Sketchy Pics Flashcards
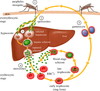
Describe how cholesterol is transported throughout the body
- Absorbed into enterocytes and packaged into chylomicrons as cholesterol esters
- chylomicrons drop TG off into peripheral tissues via LPL - once depleted of TGs chylomicron remnantes are taken up by liver by apoE binding to LDL-R (receptor mediated endocytosis)
- Cholesterol either uesd in bile acid resins or repackaged and sent out as VLDL
- VLDL deliver TG from liver to periphery, converted to LDL as lose TG
- then LDL taken up by liver via receptor-mediated endocytosis

2 actions that make HDL the ‘good’ cholesterol
(a) LCAT
(a) LCAT enzyme converts free cholesterol into cholesterol esters that can be transported by HDL
Fxn of HDL: extracts cholesterol from peripheral tissues
- HDL transports chol esters to LDL and VLDL to be transported back to the liver
- HDL directly delivers chol esters to liver via scavenger-1 receptor
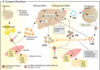
Explain how NSAIDs cause anti-inflammatory effects and unwanted side effects
NSAIDs = says in the name ‘non-selective’ = inhibits BOTH COX1 and COX2
- COX1 responsible for making TXA2 (stimulates plt aggregation) and prostaglandins (stimulates gastric mucus secretion
- COX2 makes prostaglandins that stimulate inflammation, pain, and fever
- so benefits of NSAIDs come from inhibition of COX2, while side effects come from inhibition of COX2

Mechanism of aspirin
(a) Risk to GI tract
(b) Anti-platelet
(c) Anti-inflammatory
Aspirin (NSAID) inhibits COX1 and COX2, but mostly COX1 at low doses
(a) COX1 catalyzes arachadonic acid –> prostaglandins that stimulate GI mucus production
(b) COX2 catalyzes arachidonic acid –> TXA2 that stimualates platelet aggregation
(c) Since mostly COX1 inhibition at low doses, low dose aspirin is much more an anti-platelet than an anti-inflammatory, use Iburprophen instead as anti-inflammatory

Mechanism of allopurinol
Allopurinol = xanthine oxidase inhibitor to inhibit 2 steps in urate production

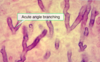
How to differentiate gout and pseudogout
Gout: from urate crystal deposition, urate crystals are negatively birefringent and needle shaped
Pseudogout: calcium pyrophosphate crystals are positively birefringent (blue colored) and rhomboid shaped
- very similar clinially! acute monoarticular inflammation
- same acute tx: NSAID, if needed prednisone, can add colchicine

Differentiate mechanism of 5-FU and MTX
5-FU inhibits thymidylate synthase to reduce dUMP –> dTMP (inhibit thymidine synthesis)
While MTX irreversibly inhibits dihydrofoate reductase (DHF –> THF)
-both hit cell cycle during S-phase (inhibit synthesis of new DNA material)

Explain adjustment that must be made when starting a pt on azathioprine on allopurinol therapy
Azathioprine (prodrug of 6-MP) is broken down in part by xanthine oxidase (inhibited by allopurinol)
-when allopurinol on board, need to reeduce azathioprine dose by 75% to prevent toxicity (b/c you’re excreting so much less)

Mechanism of azathioprine
Azathioprine is quickly converted to 6-MP
6-MP then activated by HGPRT to block IMP synthesis
-IMP = precursor used to make both AMP and GMP in purine synthesis
=> azathioprine (via 6-MP) acts as a cyto-toxic agent via inhibiting de novo purine synthesis (cell-cycle specific to S-phase)

Differentiate mechanism of azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil
Both Azathioprine (6-MP) and mycopheolate mofetil work to inhibit de novo purine synthesis
- 6-MP inhibits IMP production from PRPP
- while mycophenolate mofetil inhibits IMP dehydrogenase which is needed to convert IMP to GMP (so just one step down in the same pathway)

Describe the presentation of opioid abstience syndrome
Abstinence syndrome from opioids (aka opioid withdrawal): “moist”
- rhinorrhea, lacrimation, vom/dio
- classic yawning
- mydriasis
- hyperventilation, hyperthermia, anxiety, muscle aches

Name 4 bacteria that form pink colonies on MacConkey agar
Lactose fermenters grow pink on MacConkey agar
4 lactose fermenters: E. Coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia

Two bacteria that exhibit bipolar ‘satefy-pin’ staining
Meaning the two ends of the cells take up the most stain
- Yersinia pestis- gram neg bacilli of the GI tract that causes bloody diarrhea
- Pasteurella multocida: zoonotic that causes cellulitis or osteo after cat or dog bite

What is the Warthin-Starry stain used to visualize?
Bartonella Henselae (G- bacilli that causes cat scratch disease and bacillary angiomatosis) visualized by Warthin-Starry stain (special type of silver stain)
Clinically used when biopsy skin lesion of HIV pt to differentiate Bartonella Henselae (tx w/ Doxycycline) vs. Kaposi sarcoma

Differentiate the two stages of chlamydia in its life cycle
Chlamydia species: ‘elementary enters, reticular replicates’
Elementary body is the infectious form that enters the cell (chlamydial species are obligate intracellular organisms b/c can’t produce their own ATP), while the reticular body is the active dividing form that replicate inside the cell

Mechanism of bactrum
Bactrum = combo drug w/ synergistic activity (bacteriostatic alone, bacteriocidal togther), blocks folate synthesis at two sequential steps
- SMX (sulfa drug) = PABA analog that blocks PABA –> DHF
- TMP blocks dihydrofolate reductase to block DHF –> THF

Which viral infection of upper airway of this child?

‘Steeple sign’ like the steeple of a churc seen in croup = laryngotracheobronchitis = parainfluenza
-member of paramyxovirus family: ss negative sense RNA viruses, enveloped
Clinically: seal bark cough w/ inspiratory stridor

Histologic finding diagnostic of rhabdovirus
(a) Location
Rhabdovirus (negative ssRNA, enveloped w/ helical capsid) causes rabies
Histologic finding pathognomonic for rabies = Negri bodies (eosinophilic inclusions) in
(a) hippocampal pyramidal cells and Purkinje cells

What are Cowdry bodies?

Cowdry bodies = eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions seen in cells infected w/ herpes virus family (HSV, CMV, VZV, HHV)
-key is that they’re intranuclear (not in the cytoplasm)
Essentially diagnostic for HSV (MC)

FIndings of HSV Encephalitis

HSV causes temporal lobe encephalitis = necrosis and hemorrhage of temporal lobe b/l
-Clinically: seizures, confusion, personality changes
MC cause of sporadic encephalitis in the US

Peripheral smear findings of EBV
Irregular/atypical lymphocytes called Downey cells = reactive cytotoxic CD8 T cells
-lymphocytes w/ more than usual cytoplasm, irregularly shaped nucleus

Dx

‘Owl eye’ intracellular inclusions pathognomonic for CMV

HIV pt w/ CD under 200 p/w progressive personality change and neurologic symptoms

Dx = PML = progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
-see non-enhancing multifocal lesions of the white (leuk) matter
Triad of congenital toxo
- intracranial calcifications
- chorioretinitis
- hydrocephalus => seizures