S9-10) Pharmacodynamics Flashcards
How do drugs exert their effects?
Drugs exert their effects by binding to a target (mainly proteins)
The concentration of drug molecules around receptors is critical in determining drug action.
Account for the measure of concentration
Concentration is measured in terms of molarity

What are the prefixes for the following:
100
10-3
10-6
10-9
10-12
- Molar (M): 100
- Millimolar (mM): 10-3
- Micromolar (μM): 10-6
- Nanomolar (nM): 10-9
- Picomolar (pM): 10-12
Why do most drugs bind reversibly to receptors?
Binding is governed by association and dissociation

What are the two effects of most drugs?
- Agonist: activate a receptor
- Antagonist: block the binding of an endogenous agonist

How do drugs act on receptors?
- They must bind to the receptor
- They must have an affinity for the receptor in order to bind
- receptor must have a conformational change in order to evoke a response = intrinisc efficacy
After the receptor is activated, things must occur to evoke a response.
What is the concept that governs this?
- Efficacy is the ability of a ligand to evoke a response
- Activation is governed by intrinsic efficacy (agonists only)

Compare and contrast efficacy in agonists and antagonists
- Agonists have affinity, intrinsic efficacy and efficacy
- Antagonists have affinity only (no efficacy)

Binding is how we quantify drug-receptor interaction.
In light of this, what is Kd?
- Kd = dissociation constant
- Kd is the concentration of ligand (drug) required to occupy 50% of available receptors
- measures the strenght between the ligand and target // affinity
- lower the Kd value the higher the affinity

Which of the following drugs have a higher affinity?
- Drug A: Kd = 10-9
- Drug B: Kd = 10-3
- Drug A as a lower concentration is required to occupy 50% of receptors
- For Kd, the lower the value, the higher the affinity (reciprocal)
Why is affinity important for ligands?
High affinity allows binding at low concentrations of hormones, neurotransmitters and drugs
What form of regression does drug concentration follow?
Logarithmic

The terms concentration and dose are often used interchangeably.
Distinguish between them
- Concentration is the known amount of drug at site of action
- Dose is the amount of drug at site of action is unknown
What is potency?
- Potency (EC50) is the effective concentration giving 50% of the maximal response
- It depends on both affinity and intrinsic efficacy plus cell/tissue specific components
- does the drug have bith affiity and efficacy

How do cell/tissue dependent factors such as receptor number influence agonist potency?
- ‘The greater the receptors = the greater the response’ is not always true
- Response is often controlled/limited by other factors
- E.g. a muscle can only contract so much, a gland can only secrete so much*
This revolves around the concept of spare receptors

What does the presence of spare receptors indicate?
Spare receptors means < 100% occupancy = 100% response

Spare receptors allow for amplification is a signal transduction pathway.
In terms of GPCRs, illustrate this.
A few adrenaline molecules can cause a massive cellular response:
- The β-adrenoceptor → Gs protein → adenylyl cyclase part of the cascade causes relatively little amplification
- Nevertheless, activation of adenylyl cyclase generates many molecules of cyclic AMP which then activate the enzyme PKA

Why are there spare receptors?
- Spare receptors increase sensitvity
- It allows responses at low concentrations of agonist
- more opportunity for for binding and inducing a theraputic effect
- not all the target protein binding sites need to be occupied to get a maximal response
What is the effect of changing receptor number?
Changing receptor number changes agonist potency and can affect the maximal response

Discuss the relevance of altered receptor number
Receptor numbers are not fixed:
- Tend to increase with low activity (up-regulation)
- Tend to decrease with high activity (down-regulation)
What are full and partial agonists?
Partial agonists are drugs that bind to and activate a given receptor, but have only partial efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist they exhibit a lesser potency

In terms of EC50, compare and contrast partial and full agonists
- Full agonist: EC50 < Kd
- Partial agonist: EC50 = Kd
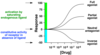
Describe the properties of a partial agonist
- Lower intrinsic activity
- Lower efficacy
- Insufficient intrinsic efficacy for maximal response

What is the clinical relevance of partial agonists?
- Allows for a more controlled response e.g. adequate pain control
- Works in the absence/low levels of endogenous ligand
- Acts as antagonist if high levels of full agonist










