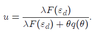Search models Flashcards
(22 cards)
Basic optimality condition search models
There’s a reservation wage in which the worker is indifferent between being unemployed and continuing searching
In the simple framework consumers become more picky when:
- There’s an increment of c
- There’s a mean preserving spread
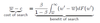
Mean preserving spread
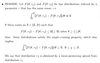
Value function in the continuous time version
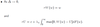
Expression for unemployment rate, discrete time

Expression of unemployment, continuous time
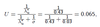
Matching models basic idea
- Labor market is a decentralized adtivity and finding jobs and filling vacancies is costly to firms and workers
- Matching function captures frictions, once a vacancy is posted there is nothing a firm can do to attract workes.
- m(uL,vL) is
- Increasing in both arguments
- concave
- CRS
Market tightness
theta=v/u
Rate at which vacant jobs are filled

Job finding rate (matching)
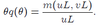
Beveridge curve
- The only way that the job finding rate is high is that the unemployment rate is low
- Lambdda is the rate at which jobs are destroyed
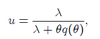
Value functions J, V

Job creation condition

Value function for the worker problem
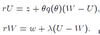
Wage condition derivation
Wages are determined by Nash Bargaining. Beta is the weight of the worker in the bargaining
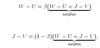
Wage curve

Equilibrium matchiing model
The equilibrium is defined by three equation:
- Beveridge curve
- Job creation condition
- Wage curve
For efficiency in the competitive market allocation we requiere that beta=elasticity of m with respect to unemployment rate
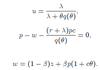
Value functions in stochastic case
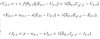
Free entry condition, stochastic case
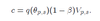
General conclusion Shimer 2005
This model cannot deliver fluctuations in theta based on measured fluctuation in p
Pissarides JD condition
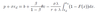
Pissarides, JC condition
Potential benefit of the job = cost of the creation of the vacancy
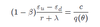
Beveridge curve