session 2: cells/tissues + connective/ adipose tissue Flashcards
what are cell junctions?
types?
structures found between adjacent cells, making sure they are tightly adhered together

What are the 3 cell junctions?
Tight junction
Desmosomes
Gap junctions
What are tight junctions ?
impermeable junction that prevents moleculs from passing

What are desmosomes ?
anchoring junctions that bind adjacent cells together

What are gap junctions?
communicating junctions that allow ions and small molecules to pass

All cells sit on..?
basement membrane
How are cells attached to the basement membrane?
Hemi-desmosomes
Focal adhesion
Hemi-desmosome?
While desmosomes link two cells together, hemidesmosomes attach one cell to the extracellular matrix
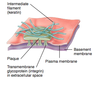
What are the functions of focal adhesions?
Anchor intraellular actin filaments to the basemment membrane
play a role in call movement “migration of epithelial cells of skin”

What are the functions of integrins?
- attach cell to ECM
- activate signal transductionpathways from ECM to cell upon ligand binding
- immune patrolling
- cell migration
- binding to cells by certain viruses
what are integrins?
transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion.
Which of the following is involved in cell migration?
(Gap junctions, desmosomes, focal adhesions, hemi-desmosomes, integrins)
focal adhesions
integrins
which of the following in NOT involved in lateral domain cell contact?
(desomosomes, gap junctions, hemi-desmosomes, tight junctions)
hemi-desmosomes
What is this communication called?

autocrine
Why are cultured cells different than normal cells?
when they come into contact with other cells they stop growing “Contct inhibition”
they have a limitd life span “senescence”
Explain Senescence?
loss of a cell’s power of division and growth
What are gap junctions made of?
channels of Connexon

Explain the paracrine communication?
cell-cell communication in which a cell produces signals/ chemicals to induce changes in nearby cells

Explain the endocrine communication?
Communication between endocrine organs, as they are ductless and secrete directly into the blood stream

Explain the synaptic communication?
Communication between neurons is achieved at synapses by the process of neurotransmission and the release of neurotransmitters
NA - sympathetic
Ach - parasympathetic
Explain the neurocrine communication?
What 3 areas can we find them in our body?
electrical signaling traveling along the nerve and releases chemicals into the blood stream instead of at a synapse
Examples: hypothalamus, posterior pituitary, adrenal medulla

What process involved in cell replacement?
mitosis
Necrosis vs. apoptosis?

explain necrosis?
Physical distrusting through cell injury,
bacterial toxins, or nutritional deprivation
-> cell swells then bursts -> cytotoxic
cellular components spill out -> damage
and inflammation

























