S1) Embryology of the Nervous System Flashcards
look at pp for images
Describe the five steps involved in the formation of the neural tube in early embryonic development
⇒ Gastrulation produces the notochord
⇒ Notochord induces neurulation
⇒ Neurulation induces the neural plate
⇒ Elevation of lateral edges of neural plate
⇒ Neural folds gradually approach each other in the midline and fuse, producing the neural tube
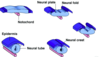
What is the role of the notochord during neurulation?
The notochord directs the conversion of the overlying ectoderm to neurectoderm

What is a neuropore?
A neuropore is a region corresponding to the opening of the embryonic neural tube in the anterior/posterior portion of the developing prosencephalon

Defects in closure of the neuropores underlie serious and common birth defects of the nervous system.
What are neural tube defects?
- Neural tube defects are defects which result from failure of the neutral tube to close
- Failure can occur caudally or cranially
What are the results of the following:
- Cranial neural tube defect
- Caudal neural tube defect
- Cranial neural tube defect results in anencephaly
- Caudal neural tube defect results in spina bifida
What is spina bifida?
- Spina bifida is a type of neural tube defect occurring when the vertebrae don’t form properly around part of the baby’s spinal cord
- It arises from the failure of neural tube closure caudally

Spina bifida can occur anywhere along the length of the spine.
What is the most common location?
Spina bifida most commonly occurs in lumbosacral region
What is anencephaly?
- Anencephaly is a neural tube defect resulting in the absence of cranial structures, including the brain
- It results from the failure of neural tube closure cranially and is incompatible with life

What is rachischisis?
Rachischisis is a neural tube defect occuring due to the failure of neural fold elevation

How can one diagnose a neural tube defect?
- Raised maternal serum α-fetoprotein
- Ultrasound
How can a neural tube defect be prevented?
Folic acid pre-conceptually (3 month) and for the first trimester reduces incidence by 70%
- given especially to woman who are obese, diabetic and epileptic ( increase 300mg to 400mg daily)
Most of the length of the neural tube gives rise to the spinal cord.
In four steps, explain how the cauda equina forms
⇒ A 3 months, the spinal cord is the same length as the vertebral column
⇒ Thereafter, the vertebral column grows faster
⇒ The spinal roots must elongate in order to exit at their intervertebral foramen
⇒ Cauda equina is formed

During neural fold formation three primary brain regions can be distinguished.
Identify these primary brain vesicles
- Embryonic forebrain (prosencephalon)
- Embryonic midbrain (mesencephalon)
- Embryonic hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
At 5 weeks of development, the three primary brain vesicles become five secondary brain vesicles.
Identify these

Identify the mature derivatives of the following secondary brain vesicles:
- Telencephalon
- Diencephalon
- Mesencephalon
- Metencephalon
- Myelencephalon

How are flexures formed in the embryological development of the nervous system?
Growth & development at the cranial neural tube exceeds available space linearly, so it must fold up to form flexures
Which two flexures are formed in the embryological development of the nervous system?
- Cervical flexure
- Cephalic flexure
Where are the cervical and cephalic flexures located respectively?
- Cervical flexure – hindbrain junction
- Cephalic flexure – midbrain region

What is the role of the ventricular system?
The ventricular system cushions the brain & spinal cord within their bony cases
Compare and contrast the ventricular system in development and adults
- In development, it is a tubular structure of the developing CNS persisting as development proceeds
- In the adult, it is comprised of interconnected “reservoirs” filled by CSF, produced by cells of ventricular lining
Relate the secondary brain vesicles to their corresponding ventricle in the ventricular system
- Telencephalon → lateral ventricle
- Diencephalon → third ventricle
- Mesencephalon → cerebral aqueduct
- Metencephalon & myelencephalon → fourth ventricle

What is hydrocephalus?
- Hydrocephalus is a condition characterised by excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain
- Is is most common in newborns with spina bifida occur due to a blockage of the ventricular system e.g. tumour, infection

How can hydrocephalus be treated?
Hydrocephalus is readily treatable by use of shunt

Explain the early organisation of the neural tube by describing its three layers
- Inner: neuroepithelial layer
- Intermediate: mantle layer (neuroblasts)
- Outer: marginal layer (processes)
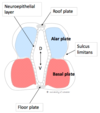
What is the function of the roof and floor plates of the neural tube?

