Separate Physics - P7 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Flashcards
Name the three magnetic materials.
- Iron
- Cobalt
- Nickel
What happens when two ‘like’ poles are brought together?
They repel each other
Is magnetism an example of a contact or non-contact force?
Non-contact force
What do you call a material that becomes magnetic when it is placed in the magnetic field of another magnet?
Induced magnet
Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.


What happens when two opposite poles are brought together?
They attract each other
Complete the diagram to show the directions that the plotting compasses will point.


Draw the magnetic field around an electromagnet.


What happens when a current flows through a wire?
A magnetic field is produced
Describe the magnetic field lines in the middle of an electromagnet.
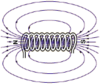
Strong and uniform
Give three ways in which you can increase the strength of an electromagnet.
- Increase the voltage
- Increase the number of coils on the wire
- Use a soft iron core in the middle
Higher Q. In Fleming’s left-hand rule, what do the following represent?
a) First finger
b) Second finger
c) Thumb
a) Field (North to south)
b) Current (positive to negative)
c) Movement
What is a coil of wire called?
A Solenoid
Give two advantages of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet?
- You can turn an electromagnet on and off.
- You can change the strength of the electromagnet
What causes the Earth to have a magnetic field?
Liquid iron in the Earth’s core
Higher Q. What is the motor effect?
A conductor carrying a current placed in a magnetic field causes the magnet and the conductor to exert a force on one another.
Separate Higher Q. What three things affect the size of the force on a conductor in a magnetic field?
- The magnetic flux density.
- The length of the conductor that’s in the magnetic field.
- The size of the current through the conductor.
Separate Higher Q. In a loudspeaker or headphones, how is the frequency of the sound wave determined?
The frequency of the sound wave is the same as the frequency of the AC.
Separate Higher Q. What two things could you do to induce a potential difference across the ends of a conductor?
- Move a magnet in and out of a coil of wire
- Moving a conducting wire inside a magnetic field
Separate Higher Q. What type of current is generated by an alternator?
Alternating current - AC
Separate Higher Q. Describe how loudspeakers and headphones work.
- AC current is passed through a coil of wire.
- The coil is wrapped around one pole of a magnet (e.g. South).
- This is placed inside a magnet of the opposing pole (e.g. North).
- A paper cone is attached to the coil of wire.
- As the current alternates, this moves the paper cone out and in.
- As the cone oscillates, this cause vibrations in the air outside the cone and hence a sound wave is produced.
Separate Higher Q. What is the generator effect?
- A potential difference induced across the ends of a conductor if the conductor moves relative to a magnetic field.
- If the circuit is complete, a current will be induced.
Separate Higher Q. Give two ways that you could increase the size of an induced potential difference/current.
- Increasing the speed of movement of the conducting wire relative to the magnetic field
- Increasing the strength of the magnetic field
Separate Higher Q. What type of current is generated by a dynamo?
Direct current - DC





