Separate Physics - P6 Waves Flashcards
(93 cards)
What two types of wave are there?
- Transverse
- Longitudinal
Give an example of a longitudinal wave
Sound
Describe how longitudinal waves transfer energy.
Vibrations are parallel to energy transfer
Give an example of a transverse wave
- All electromagnetic waves
- A ripple on water
- A wave on a string
Describe how transverse waves transfer energy.
Vibrations are perpendicular to energy transfer
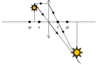
Compare the sound of the two waves in the image in terms of loudness and pitch.

- They have the same loudness.
- Wave B has a higher pitch.

Name the properties of the wave labelled a) and b)

a) Wavelength
b) Amplitude

Name the two regions of a longitudinal wave labelled ‘C’ and ‘R’.

C = compression
R = rarefaction

What equation links wave speed, frequency and wavelength?
Wave speed = frequency x wavelength
V = 𝘧 λ
What are X-rays used for?
Medical imaging
What EM waves can our eyes detect?
Visible light
What are gamma rays used for?
- Killing cancer cells
- Sterilizing medical equipment
What does frequency mean?
The number of complete waves passing a certain point in a second (1 Hz is 1 wave per second)
What EM waves can have hazardous effects on human body?
Ultraviolet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Which EM wave causes skin cancer?
Ultraviolet waves cause skin cancer
Write the electromagnetic spectrum in order from longest to shortest wavelength.

Compare the sound of the two waves in the image in terms of loudness and pitch.

- They have the same pitch.
- Wave B is quieter than Wave A.

Name the EM wave that communicates with satellites
Microwaves
What danger do X-rays and gamma rays pose?
Can cause cancer
What are microwaves used for?
- Satellite communications
- Cooking food
- Mobile phone communication
What is visible light used for?
1) Communication using fibre optics
2) Anything that you need to see e.g.:
- Charging lights on battery chargers
- Traffic Lights
- Lights on displays such as TV, phone, laptop
What are radio waves used for?
Television and radio
What are infrared waves used for?
- Electrical heaters
- Cooking food
- Infrared cameras
- TV remotes
What is ultraviolet used for?
- Tanning beds
- Detecting forged bank notes