Session 10 Flashcards
What can the causes of chest pain be divided into?
Chest wall
Lungs/pleura
Heart and Great Vessels
Oesophagus and stomach
Other causes
What problems arising from the chest wall could cause chest pain?
Chest Wall (muscle/bone – rib - /skin)
Often localised, movements may increase pain, local pressure application may elicit tenderness
History of trauma/use e.g. broken ribs, overuse of muscles – muscle pain, bone metastases
What problems arising from the lungs could cause chest pain?
Lateral chest pain, sharp (accentuated) on inspiration, respiratory symptoms +
E.g. pneuomonia, pulmonary embolism
Pneumothorax (air that is trapped between a lung and the chest wall – the air gets there either from the lungs such as in rupture of alveoli or from outside the body – spontaneous)
What problems arising from the heart and great vessels could cause chest pain?
Central pain
Pain from ischaemic myocardium – tightening
Stable angina – pain on exertion and relieved by exertion
Ischaemic Heart disease is common and serious
Pericarditis (less common) - inflammation
Aortic dissection (tear in the aorta –> separation of the aorta walls –> bleeding into and along the wall of the aorta) – uncommon but an emergency
What problems arising from the gastrointestinal system could cause chest pain?
Oesophagus/stomach (Gastrointestinal system)
Chest and epigastric pain, GI symptoms +
Gastro-oesophageal reflux, GB disease (Gullain-Barre syndrome – autoimmune attack on the peripheral nervous system), peptic ulcer, Gastroesophageal reflux disease (from stomach into oesophagus), gallbladder inflammation (cholesystitis)
Discuss Ischaemic Heart Disease
Normally increases in myocardial O2 demand are met by increases in myocardial O2 supply. Myocardial ischaemia occurs when supply cannot increase to meet the demand.
Myocardial Oxygen supply depends on coronary blood flow and O2 carrying capacity of blood e.g. Hb
- Coronary blood flow depends on perfusion pressure (diastolic blood pressure – driving force) and coronary artery resistance
Myocardial Oxygen demand depends on heart rate, wall tension and contractility.
- Wall tension depends on pre-load and after-load
What is the commonest cause of Ischaemic Heart Disease?
fixed narrowing of coronary artery/arteries due to atheromatous coronary artery disease
Discuss the physiology of IHD
Coronary flow occurs from epicardium –> endocardium therefore subendocardial muscle is most vulnerable to ischaemia.
Increasing flow to meet demand is by vasodilation but any fixed narrowing of vessels interferes with vasodilation
Coronary flow occurs during diastole (shortening of diastole at rapid heart rates) decreases time for this flow
Collaterals: absent between major arteries on epicardial surface but present between smaller coronary arteries and arterioles.
- Expansion and development of new collaterals occur when myocardium is ischaemic but takes time – may not develop fast enough to prevent an infarction
Apart from atheromatous CAD, what else may cause IHD?
Rarely, ischaemia may be caused by disorders other than atheromatous CAD (but more often they exacerbate existing atheromatous CAD)
A decreased myocardial O2 supply could be due to a decrease in coronary blood flow or severe anaemia
- A decrease in coronary blood flow could be due to severe hypotension and non-atheromatous causes of coronary artery narrowing.
As myocardial O2 demand increases, this could be due to tachycardias, thyrotoxicosis and aortic stenosis (increased afterload)
What are the risk factors for Coronary Artery Disease?
Same as for atheroma
Non-modifiable: increasing age, male gender (females catch up after menopause), family history
Important modifiable: hyperlipidaemia, cigarette smoking, hypertension (high systolic / diastolic blood pressure), diabetes mellitus (doubles IHD risk)
Other risk factors include lack of exercise, obesity, stress etc.
What is the difference between a stable plaque and an unstable plaque?
Stable: Small necrotic core, thick fibrous cap, cap is less likely to fissure/rupture
Vulnerable: Large necrotic core, thin fibrous cap, cap more likely to fissure/rupture

