Shoulder Exam Flashcards
(14 cards)
Structures to Identify
clavical, humerus, scapular spine, Ac joint, acromion, glenoid, GH joint, sternoclavicular joint, infraspinatous, supraspinatous.
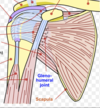

Inspection procedure (whatre you inspecting for)
looking for: wasting/atrophy, swelling, symmetry of: SWAS of the DSI
deltoids
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
looking for: abnormalities in the countour of: Con of SACA
- sternoclvicular joints
- clavicles
- AC joints
- acromion
Palpating for __ __ __ __ TDWS on both sides at which structures
tenderness, deformities, warmth, swelling. S3C2BAG
- sc joint
- clavicle
- coracoid process
- bicipital groove
- AC joint
- GH joint
- scapular spine (around the medial border and lateral border)
- Subacromial bursa for tenderness
Active ROM
forward flexion
backward extension
Abduction
Adduction
External Rotation in abduction and adduction
internal rotation in abduction and adduction
protraction
retraction
elevation
depression
When should Passive ROM be checked
if active ROM is limited, except for abduction which should always be checked actively and passively.
Passive ROM
flexion, extension, abduction, adduction,external rotation and internal rotation.
Strength training
same motions as active.
forward flexoin
backward extension
abduction/adduction
external rotation and internal rotation in (abduction and adduction)
protraction
retracton
elevation
depression
test for acromio-calvicular disorder
cross arm test
- pain in the acromioclavicular joint suggests arthritis or subluxation of this joint.
- this test puts pressure on the AC joint and will elicit pain if there is pathology in that joint
useful to differentiate from an impingement syndrome.
the cross arm test can differentiate between an ___ disorder or an ___ syndrome
between an ac disorder or an impingement syndrome
Two tests for bicipital tendonitis
- yergasons test- supinate against resistence.
- speeds test: have the patient flex forward the shoulder against resistance with the elbow in extension and foraem in supination
frozen shoulder test
Passively abduct the shoulder while having the other hand on the scapulothoracic joint. if shoulder is frozen, you will feel the scapula provide most of the movement
test for GH stability
appregension test
3 tests for impingement syndrome
- painful arc test: passively abduct the patients arm through 180 degrees. if the patient has pain throuhg the mid portion of this arc, it may suggest rotator cuff disorder or subacromial bursitis
- neers test: passive or active: stabilize the scapular to minimize movement of the scapulothoracic joint. when the arm is in prone position, the arm is flexed though 180 degrees .if the patient feels pain in the subacromial area, this suggests a rotator tendon impingement.
- hawkins test. flex the shoulder to 90 degrees. bend the elbow inwards 90 degrees the foricbly internally rotate the shoulder


