Schwannoma, ear and cranial nerves Flashcards
Define the term tinnitus.
Perception of sounds in the absense of external auditory stimulus
What three things cause tinnitus.
- Hearing loss
- Sounds produced by adjacent structures
- Other disease processes
What sounds can be produced by tinnitus
- Ringing of the ears
- Hissing
- Roaring
- Buzzing
- Humming sound
Which two ways can tinnitus be defined?
- Objective tinnitus
- Subjective tinnitus
What is objective tinnitus?
Sound is potentially detectable by another observer
What are the causes of objective tinnitus?
Vascular abnormalities or neuromuscular disorders- sounds generated by turbulent blood flow conducted into auditory system - pulsatile
What is subjective tinnitus
Noise perception when there is no noise stimulation in the cochlear
What can cause transient tinnitus in normal people?
- Aspirin
- Nicotine
- Coffee
What is the suggested pathophysiology of tinnitus?
- Abnormal firing of auditory receptors
- Dysfunction of cochlear neurotransmitters function or ionic balance
- Alterations in central processing of the signal
Define vertigo.
Illusion of motion associated with disorders of vestibular function
Define objective and subjective vertigo?
Objective - person is in motion and environment is stationary Subjective - person is stationary and environment is in motion
What are some differential diagnoses of vertigo?
- Light-headedness
- Syncope
- Faintness
Vertigo can be caused by peripheral and central vestibular problems, what is the difference between them?
- Peripheral - severe in intensity, and episodic
- Central - mild and consistent
Describe motion sickness.
Normal physiological vertigo caused by repeated rhythmical stimulation of vestibular system
Symptoms of motion sickness
Vertigo
Malaise
Nausea
Vomiting
Autonomic symptoms: lowered BP, tachycardia, sweating
Hyperventilation - can causes pooling of blood in lower extremities
What is the pathology of Ménière’s disease?
Excessive accumulation of endolymph in the membranous labyrinth - increases with the distention of the scala media until the membrane ruptures Cochlear organs degenerate
What is the ‘triad’ of Ménière’s disease?
- Vertigo
- Tinnitus
- Hearing loss
What are the suggested mechanisms that may cause Ménière’s disease?
- Increased endolymph production
- Decreased production of perilymph accompanied by a compensatory increase in endolymph sac
- Decreased endolymph absorption- caused by malfunction of endolymph sac or blockage of endolymphatic pathways
Name five things which are thought to cause Ménière’s disease.
- Viral and bacterial agents - syphilis
- Trauma
- Immunological - Allergies
- Metabolic derangements
- Vascular disorders
What is Ménière’s disease characterized by?
Fluctuating episodes of tinnitus, feeling of ear fullness, violent rotatory vertigo
What happens to hearing loss as Ménière’s progresses?
Stops fluctuating and progressively worsens
Both ears become affected
What happens to the vertigo as the Ménière’s progresses?
Episodes of vertigo diminish and disappear although the person may be unsteady
List the differential diagnoses of Ménière’s disease
ENT causes
- acoustic neuroma
- otitis media
- earwax
- too toxic drugs
Intracranial pathology
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency
- tumours
- migraine
Systemic illness
- Anaemia
- hypothyroidism
- DM
- autoimmune disease
- syphilis
What is a schwanomma of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
Benign Schwann cell tumour affecting CN VIII
How does a schwanomma cause unilateral sensorineural hearing loss?
Compresses the cochlear nerve, interferes with the blood supply to the nerve and cochlear
What genetic problem is thought to cause tumour growth in schwannoma?
Tumour suppressor gene abnormality on chromosome p22 (schwanomma protein)
How do patients with a schwannoma present?
Decreased hearing Episodes of vertigo
What does unilateral hearing loss do to your hearing?
Leaves you unable to localise sound
Which other nerves are likely to become affected if the tumour grows too big - and what problems will that cause?
Facial nerve
- nystagmus
- slowed blink
- altered taste
- altered tearing
Trigeminal - facial numbness
What is the differential diagnosis for a schwannoma?
