sensory pathways Flashcards
draw and label the anatomy of the peripheral sensory nervous system
and segmental spinal nerves
30 pairs of spinal nerves

draw and label spinal cord anatomy (sensory)
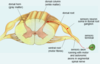
what are dermatomes?
what are their characteristics?
the regions of skin supplied by individual spinal nerves
they do not have sharp boundaries
what is the face/scalp innervated by?
NOT by DRG neurons
by trigeminal ganglion neurons/trigeminal nerves
why do dermatomes arising from DRG neurons not have sharp boundaries?
sensory branches may innervate the edges of different dermatomes
how can dermatomes be useful in diagnosis of visceral problems?
knowledge of which spinal nerves innervate which dermatome
- damage to internal organs can be perceived as pain in skin
- aiding to identify damaged organ
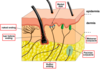
how is skin sensation achieved?
most peripheral sensory neurons have endings in skin
naked endings are from small non- or thinly myelinated DRG fibres (nociceptive neurons)
name the sensory endings and what type of sensation they receive
draw and label where in skin
sensory ending type of sensation
naked ending pain, temperature, itch
hair follicle ending hair movement
Merkel’s endings sustained pressure - texture & shape
Meissner’s ending touch - brief response, transient contact
Pacinian corpuscle vibration
Ruffini ending shear stress
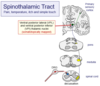
describe the spinothalamic tract
pain, temperature, itch, simple touch
- Drg neuron central axon into dorsal horn
- Projection interneuron crosses midline – until reach thalamus
- Synaptic connection with thalamic nuclei :
- Either
- Ventral posterior lateral thalamic nuclei
- Ventral posterior inferior thalamic nuclei
- Can be precisely localised
- Thalamicortical neurons project from thalamus to primary sensory cortex
- Perceive pain
describe the dorsal column pathway
discriminative touch & conscious proprioception
- DRG neuron projects to dorsal horn
- Main branch of DRG neuron travels towards brain in dorsal columns
- Axons project the length of the spinal cord and make synaptic connections in the medulla with dorsal column nuclei.
- Either
- Nucleus cuneatus
- Nucleus gracilis
- Axons have not crossed to opposite side yet
- Neurons in dorsal column nuclei project axon which crosses midline travels through fibre tract medial lemniscus
* synaptic connection with ventral posterior thalamic nuclei - Projection to primary sensory cortex

what is two point discrimination?
The ability to distinguish between two points of sensory contact on the skin varies for different regions of the body and depends on the density of sensory innervation
describe the spinocerebellar pathway for non-conscious proprioception
reflex circuit
Proprioception – limbs spatial awareness
Reflex circuit
- Proprioceprtive neuron innervates skeletal muscle
- Passes through dorsal horn and branches
- Other branch synapses with nucleus of Clarke
- Project axon to synapse with lateral cuneate nucleus
- To cerebellum
- Coordinates balance
- Outcome of motor movements
- To cerebellum
- Project axon to synapse with lateral cuneate nucleus
- Therefore is non-conscious
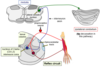
what are the ascending sensory tracts within the spinal cord?
draw and label where they are located
Dorsal columns
Spinothalamic tracts
Spinocerebellar tracts

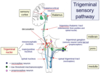
describe the trigeminal sensory pathway
central axons from the nociceptors make synaptic connections with the trigeminal nuclei :
- mesencephalic nucleus
- pontine nucleus
- spinal nucleus
decussate
form the trigemino-thalamic tract
reach thalamus
pass thalamocortical neuron
to sensory cortex
what are the trigeminal nuclei?
what are their roles?
mesencephalic nucleus
- cell bodies of trigeminal proprioceptors
- innervate muscles of mastication & facial expression
main / pontine nucleus
- receives input from trigeminal ganglion neurons that detect discriminative touch sensation
spinal nucleus
- receives input from trigeminal ganglion neurons detecting pain, temperature, itch, simple touch
- somatic sensory input also from cranial nerves VII (geniculate ganglion), IX (petrosal ganglion) and X (nodose ganglion) and spinal nerves C2-C4
how is the face innervated and mapped?
spinal trigeminal tract
- Input to the spinal trigeminal nucleus is arranged in a posterior to anterior fashion.
- As a result, the face is mapped in a series of five concentric dermatomes with sharp borders for pain, temperature, itch and simple touch.
describe sensory innervation of the head and neck?
draw and label
- each circular dermatome is innervated by all three branches of the trigeminal nerve
- cranial nerves VII IX and X provide somatic sensory innervation to the external ear and auditory canal
- cranial nerve VII associated somatic sensory neurons are in geniculate ganglion
- cranial nerve IX associated somatic sensory neurons are in petrosal ganglion
- cranial nerve X associated somatic sensory neurons are in nodose ganglion
- Spinal nerves C2-C4 provide somatic sensory innervation to the lower rear of scalp, lower edges of the jaw and neck
- The central axons of somatic sensory neurons from C2-C4 DRG and geniculate, petrosal and nodose ganglia innervate second order neurons in the spinal trigeminal nucleus

draw and label a diagram showing the sensory innervation of the internal structures of the head



