Six Sigma Tools (Measure) Flashcards
1
Q
7 Basic Quality Tools
A
- Provide a structured approach to understanding process variation, identifying its causes, and eliminating the causes
- The tools include: process flow diagrams/value stream maps; checksheets; bar charts/histograms; run chart; pareto analysis; scatter plots; fishbone/cause-and-effect diagrams.
2
Q
Process flow diagrams
A
- Circle: start and end points
- Square: tasks
- Arrows: flows
- Downward triangle: waits
- Diamond: decision points

3
Q
Value stream mapping (why use it)
A
- Helps visualize the flow across more than just a single process
- Helps see waste (muda) and sources of waste
- Ties together the principles of lean thinking (avoid “cherry picking”)
- Forms the basis of an implementation plan to help design the whole door to door flow
- Shows the relationship between material and info flow
- provides a common language
4
Q
Value stream mapping (how)
A
- Select a product family
- Draw current and desired states (Gemba, go back and forth between current and desired states, which could take between 3-6 months).
- Work plan
5
Q
Checksheets
A
- List problems;
- Count numbers of occurrence

6
Q
Hard savings
A
- Directly flow to the P &L
- Do the same amount of biz with less employees (cost savings) or handle more biz without adding people (cost avoidance).
7
Q
Soft savings
A
- Hard to quantify
- Benefits such as reduced time to market, cost avoidance, lost profit avoidance, improved employee morale, enhanced image for the organization and other intangibles.
8
Q
Gage R&R
A
- A statistical tool that measures the amount of variation in the measurement system arising from the measurement device and people taking the measurement.
- Application: Each employee will measure each item multiple times (repeatability) and their average measurement of each item will be compared to the average for the operators or measurement tools (reproducibility).
- If the variation of repeatability and reproducibility exceeds 10% of the tolerance width (upper limit – lower limit), then it is recommended to make improvements in the measurement system to reduce the variation.
9
Q
Defects
A
Non-conformance to customer specifications
10
Q
DPMO
A
- Defects per million opportunities
- DPMO = (No. of defects observed)/ (No. of units produced) * (Number of defect opportunities) * 1, 000,000
- Convert DPMO into a sigma level - A 1.5 sigma shift (“process walk” ) process should be considered in most cases, as short-term measurement is used to predict long-term performance of the process.
11
Q
Urgent/Important Matrix
A
- Basically a prioritization tool
- Prioritize urgent & important
- Delegate urgent & unimportant
- Schedule non-urgent and important
- Don’t do non-urgent & non important
12
Q
Breakthrough Equation
A
- Basically, an equation that summarizes six sigma
- The objective is to discover an appropriate level of knowledge regarding the Xs and their deterministic effect on Y so that only a tolerable level of ε risk remains.
- Y is the outcome/results
- X represents the inputs
- f is the function, the way or process by which the inputs are transformed into outputs
- e is the error, or uncertainty surrounding how accurately the Xs are transformed to create the outcome.
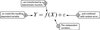
13
Q
Takt time
A
- Takt time is the rate at which a finished product needs to be completed in order to meet customer demand.
- e.g. if a company has a takt time of 5 minutes, that means every 5 minutes a complete product, assembly or machine is produced off the line because on average a customer is buying a finished product every 5 minutes.
- It’s a pull system, try to avoid overproduction
- Takt time = Available time for production per day / Customer demand per day

14
Q
Capability analysis
A
- Cp
- Cpk
- Whether meet customer specifications.


