S11) Introduction to Molecular Diagnosis Flashcards
What are restriction endonucleases and what do they do?
Restriction endonucleases are a group of bacterial enzymes which cleave dsDNA, at a specific nucleotide sequence, into smaller fragments for DNA analysis

What are “sticky” ends and what do they do?
Sticky ends are single-stranded staggered cuts of DNA produced when the restriction enzyme cuts at one end of the sequence, between two bases on the same strand, then cuts on the opposite end of the complementary strand
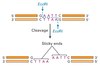
What are restriction sites?
Restriction sites are areaa on a DNA sequence that is recognised and cut by a restriction enzyme

What is DNA cloning?
DNA cloning is a molecular biology technique used to make identical copies of a gene by assembling recombinant DNA molecules and directing their replication within host organisms

Identify the 5 steps involved in cloning
⇒ Digest gene of interest with restriction enzymes
⇒ Isolate gene of interest
⇒ Insert gene of interest into plasmid vector
⇒ Introduce recombinant DNA molecule into suitable host cells e.g. E.coli
⇒ Identify and isolate the clone containing the DNA of interest

What is the purpose of DNA cloning?
- To make useful proteins e.g. insulin
- To find out what genes do e.g. HTT
- Genetic screening e.g. Huntington’s, BRCA1/2, Cystic Fibrosis
- -* Gene therapy e.g. Cystic Fibrosis
What is a vector?
A vector is a molecule of DNA to which the fragment of DNA to be cloned is joined e.g. plasmid

What are prokaryotic plasmids?
Plasmids are small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecules which may carry genes that convey antibiotic resistance to the host bacterium, and may facilitate the transfer of genetic information from one bacterium to another

What is the polymerase chain reaction?
- PCR is a molecular technique used to amplify selected DNA sequences that does not rely on the biologic cloning method
- It uses Taq DNA Polymerase and DNA primers to synthesise of millions of copies of a specific nucleotide sequence in a few hours
Briefly describe the process of PCR

What is the purpose of PCR?
- To amplify a specific DNA fragment
- To investigate single base mutations e.g. Tay Sachs, Sickle Cell disease
- To investigate small deletions/insertions e.g. Cystic Fibrosis
- To investigate variation, genetic relationships e.g. DNA profiling
What is the Microarray analysis of gene expression?
A DNA microarray is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface used to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously / to genotype multiple regions of a genome
Briefly describe the process of the microarray analysis of gene expression

What are Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays?
ELISA is a type analytic biochemistry assay which uses a solid-phase enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a substance – measure the concentration of a protein in solution e.g. hormone, antigen
Briefly describe the process occurring in ELISA

What is proteomics?
Proteomics is the study of all proteins expressed by a genome, including their relative abundance, distribution, posttranslational modifications, functions, and interactions with other macromolecules
Briefly describe the process occurring in proteomics

Compare and contrast proteomics with molecular diagnosis
- Proteomics: analysis of all proteins expressed from genome
- Molecular diagnosis: analysis of a single purified protein
Compare and contrast polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies
- Polyclonal antibodies are produced by many B lymphocytes, contain multiple different antibodies which a specific to 1 antigen and have multiple epitopes
- Monoclonal antibodies are produced from 1 B lymphocyte, contain 1 identical antibody which is specific to 1 antigen and has 1 epitope

What is DNA gel electrophoresis?
- DNA gel electrophoresis is a method for the separation and analysis of DNA and their fragments, based on their size and charge
- DNA is negatively charged and will move towards the anode if placed in an electric field

Identify and describe the requirements for DNA gel electrophoresis
- Gel – a matrix that allows separation of DNA fragments
- Buffer – allows charge on the DNA samples across the gel
- Power supply – generates charge difference across the gel
- Stain/detection – identifies presence of the separated DNA
What are the uses of restriction analysis?
- To investigate the size of DNA fragments e.g. small deletions
- To investigate mutations e.g. Sickle Cell disease
- To investigate DNA variation e.g. DNA fingerprinting
- To clone DNA
What is protein gel electrophoresis?
- Protein gel electrophoresis is a method for the separation and analysis of proteins based on their size and charge
- Proteins are charged molecules and will move towards the anode / the cathode if placed in an electric field

Identify and describe the requirements of protein gel electrophoresis
- Gel – a matrix that allows separation of the protein sample
- Buffer – maintains charge on the protein samples
- Power supply – generates charge difference across the gel
- Stain/detection – identifies presence of the separated proteins





