Salivary and Gastric Secretions Flashcards
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
- exocrine use ducts to secrete (salivary and gastric glands)
- endocrine are ductless (enteroendocrine cells)

What do the secretions in the GIT do?
- digest
- lubricate
- protect
What is a hypotonic solution?
- low concentration of solutes outside cells
- high concentration of water outisde the cell
- water therefore moves into cell and cell swells

What is a hypertonic solution?
- high concentration of solutes outside cells
- low concentration of H2O outside the cell
- water leaves the cell to dilute and shrivels up

What is saliva?
- high volume hypotonic solution
- pH 6-7
- 99% H2O
- some electrolytes and enzymes
What are the 3 main functions of saliva?
- lubrication
- protection – oral hygiene/antimicrobial agents
- initiate chemical digestion
What are the 3 main salivary glands?
1 - parotid glands
2 - submandibular glands
3 - sublingual glands

The parotid glands are exocrine glands that secrete saliva in the oral cavity. What % do they contribute to total saliva and how and where are they located?
- contribute around 25% of total saliva
- parotid means behind the ears
- located towards back of jaw under the ears

The submandibular glands are exocrine glands that secrete saliva in the oral cavity. What % do they contribute to total saliva and how and where are they located?
- contribute 70% of total saliva
- secrete serous and mucus
- located at bottom of the jaw

The sublingual glands are exocrine glands that secrete saliva in the oral cavity. What % do they contribute to total saliva and how and where are they located?
- secret around 5% of mucus
- located under the tongue

What are dispersed salivary glands?
- small glands in oral cavity
- located in lips, cheeks, tongue and mucosa of the mouth

What are the main electrolytes secreted in saliva and why are they important?
- K+, HCO3-, Na+, Cl-
- maintain oral pH
What antibody is commonly present in saliva?
- IgA
- main antibody secreted in bodily fluids
What are the 4 enzymes in saliva?
1 - alpha amylase
2 - lysozyme
3 - lingual lipase
4 - lactoferrin
What is the function of alpha amylase present in saliva?
- hydrolysis of a-1,4 glycosidic bonds in starch
- hydrolyises to disaccharide maltose, trisaccharide maltotriose and a-dextrin
- accounts for aproximaltye 75% of starch digestion
What is the function of lysozyme present in saliva?
- antimicrobial
- hydrolyses (breaks down) peptidoglycans in walls of bacteria
What is the function of lingual lipase that is secreted by the dispersed salivary glands of the tongue?
- hydrolysis of lipid triglycerides
- chelates iron to prevent microbial multiplication
What is the function of lactoferrin that is secreted in saliva?
- iron building protection
- antimicrobial properties
What is the function of mucin in the oral cavity?
- lubrication
What are the 2 main waste products that are collected in the oral cavity?
- urea
- uric acid
What does acinus mean?
- group of cells clustered together
- resemble a berry

What are myoepithelial cells?
- hybrid of smooth muscle and epithelial cells
- generally found in exocrine ducts and around acinar cells
- able to contract increasing secretion
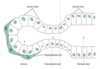
What are the 2 stages of saliva production, which include exocrine secretion and funneling of secretions?
1 - acinar phase (secretion of exocrine secretions)
2 - duct phase (exocrine secretions move into oral cavity)
In the first phase of saliva production, called acinar phase, which electrolytes are high in concetration, and what follows these?
- Na+
- Cl-
- H2O always follows Na+