- Meningioma
- Epidermoid
- Facial nerve schwannoma
- Trigeminal schwannoma
Where does the vestibulocochlear nerve arise?
Vestibular nuclei
- superior and lateral
- medial and inferior
Cochlear nuclei (auditory component) - dorsal-lateral medulla
- posterior
- anterior
Where does the vestibulocochlear nerve leave the cranium?
Through the internal acoustic meatus
Where do the two parts of the vestibulocochlear merge when travelling back to the brain?
Inside the petrous part of the temporal bone
What does the vestibular nerve (vestibular ganglion) supply?
- Three semi-circular ducts
- Utricle
- Saccule
How does the cochlear nerve innervate the cochlear?
Enters the base of the cochlear and passes up through the modiolus - branches pass through lamina of modiolus to innervate receptors on spiral organ
Describe what a neoplasm is
Abnormal mass of tissue with uncoordinated growth - growth persists excessively after cessation of the initial stimuli
Describe the growth pattern of a benign tumour.
- Expansive
- Capsule
- Localised
- Slow
Describe the growth pattern of a malignant tumour.
- Infiltrative
- No capsule
- Metastasis
- Rapid
What effects can a slowly enlarging space occupying lesion have on the brain or spine
Atrophy of adjacent brain or spinal tissue
What effects can a rapidly enlarging space occupying lesion have on the brain or spine
Rise in pressure in affected compartment from the normal level of
What clinical signs can be seen when a space occupying lesion distorts the meninges and blood vessels?
Headache
What clinical signs can be seen when a space occupying lesion compresses the optic nerve
Papillodema
What clinical signs can be seen when a space occupying lesion distorts the medulla?
Vomiting
What clinical signs can be seen when a space occupying lesion compresses the occulomotor nerve
Pupillary constriction and then dilation
What clinical signs can be seen when a space occupying lesion causes traction of the abducens nerve?
Abducens palsy - false localising sign
What clinical signs can be seen when a space occupying lesion compresses the posterior cerebral artery?
Occipital infarction
What clinical signs can be seen when a space occupying lesion causes traction on brainstem arteries?
Fatal infarction of brainstem/heamorrhage
What are the two layers of the dura mater called?
- Endocranial layer
- Meningeal layer
Where is an intracranial venous sinus located?
In certain areas, the dura mater splits into its two layers to enclose venous channels
Where does venous drainage leave the skull?
Jugular foramen
What is the relation between the inferior sagittal sinus and the flax cerebri?
Located in the lower margin of the fall
Which two veins join to become the straight sinus - and where does this sinus run?
- Inferior sagittal sinus and the great cerebral vein
- Runs in the junction between the falx and the tentorium cerebelli
Which transverse sinus does the superior sagital sinus drain to?
Right
Which transverse sinus does the inferior sagittal sinus drain to?
Left
Which sinus does the internal carotid artery, the three nerves that supply the eye muscles and V1 + V3 branches of the trigeminal nerve pass?
Cavernous sinus
How can schwannoma removal surgery cause other nerve problems?
Vestibulocochlear and facial nerve share a common cause through the internal auditory canal. This proximity means the facial nerve is easily damaged during surgery = facial palsy
How does facial palsy present?
- Weakness of muscles of facial expression and eye closure
- Face sags
- Face drawn to opposite side when smiling
- Corneal and conjunctiva damage because the eye is open all the time
- Mild dysarthria
- Difficulty eating
What can occur in very severe cases of facial palsy?
Loss of taste over anterior tongue Intolerance to high-pitched or loud noises
How to distinguish between facial palsy and a lower motor neuron.
In lower motor neuron disease - Patient can’t wrinkle forehead because the final common pathway to the muscles is destroyed Lesion must be in pons or outside the brainstem
How to distinguish between facial palsy and an upper motor neuron.
In upper motor neuron disease - upper facial muscle are partially spared (other pathways in brainstem) - appear to be different pathways for voluntary and emotional movement - face sagging is less obvious