Roof & floor plates regulate dorsal & ventral patterning
Describe the modality of the alar and basal plates respectively

- Alar plate = sensory
- Basal plate = motor

Describe the location and function of neural crest
- Location: cells of the lateral border of the neuroectoderm tube
- Function: become displaced and enter the mesoderm and undergo epithelial to mesenchymal transition

Identify 8 neural crest derivatives in the nervous system
- Cranial nerve ganglia
- Spinal root ganglia
- Sympathetic ganglia (chain & pre-aortic)
- Parasympathetic ganglia
- Schwann cells
- Glial cells
- Leptomeninges (arachnoid & pia)
- Connective tissue & bones of the face & skull
Identify 3 neural crest derivatives in the head, neck and midline
- Odontoblasts
- Dermis (face & neck)
- C cells of the thyroid gland
Identify 3 miscellaneous neural crest derivatives
- Conotruncal septum (heart)
- Melanocytes
- Adrenal medulla
what is neurolation?
- formation of the neural tube
- induced by the notochord
- fusion of the folds in the midline at around the neck level
- once folds fuse, neural crest cells detach and ,migrate
what direction does the neural zip close up
- rostrally and caudally
what two parts does the forebrain split into?
- telencephalon → becomes most of cerebral hemisphere
- diencephalon → thalamus, hypothalamus an optic nerve
what does the rhombencephalon split into?
- metencephalon → pons and cerebellum
- myelencephalon → medulla
what is the relationship between the sensory and motor neurones
- motor structures sit anteriorly and sensory sit posteriorly
- due to the neural tube making the floor give rise to motor neurones and roof sensory
give some examples of the relationship of sensory and motor neurone’s
Medulla
The medial lemniscus (sensory) sit posterior to the
pyramids of the medulla (motor)
o Midbrain
The colliculi
(sensory) sit posterior to the cerebral peduncles (motor)
development of the caudal equina
- initially spinal chord and spine grow at same pace
- soon spine grows faster at lumbar level
what can happen to the caudal equine to cause hydrocephalus?
- tethering of chord at sight of defect
- as spine grows the cord can’t
- 4th ventricle gets pulled down foramen magnum and becomes occluded
what is a meningomyelocoele?
- failure of somite to form bone precursors around neural tube (neural tube still fully developed)
- cyst filled with CSF
- spinal chord gets stretched and pulled and damaged
- transilluminates poorly due to solid tissue in cyst

what is a meningocele?
- failure of somite to form a bone precursor around the neural tube
- here spinal cord isn’t being pulled and is in correct position
- presence of a cyst full of CSF
- transilluminates well
- good prognosis

what is a myelocoele?
- neural tube fails to develop
- neural tube exposed to outside world
- susceptible to meningitis
what is spinal bifida occulta
- lack of posterior vertebral arch
- manifest with hair tuft on back
- no significant neurological problems

neural crest cells
- highly specialised
- multifunctional and give rise to wide range of tissues
- derived when the neural folds fuse
what are some of the derivatives of neural crest cells
- sensory neurones in the PNS
- enteric neurones
- Schwann cells
- cells of adrenal medulla
- head mesenchyme
which tissues receive a significant contribution from neural crest cells
- thymus
- thyroid
- parts of heart and teeth
As streams of neural crest cells migrate from the dorsal part of the embryo, defined populations become left behind at certain points
from dorsal to ventral:
- The dorsal root ganglia (sensory neurones)
- The sympathetic ganglia (sympathetic postganglionic
neurones)
- The preaortic ganglia (sympathetic postganglionic
neurones that receive input from splanchnic nerves)
- The adrenal medulla (chromaffin cells, which are
homologous to sympathetic postganglionic neurones)
The but wall (enteric nervous system)
Di George syndrome
- disorder of the neural crest cells:
- Immunodeficiency (due to involvement of the thymus)
- Facial anomalies (due to contribution of neural crest to
facial development)
- Heart anomalies
- Hypocalcaemia (involvement of parathyroids)
Hirschprung’s disease
- disorder of neural crest cells
Lack of enteric neurones in sections of the large intestine → no peristalsis inside parts of the colon
This leads to hypomotility and constipation
what does the term meningo refer to
CSF
what does the term myelo refer to
cord
what other tissue does the CNS share embryological origin
it derives from ectoderm same as the skin
what organ develops from the same origin as the nervous system
skin, from ectoderm
what is another name for cerebral peduncles
crus cerebri
which part of the brainstem lies directly at the level of the tenotrium cerebellum
midbrain
the falx cerebri is composed of which meningeal layer
meningeal dura