What may happen to a Vulnerable/Unstable Plaque?
Fibrous cap can undergo erosion or fissuring.
This exposes blood to the thrombogenic material in the necrotic core, initiating platelet adhesion and aggregation –> activating platelet clotting cascade –> platelet ‘clot’ followed by fibrin thrombus
- Sudden reduction in artery lumen à acute severe reduction in blood flow à critical ischaemia
- May be sufficient to cause myocyte injury / necrosis
Clinically present with Acute Coronary Syndrome – medical emergency
NOTE; thrombus doesn’t always form – maybe endothelialised – plaque grows bigger
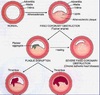
What symptoms does a Stable Plaque present?
No symptoms or stable angina
Discuss Stable Angina Pectoris
Moderate reduction in blood flow
Flow sufficient at rest
Transient ischaemia during periods of increased O2 demand relieved when demand stop – chest pain during exercise, exertion
No myocyte injury or necrosis
May progress gradually over time to severe fixed narrowing –> over the years , could lead to ischaemia with less demand
Site: central, diffuse (‘spread out’) chest pain
Quality of pain: tightening (heavy, pressing)
Picture shows typical radiation of power
Brief episodes; mild to moderate central crushing pain with typicalradiation to left/right/both arms or shoulders, neck, jaw, back and epigastrium

How does Stable Angina present?
Brought on by exertion, emotional stress
Particularly exertion after meals, in cold weather.
Pain, is often predictable: i.e. a reproducible with same amount of exertion.
Relieved by rest or nitrates within about 5 minutes
Presence of risk factors
How is a Clinical Diagnosis of Stable Angina made?
based on history:
Examination: no specific signs but may have signs related to risk factors e.g. increased blood pressure, corneal arcus in hyperlipidaemia
Signs of atheroma elsewhere e.g. absent pulses (PVD) in the feet
LV dysfunction
Resting ECG – usually normal. May show changes (pathological Q waves) of previous MI
What happens if the diagnosis of stable angina is uncertain?
Exercise (ECG) stress test may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Graded exercise on a treadmill until target heart rate reached or chest pain occurs or ECG changes + or other problems – arrhythmias, decreased blood pressure
Transient sub-endocardial ischaemia with exercise in stable angina – manifests as ST segment depression.
With rest, the ischaemia disappears – ST segment back to baseline
Test is positive if ECG shows ST depressions of greater than or equal to 1mm (horizontal/down slopping)
Test is negative if target heart rate is reached without any ECG changes
A strongly positive test indicates critical stenosis

What are the ways to treat stable angina?
- Reduce myocardial O2 demand
- Increase blood flow by revascularisation
- Prevent progression of atheroma, stabilise plaques, prevent thrombosis
How does treatment to reduce myocardial oxygen demand for stable angina work?
- Reduce preload and afterload (nitrates are venodilators and decrease preload, calcium channel blockers decrease afterload by peripheral vasodilation)
- Reduce heart rate (beta blockers decrease heart rate and contractility)
- Reduce myocardial contractility
When treating stable angina, what is meant by revascularisation (to increase blood flow)?
An angiography is undertaken to study coronary artery anatomy when revascularisation is planned
Revascularisation: stenting (carried out by using a percutaneous coronary intervention – PCI – method) and/or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
Choice of procedure is influenced by angiography findings

What arteries and veins are used in a CABG?
internal mammary artery (aka internal thoracic artery), radial artery and saphenous vein (using reversed segment of vein so valves ensure correct blood flow) – grafts are used.

Explain about treatment used to prevent progression of atheroma
To prevent progression of atheroma, stabilise plaques, prevent thrombosis
- Aspirin: decreases platelet aggregation hence thrombus formation if plaques disrupted
- Statins decrease LDL cholesterol and decrease progression of atherosclerosis and increase plaque stability, secondary prevention
What is Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Plaque fissure and thrombus formation can cause: STEMI, NSTEMI, Unstable Angina
- STEMI: ST segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (persistent complete cocclusion of an artery resulting in necrosis), biomarkers of necrosis (+ve) – leaked cellular contents; ECG: ST segment elevated
- NSTEMI: Non ST segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (no ST elevation on ECG, necrosis, biomarkers (+VE))
- Unstable Angina: ischaemia but no myocyte necrosis (ECG – no ST elevation, no necrosis, biomarkers (-ve) – as no leakage of cell contents)
What is a STEMI?
90% of STEMIs have total occlusion of an artery; persistent complete occlusion of an artery supplying a significant area of myocardium without adequate collateral circulation
Injury extends to sub-epicardal area –> manifested as ST elevation in leads facing injured area
Proved benefit from emergency re-opening artery by PCI (stenting) or Thrombolysis (i.e. dissolving thrombus)

