Session 5: The Airway and its Relations A Flashcards
What type of epithelium lines the conchae? Why is this type of epithelium beneficial? Is this type of epithelium present throughout the airway?
Respiratory Epithelium: ciliated, pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells. It increases the surface area for warming and humidifying the inspired air (conchae are also referred to as turbinate bones).
Most of the respiratory pathways is lined by this type of epithelium (including pharynx, which has respiratory epithelium + stratified squamous epithelium). However, bronchioles have ciliated simple cuboidal epithelium

What name is given to the gaps between conchae?
Meati (superior, middle, inferior)
What is the name of the space superior to the superior concha?
Sphenoethmoidal Recess- this is an area above the superior conchae and it has an opening which enters the sphenoidal sinus

Which sinus drains into the sphenoethmoidal recess?
Sphenoidal Sinus
What is the word used to describe the action does the epiglottis perform to close off the laryngeal inlet?
Retroflexion
What is the role of the pharyngotympanic tube (Eustachian tube)?
Equalises the pressure on either side of the tympanic membrane by allowing a connection between the middle ear and the nasopharynx
Where are the ethmoidal cells found?
Medial to the orbit
What is the clinical relevance of the sphenoid sinus in relation to the pituitary gland?
It is penetrated in transphenoidal hypophysectomy
Where do the posterior ethmoidal air cells drain?
Lateral wall of the superior meatus
What significant structure is found inferior to the middle nasal concha?
Semilunar Hiatus : crescent-shaped groove in the lateral wall of the nasal cavity just inferior to the ethmoidal bulla
semilunar shaped, hiatus=fissure ethmoidal bulla: Bulging of inner wall of the ethmoidal labyrinth in middle meatus of nose, it is the largest and most consistent ethmoidal air cell

Where does the sphenoidal sinus drain?
Into the sphenoethmoidal recess. this is an area above the superior conchae and it has an opening which enters the sphenoidal sinus
What are the three parts of the ethmoidal air cells and where do each of them drain?
Anterior, middle and posterior ethmoidal air cells
Posterior – lateral wall of superior meatus
Middle – ethmoidal bulla
Anterior – top of the semilunar hiatus via the frontonasal duct.
Frontonasal duct drains both the FRONTAL sinus and the anterior ethmoidal air cells slide 10
Where does the maxillary sinus drain?
To the bottom of the semilunar hiatus
Where does the nasolacrimal duct drain and what is its role?
To the lateral wall of the inferior meatus It drains tears from the lacrimal sac to the nasal cavity
State some roles of the sinuses in the skull.
It makes the skull lighter
Acts as a crumple one for the brain
Increases projection of the voice
Mucous production into the nasal cavity!
What are the mastoid air cells and describe its connection with the middle ear.
They are small sinuses (air cells) within the mastoid part of the temporal bone The mastoid air cells communicate with the middle ear via the aditus ad mastoid antrum and the mastoid antrum This is a possible route for infection of the middle ear
aditus= opening
ad= to
antrum= a natural cavity in bone

What is the name given to the thin plate of bone that forms the roof of the tympanic cavity?
Tegmen tympani
tegmen= cover/roof

Through which membrane is a cricothyroidotomy performed?
Cricothyroid ligament

What important cartilage is found attached to the top of the cricoid cartilage?
Arytenoid cartilage (attached to the cricoid but behind the thyroid cartilage) see pics

What effect does tilting the thyroid cartilage forwards have on the vocal folds? Which muscles perform this action?
Cricothyroid muscles can tense and tilt the thyroid cartilage forwards. This puts tension on the vocal folds and allows higher pitched voices to be produced.
try doing do re mi fa so

What are the two parts of the cricoid cartilage?
Lamina (the main body part of the cricoid, located POSTERIOR to the arch.) and Arch (ring part of the cricoid). The arch is the thin ring bit and the lamina is the thick board at the back

What two things do the cricoid cartilage articulate with?
Arytenoid cartilage
Inferior horns of the thyroid cartilage
if u look at a diagram, the cricoid cartilage has facets for arytenoid cartilage and facets for thyroid cartilage

What name is given to the protrusion between the laminae of the thyroid cartilage and what notches are found above and below this point?
Laryngeal prominence
Superior and inferior thyroid notch are found above and below the laryngeal prominence (NOT THE SAME AS SUPRASTERNAL NOTCH/JUGULAR NOTCH)

