Section 7 - Spondylolisthesis Flashcards
What is type I of Spondylolisthesis?
Dysplastic (Formally called congenital) Spondylolisthesis usually occurs at L5-S1 and is caused by a congenital defect in the sacral articulated processes (sacral horns) or in the posterior elements of the L5 vertebra. This allows the L5 vertebra to slip forward on the sacrum.
What is type II of Spondylolisthesis?
Isthmic is caused by a defect or fracture in the pars interarticularis area of the lamina and is the most common type of Spondylolisthesis. Type II is subdivided into 3 sub categories
What is type IIA of Spondylolisthesis?
Sometimes called lytic or stress Spondylolisthesis and is most likely caused by recurrent micro-fractures in the pars interarticularii from hyperextension. Involves a complete separation of the posterior elements from the vertebral body. Also known as stress fracture of the pars and is much more common in males. Gymnasts, weight lifters and football linemen have a higher incidence of Type IIA b
What is type II B of Spondylolisthesis?
Probably also occurs from micro-fractures in the pars. However, in contrast to Type IIA, the pars interarticularii remain intact but becomes elongated as the fracture fill in with new bone. The progressive lengthening of the pars allows the body to slide forward. Eventually when the anterior and posterior elements are divided a Type IIB will become a Type IIA
What is type II C of Spondylolisthesis?
Occurs very rarely and is caused by an acute fracture of the pars. It may be difficult to differentiate a Type II C from a Type II A. Acute fracture of the pars but no fibrous tissue
What is type III of Spondylolisthesis?
Most commonly occurs at L4-5 and is the result of degenerative changes in the facet joints. No abnormalities of the pars interarticularis. Also, the L4-5 disc becomes markedly degenerated, resulting in hypermobility of the motion segment. L5 nerve root is often compressed in Type III.
What is type IV of Spondylolisthesis?
Also called traumatic Spondylolisthesis, results from a fracture of the vertebrae in some area other than the pars. These fractures may be in the pedicles, lamina, or facets.
What is type V of Spondylolisthesis?
Is a pathologic Spondylolisthesis caused by tumor or a metabolic type of bone disease.
What is type VI of Spondylolisthesis?
An iatrogenic Spondylolisthesis is usually caused by excessive surgical decompression or the posterior element.
Low dysplastic Spondylolisthesis
Has a translational shift of one vertebrae.
High Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis
Has significant segmental kyphosis associated with the kyphosis.
Which Wiltse type does the following picture represent?

Type I
Which Wiltse type does the following picture represent?

Type II-A
Which Wiltse type does the following picture represent?
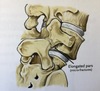
Type II-B
Which Wiltse type does the following picture represent?

Type II-C
Which Wiltse type does the following picture represent?

Type III
Which Wiltse type does the following picture represent?

Type IV
Which Wiltse type does the following picture represent?
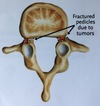
Type V
Using the Meyerding Grading System, what grade slip is the following picture?

Grade 1
less than 25% translation
Using the Meyerding Grading System, what grade slip is the following picture?

Grade II
25-49% translation
Using the Meyerding Grading System, what grade slip is the following picture?

Grade III
50-74% translation
Using the Meyerding Grading System, what grade slip is the following picture?

Grade IV
75-99% translation
Using the Meyerding Grading System, what grade slip is the following picture?

Grade V
Body slipped off the level below.
Also known as Spondyloptosis.
____________________ Method

Standard Slip Angle Method
____________________ Method

Slip Angle Method
(When inferior L5 end plate is irregularly shaped or when sacrum is dome shaped)
____________________ Method

Sacral Inclination Method
Describe “tilt” and “slip” as those terms relate to the Modified Newman Method
Slip = Measured from the posterior inferior angle of the body perpendicular tot he sacral end plate line.
Tilt = Measured from the anterior inferior corner of the vertebrae perpendicular to the line on the anterior surface of the sacrum.