What is NSTEMI and Unstable Angina?
Results from non-occlusive thrombus, small risk area, brief or partial occlusion or an occlusion with adequate collaterals
Manifested as ST depression in leads facing injured area
- NSTEMI: cell necrosis + cardiac biomarkers are (+ve)
- Unstable angina: no cell necrosis = biomarkers are (-ve)

What is the History of Unstable Angina?
(Crescendo angina)
More frequent
More severe pain
Longer, more persistent duration
Angina at rest (previously angina upon exertion)
Recent onset of new, effort-limiting angina
Presence of risk factors
Important to realise at the moment thrombus is partially occluding artery à could lead to complete occlusion
What is the History of Myocardial Infarction?
Central, crushing chest pain with typical radiation (shoulders, arms, jaw, back, epigstrium)
Severe pain, patient distressed, ‘feeling of impending death’
Persistent pain
Pain at rest, often no precipitant (50% of time)
Not relieved by rest / nitrate spray
Autonomic features present: sweating, pallow
Other features: nausea, vomiting, breathlessness, (due to LV dysfunction), Faint
Risk factors +
What is the Examination for Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Patient anxious, distressed
Sweating, pallor
Cold, clammy skin
Tachycardia / Arrhythmias +/-
Low BP +/-
Signs of Heart failure: S3, S4, crackles in lung bases (Left ventricular failure –> pulmonary oedema)
What initial investigations would you do for Acute Coronary Syndrome?
ECG
Cardiac Biomarkers
Discuss the management of Acute Coronary Syndrome
Priority is to differentiate STEMI from NSTEMI/UA because the treatment is different
Clinical history alone may not differentiate
ECG for a STEMI: ST elevation in 2 or more leads facing same area (1mm in limb leads, 2mm in chest leads); New Left bundle branch block (LBBB)
ECG for a UA/NSTEMI: ST segment depression, T wave inversion OR no ECG changes
What Biomarkers are there for myocyte damage?
Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI) and Troponin T (cTnT)
- Protein important in actin/myosin interaction
- Released in myocyte death
- Very specific and sensitive marker
- Starts to rise 3-4 hours after onset of pain
- Peak at 18-36 hours
- Decline slowly – (+) up to 10-14 day
Creatine kinase (CK)
- Enzyme present in skeletal muscle, heart, brain
- 3 iso enzymes; CK-MB is the cardiac isoenzyme
- Rise 3-8 hours after onset; peak at 24 hours
- Back to normal 48-72 hours

What are the ECG changes of a fully involved STEMI? (in the leads facing the infarcted area)
Pathological Q waves
ST segment elevation
T wave inversion
Describe the genesis of a pathological Q wave
The dead tissue creates an electrical hole or ‘window’ as it is no longer able to conduct an electrical current.
As a result, all of the electrical forces of the heart will be directed away from the area of the infarction.
An electrode overlying the infarct will therefore record a deep negative deflection, a Q wave.
Q waves are normally isoelectric

What causes ST elevation?
When cardiac myocardium gets damaged, it becomes leaky so there is an efflux of K+ ions making it more prone to depolarisation causing ST elevation
Describe the evolution of the ECG during a STEMI
Normal
Hyperacute T-wave minutes-hours
ST-elevation 0-12 hours
Q wave develops over 1-12 hours
ST elevation with T-wave inversion 2-5 days
T-wave recovery weeks-months

If there was an a Inferior area of infarction, what leads would show the ECG changes and what artery is occluded?
Leads II, III, aVF
Artery: Right Coronary Artery

If there was a antero-septal infarction, what would the ECG leads and artery be?
Leads: V1 - V2
Artery: Left anterior descending artery