What two bits of cartilage are found on top of the arytenoid cartilage?
Corniculate (small horn) and Cuneiform (means wedge shaped) Cartilage
What are the two folds in the mucosa in the laryngeal inlet and how are they arranged?
Vestibular Fold (false vocal fold)
Vocal Fold (true vocal fold)
Vestibular folds are lateral to the vocal folds

What membranous outpouching is formed between these two folds?
Laryngeal ventricle. Laryngeal saccule is the top outpouching of the laryngeal ventricle

What is the name given to the opening between the vocal folds?
Rima glottidis (gap between the vocal folds)
Which muscles are attached only to the arytenoids?
Transverse and Oblique Arytenoid muscles
Oblique is continuous with aryepiglottic muscle but they are sometimes refereed as seprate muscles

Which muscles are involved in abducting (move away from midline) and adducting (towards midline) the vocal folds?
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle – abduction
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle – adduction

Which nerve provides sensory and motor control of the larynx?
Vagus Nerve - L and R recurrent laryngeal nerves MOTOR supply to all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. (see next card)
What are the different laryngeal branches of the vagus nerve and what do these branches do?
- Superior Laryngeal Nerve – separates into internal and external laryngeal:
Internal Laryngeal – sensory above the vocal folds
External Laryngeal – motor to cricothyroid muscles
- Recurrent Laryngeal – sensory below the vocal folds + motor to all other muscles of the larynx

Which arteries do the superior and recurrent laryngeal nerves run alongside?
Superior – Superior thyroid artery Recurrent – Inferior thyroid artery
Why is the left recurrent laryngeal nerve more susceptible to damage by bronchial/oesophageal tumours and swollen mediastinal lymph nodes than the right recurrent laryngeal nerve?
Because the left recurrent laryngeal nerve branches off the vagus much more inferiorly than the right so it has more of its length that is near the bronchus, oesophagus and mediastinal lymph nodes
What are the common changes that occur during sneezing and coughing?
- Inspiration
- Closed glottis (same as rima glottidis) and contraction of abdominal muscles leading to increase in intrathoracic pressure
- Sudden abduction of the vocal folds to release the intrathoracic pressure

What is the difference in the oropharyngeal isthmus in coughing compared to sneezing?
The oropharyngeal isthmus is basically the hole that leads to the ‘entry’ into oropharynx. Isthmus=passageway

In coughing, the oropharyngeal isthmus is open
When sneezing, it is closed
See the middle parts of the diagram below
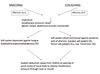
Which afferents take information from laryngeal receptors to trigger the cough reflex?
Vagus
Which afferents take information from laryngeal receptors to trigger the sneeze reflex?
Maxillary branch of the Trigeminal nerve (during a sneeze, it is normally caused by irritation in nasal cavity (irritation of nasal mucosa). Nasal cavity is innervated by V2
How is the movement of the soft palate different in cough reflex compared to a sneeze?
Cough – soft palate is raised and tensed against the posterior wall of the pharynx, this allows air to come out from the mouth
Sneeze – soft palate is depressed (raised DOWN) against the tongue, this forces air to leave via nose
The soft palate is depressed (which is what its normally like) against the tongue when sneezing to prevent the release of the pressure through the mouth. Which nerve and muscles are involved in this?
Vagus – palatoglossus and palatopharyngeus muscles
Palatoglossus is involved in pulling the posterior tongue upwards (only muscle of tongue not innervated by hypoglossal nerve CNXII)
palatopharyngeus is involved mainly in swallowing, it elevates the larynx and pharynx
NOTE these are NOT the same as palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches
What happens to the vocal folds when sneezing and coughing?
They abduct (away from midline ie open)
The soft palate is raised and tensed against the posterior wall of the pharynx when coughing. Which muscles are involved in this action and which nerves innervate these muscles?
Tensor veli palatini (mandibular of trigeminal (V3))
Levator veli palatini (X)
Superior pharyngeal constrictor (X)
Tensor and levator veli palatini both contract to elevate soft palate such that food does not enter nasopharynx
Superior pharyngeal constrictor’s main function normally is to contract to push food down towards esophagus. For coughing, its contraction acts as a sphincter which blocks the air and stops it from leaving via the nasal pathway

What is the vallecula?
Behind the root of the tongue between the epiglottis and the tongue– they serve as spit traps, saliva is temporarily held in the valleculae to prevent initiation of the swallowing reflex

3 parts of the ear?
outer, middle, inner


