Rivers Flashcards
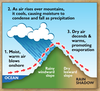
The water cycle What do we call the water drops that fall as rain or hail or sleet or snow.
Precipitation
What is the water cycle? What happens when the air rises higher where it is cooler. Water vapour ???????? into tiny water droplets. These form clouds.
Condenses
What is the water cycle? The Sun warms oceans, lakes and seas, turning water into water vapour , the gas. What is this called?
Evaporation
How rainfall reaches the river If the ground is hard or very wet, rain water just runs along it. What is this called?
Surface runoff
How rainfall reaches the river What is it called when the rain soaks into the ground?
Infiltration
How rainfall reaches the river Some of the rain that soaks into the ground flows sideways through the soil. what is this called?
Throughflow
How rainfall reaches the river What water is always on the move? It flows along slowly.
Groundwater
Parts of the river What do we call the startIng point of the river. It could be a springa lake, or a marshy area where a lot of rain gathers
Source
Parts of the river What do we call the point where two rivers join?
Confluence
Parts of the river What do we call the smaller rivers that joining the main one
Tributaries
Parts of a river What do we call the imaginary line that separates one drainage basin from the next?
Watershed
Parts of the river What do you call the land that may get flooded when a river overflows
Flood plain
Parts of the river What happens to the river as you go from the source to the mouth?
It gets wider
Parts of the river The river is fed by the rain that falls in area that we call the??????
Drainage basin
Parts of the river What is the highest point of the river?
Source
River erosion some rock in the river bank is broken down into stone and soil by?????
Weathering
River erosion Sand and stones in the river scrape the bed and banks, and wear them away. What is this called?
Abrasion
River erosion Rocks and stones knock together and wear each other away. What is this called?
Attrition
River erosion In a fast flowing river, water is forced into cracks in the bank. Over time it breaks up the bank. What is this called?
Hydraulic action
River erosion Water dissolves soluble minerals from bed and banks. This helps to break them up. What is it called?
Solution
Transport The material the riverbed carries its called?????
Its load
Transport The heavier material is carried along the bottom it is called??????
Bedload
Transport Small light particles of rock and soil are carried along. they make the water look cloudy or muddy. What is it called?
Suspension
Deposition When it reaches flatter land the river slows down. it no longer has the energy to carry its load, so it deposits it. The deposit material is called?????
Sediment
Deposition What happens to dissolved material in the river?
It stays in the water and is carried out to the lake or sea.
What is the water cycle? What do we call rock that will not let water pass through?
Impermeable
What is a longer name for rainfall, beginning with P?
Precipitation
Parts of a river What is the name for the part of the river where it flows into the sea?
Mouth of the river
Parts of a river What do we call the parts between two river banks where the water flows?
The channel
Rivers at work What are the three stages for a river flowing?
1) pick up or ERODE material from one place 2) carry or TRANSPORT the material to another place 3) then the river drops or DEPOSIT
Rivers Rocks and stones knock together and wear each other away. What is this called?
Attrition
Rivers When it reaches flatter land, the river slows down. It no longer has the energy to carry its load, so it deposits it. The deposited material is called?
The deposited material is called sediment.
As the river slows, it deposits its load. How?
The river deposits the largest stones and pebbles first, then smaller ones Then finally, the smallest particles.
Rivers What are 6 uses of a river?
1) water supply 2) to make hydro electricity (maybe including a dam) 3) for (irrigation and food) for crops / farming 4) for industry - many factories use rivers to clean / wash them or to cool tanks where chemicals are reacting 5) transport (barges and boats, but more in some other countries than the uk) 6) for leisure and pleasure - walks, fishing, boating, swimming etc 7) as a dump some people dump rubbish, sometimes factories dump ‘cleaned’ waste liquid into rivers