What is the treatment for Meniere’s disease?
Symptomatic relief - antiemetics, diuretics and anticholinergics Lifestyle changes: stop smoking, low-sodium diet, stress management, caffeine elimination Surgical: shunts to drain excess endolymph, removal of portion of vestibulocochlear nerve and destruction of the membraneous labyrinth
What are the 2 branches of the Vestibulocochlear nerve and where do they form?
Vestibular branch Cochlear branch - within the acoustic meatus
Where does the Vestibulocochlear nerve attaches to the brainstem?
At the cerebellopontine angle - most laterally of all the nerves
Where do the secondary neurons of the vestibulocochlear nerve pass to?
Bilaterally to the midbrain, medial geniculate bodies and to the auditory cortex in the upper part of the temporal lobe
What are the clinical features of Schwannoma?
Unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, intermittent dizziness and facial numbness Headaches, coordination difficulties, obstructive hydrocephalus May be life threathening
Describe hydrocephalus
Accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull.
How can you test vestibulocochlear nerve?
Tuning fork tests and audiometry to distinguish between external and middle ear deafness and inner ear nerve deafness Others - electrical neurophysiological testing - Caloric test
Describe the basis of the caloric test
Irrigating the external acoustic meatus with warm and cold water, convection currents affect the lateral semi-circular duct which provokes nystagmus (jerky eye movements), duration measured and compared to normal subject
What is Bell’s palsy?
Unilateral lower motor lesion affecting face - forehead not wrinkled - eyeballs rolls up, eyelid does not close - flat nasolabial fold, paealysis of lower face
What is the treatment of acoustic schwannoma and its symptoms??
Cerebreal oedema - managed with steroids, intravenous or oral dexamethasone Epilepsy - anticonvulsants Oral alkylating agents (chemo) - Vincristine, procarbazine and temozolomide Surgery - can be removed, but 10% mortality rate
What is tarsorrpathy and when is it used?
Surgical procedure in which the eyelids are partially sewn together to narrow the eyelid opening - done to protect the eyes eyes, associated pain with them drying up
Name the 4 stages of Schwannoma
Intracanalicular Cisternal Compressive Hydrocephalus
What does the olfactory nerve do?
Sensory - sense of smell
What does the optic nerve do?
Sensory - sight
What does the occulomotor nerve do?
Motor - eyelid movement - eyeball movement (medial, superior and interior rectus and inferior oblique) - pupillary constriction - accommodation of lens for near vision
What does the trochlear nerve do?
Motor- eyeball movement (superior oblique)
What does the trigeminal nerve do?
Both sensory and motor - sensory to the face (opthalamic, maxillary and mandibular) - motor to the muscles of mastication (masseter, temporalis, pterygoids)
What does the abducens nerve do?
Motor- movement of eyeball (lateral rectus)
What does the facial nerve do?
Both - sensory to skin of external ear and anterior tongue - motor to muscles of facial expression and helps secrete saliva and tears
What does the vestibulocochlear nerve do?
Sensory- hearing and equilibrium
What does the glossopharyngeal nerve do?
Both sensory and motor - motor is for swallowing and speech and secretion of saliva - sensory: carotid body and sinus; tonsils, pharynx and taste for posterior tongue
What does the vagus nerve do?
Both sensory and motor innervation - swallowing and speech - parasympathetic innervation
What does the accessory nerve do?
Motor - sternocleidomastoid and trapezius -movement of head and shoulders
What does the hypoglossal nerve do?
Motor- movements of the tongue
What are the layers from skin to brain?
Skin Aponeurosis Periosteum Bone Meninges - dura, arachnoid an pia
What are the layers of the bone of the skull?
Outer table - cortical compact bone, thick and tough Diploe - the spongy cancellous bone separating the inner and outer layers of the cortical bone Inner table - cortical bone, thin, dense and brittle
What is a vault?
Something resembling arched dome
What is Crista galli?
