of the granular layer of the epidermis to the base of the neoplasm.
Breslow depth is recorded in millimeters with lesions less than 1.0 mm having an excellent prognosis with infrequent metastases and melanomas thicker than 4mm having a rather poor prognosis with a 5-year survival of approximately 50%. The most common sites of local and/or regional metastases are the draining lymph node basins and the skin between the primary site and these lymph nodes whereas the most common sites of systemic metastases are the lung, liver, brain, and gastrointestinal tract.

What is Clark’s level?
Another system, called the Clark level, describes how far a melanoma has penetrated into the skin instead of actually measuring it. The Clark level of a melanoma uses a scale of I to V (with higher numbers indicating a deeper melanoma) to describe whether:
–>the cancer stays in the epidermis (Clark level I)
–>the cancer has begun to invade the upper dermis (Clark level II)
–>the cancer involves most of the upper dermis (Clark level III)
–>the cancer has reached the lower dermis (Clark level IV)
–>the cancer has invaded to the subcutis (Clark level V)
Malignant melanoma treatment:
•Surgical excision
–MM in-situ: 0.5 cm with subcutaneous tissue
–MM < 1 mm: 1 cm margin to fascia
–MM > 1 mm: 1-2 cm margins to fascia with sentinel node biopsy