If there was a Anterior Apical Infarction, what leads and artery would it be?
Leads: V3-V4
Artery: LAD (distal)
If there was a Antero-lateral infarction, what leads and artery would it be?
Leads: I, aVL, V5-V6
Artery: Circumflex
If there was a Extensive Anterior infarction, what leads and artery would it be?
Leads: I, aVL, V2-V6
Artery: Proximal Left Coronary Artery
If there was a true posterior infarction, what leads and artery would it be?
Tall R Wave in V1
Right Coronary artery
What would an Anterior MI look like?
Occlusion of proximal left anterior descending coronary artery
Leads: I, V2-V4
Pathological Q waves, T Waves inversion, ST elevation

What would a Lateral MI look like?
Occlusion of
Left Circumflex Coronary Artery
Marginal branch of left circumflex artery
Margian branch of left anterior descending artery
Leads: I, aVL, V5, V6
ST elevation, pathological Q waves, T wave inversions

What would a Posterior MI look like?
Tall R wave in V1

What does an Inferior MI look like?
Leads: II, III, aVF, V6
Artery: Right Coronary Artery
T wave inversions, Pathological Q waves

What is the aim of treatment for Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Restore perfusion, prevent muscle loss
What is the Treatment for STEMI?
Total occlusion: large amount of myocardium at risk and no time to lose
If emergency PCI (angioplasty and stenting) is available In 90-120 minutes, perform Primary PCI – gives better results
If emergency PCI is not available in the time frame, perform firbinolytic therapy if there are no contraindications (e.g. recent surgery or stroke –> risk of severe bleed), with subsequent revascularisation
General: monitoring in CCU, pain control, O2 if needed
Anti-platelet agents: aspirin + Clopidogrel
Anti ischaemic therapy: IV nitrates, beta blockers
ACEI – especially if left ventricle dysfunction – prevents harmful remodelling of heart
Statins (reduce cholesterol synthesis in tissues)
What are drugs used in ACS and how do they work?
Prevent Thrombosis by acting on platelet pathways (anti-platelet drugs e.g. aspirin) and coagulation pathways (anti coagulants e.g. heparin)
Dissolve thrombus (fibrinolytic agents)
What is the treatment of Non-STEMI?
Partial occlusion
Prevent extension of thrombus with anti thrombotic therapy
Early restoration of perfusion in partially occluded vessels – angiography -> PCI / CABG
Prevent progression of thrombosis with anti platelet agents : aspirin + clopidogrel, anticoagulants: LMW heparin
Note: Thrombolytics not used
Risk assessment: High risk – early PCI / CABG, Low risk – initially medial treatment à elective angio
General measures:anti-platelet agents, anti-ischaemic therapy, statins, ACEI
Discuss Long Term Treatment after MI
Aspirin: decrease mortality and re-infarction
Beta blocker – decrease mortality and re infarction
ACEI – improved survival
Statin – decrease mortality and re infarction
Manage risk factors – life style modifications – weight loss, exercise, diet, stop smoking, decrease alcohol
List some complications of MI
Sudden Cardiac Death – ventricular fibrillation / asytole
Arrhythmias
~Sinus tachycardia (pain, anxiety, heart failure)
~Sinus bradycardia (SA node ischaemia)
~Heart block 1/2/3 degrees – (AV node ischaemia), 2nd/3rd degree heart block may require temporary pacemaker
~Ventricular tachycardia/ Ventricular fibrillation (ventricular ischaemia causing re-entry circuits or increased automaticity)
~Atrial fibrillation
Heart failure – loss of myocardium leading to decreased myocardial contractility
Cardiogenic shock – when >40% of myocardium infracted, severely decreased cardiac output, systolic blood pressure <90mmHg, with inadequate perfusion of tissues
Explain about Pericarditis
In most cases the pericardium becomes acutely inflamed, with pericardial vascularisation and infiltration with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. A fibrinous reaction frequently results in exudate and adhesions within the pericardial sac, and a serous or haemorrhagic effusion may develop. In some conditions (eg, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, fungal infections and rheumatoid arthritis), a granulomatous pericarditis develops.
- Chest Pain (Aggravated by inspiration, swallowing, coughing and lying flat. Relieved by sitting up and leaning forward.) Other symptoms can include a nonproductive cough, chills and weakness.
- Signs: pericardial friction rub present upon auscultation, tachypnoea (rapid breathing), tachycardia, fever.
- Cardiac tamponade could arise due to restriction of heart pumping due to fluid buildup between myocardium and pericardium