Upper part of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, which rises above the cribriform plate The falx cerebri attaches to the crista galli The olfactory bulbs of the olfactory nerve lie on either side of the crista galli on top of the cribriform plate
What is the exit of the olfactory nerve?
Cribriform plate
What is the exit of the optic nerve?
Optic canal
What is the exit of the oculomot nerve?
Superior orbital fissue
What is the exit of the trochlear nerve?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the exit of the trigeminal nerve?
V1 Opthalmic - Superior orbital fissure V2 Maxillary - foramen rotundum V3 Mandibular - Foramen ovale
What is the exit of the Abducens nerve?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the exit of the facial nerve?
Internal Acoustic meatus
What is the exit of the Vestibulocochlear nerve?
Internal acoustic meatus
What is the exit of the glossopharyngeal nerve?
Jugular foramen
What is the exit of the Vagus nerve?
Jugular foramen
What is the exit of the Spinal Accessory nerve?
Jugular Foramen
What is the exit of the Hypoglossal nerve?
Hypoglossal canal
Which cranial nerves originate in forebrain?
Olfactory and optic
Which cranial nerves originate in midbrain?
Oculomotor and trochlear
Which cranial nerves originate in Pons?
Trigeminal, Abducens, Facial, Vestibulocochlear
Which cranial nerves originate in Medulla?
Glossopharyngeal Vagus Spinal Accessory Hypoglossal
Where does the olfactory nerve terminate?
In the olfactory sensory neurons embedded in the olfactory epithelium - upper part of the nasal cavity
How do you test olfactory nerve?
Give odor samples to smell, test one nostril at a time Control test: ammonia - it is an irritant causing pain and can be still detected by the nasal mucosa
Which nerve provides somatosensory innervation to the nasal cavity?
Trigeminal V1 and V2
What are the signs that oculomotor is not functioning?
Ptosis Outward and slightly downward deviation of the eye Dilated and fixed pupil
What are the signs that trochlear is not functioning?
Torsitional diplopia (double vision) Compensatory tilted head
What are the signs that abducens is not functioning?
Reduced abduction Positioned medially
How do you test eye movements?
Subject sits upright Hold head still with one hand Observe normal position and lack of spontaneous movements Eye movement: - moving object to be followed by eyes - H shape
Whar are the 3 main divisions of the trigeminal nerve?
V1 - ophtalmic V2 - Maxillary V3 - Mandibular
What are the branches of the trigeminal nerve that pass through the foramina of the fronta normalis?
Supra-orbital nerve Infra-orbital nerve Mental nerve
How do you test trigeminal nerve?
Sensory innervation of skin: The skin areas in the 3 divisions with a piece of cotton Motor function: - clench teeth - open the mouth - jaw jerk reflex
How do you test the facial nerve?
Motor function: - Raise eyebrows - frown -smile - puff out their cheeks Cornea reflex - wisp the cornea with sterile cotton
Which large glands are innervated by the facial nerve?
Sublingual and Submandibular
How do you test the vestibulocochlear nerve esp. hearing?
Whisper voice test - whisper postero laterally to the person starting at arms length - needs to repeast at least 3/6 numbers Audiometry
What are the classic physiological tests of vestibulocochlear nerve?
Rinne test - test of air vs bone conducting sound - vibrating fork behind the mastoid bone - when the subject cant hear it move it to the outer ear canal Weber test - test of symmetrical inner ear function - vibrating fork to the midline of forehead
What are the tests for glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves?
Speech Swallowing Observe - the position of the palate and the uvula Symmetrical position and movements of uvula Gag reflex - back of the throat is touched with a tongue blade
What is the test for accessory spinal nerve?
Place your arms firmly on the shoulders of your subject and ask them to raise shoulders
What is the test for Hypoglossal nerve?
Stick tongue out - tip will deviate to the weak side - check movements in all directions
Label

Label


Label


Label


Label
Label


Label


Label

Label

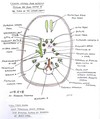
Label


Label