Risk Management Applications of Forwards and Futures - R36 Flashcards
(9 cards)
What is the formula for changing portfolio duration with bond futures?
change in the futures price =
contracts =
change in the futures price = -(MDF)(futures price)(chg in implied yield)
Where MDF is the modified duration of the futures contract.
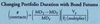
How can you find the appropriate number of contracts to sell or buy to hedge or leverage the position (reduce or increase beta)?
Formula is: number of contracts =

What is the index multiplier for:
- S&P 500 Index futures
- Nasdaq 100 Index futures
- DJIA Index futures
What is the basic strategy for creating synthetic cash or synthetic equity?
Index Multipliers
- S&P 500 = 250x index value/contract
- Nasdaq 100 = 100x index value/contract
- DJIA = 10x index value/contract
Synthetic risk-free asset = long stock - stock index futures (i.e., short position)
Synthetic equity = long risk-free asset + stock index futures (i.e., long position)
What is the formula for creating a synthetic equity index from a portfolio in T-bills?

What is the formula for creating synthetic cash?
IE, what is the required number of equity futures to sell?

What are the steps for synthetically reallocating from equity to bonds?
What are the steps to re-allocate from bonds to equity?
- Remove all systematic risk (ß = 0) by shorting the appropriate amount of stock index futures.
- Add the desired amount of duration using bond futures.
- Remove all duration (MD = 0) by shorting the appropriate amount of bond futures
- Add the desired amount of beta using stock index futures.
Demonstrate the use of futures to adjust the allocation of a portfolio across equity sectors and to gain exposure to an asset class in advance of actually committing funds to the asset class.
To transfer $V from class A to class B, use futures to first transfer $V in class A to cash, and then transfer $V in cash to class B using index futures.
Pre-investing is the practice of taking long positions in futures contracts to create an exposure that converts a yet-to-be-received cash position into a synthetic equity and/or bond position.
Explain exchange rate risk and demonstrate the use of forward contracts to reduce the risk associated with a future receipt or payment in a foreign curency.
*What are the 3 types of FX rate risk?
- Economic exposure is the loss of sales that a domestic exporter might experience if the domestic currency appreciates relative to a foreign currency.
- Translation exposure refers to the decline in the value of assets that are denominated in foreign currencies when those foreign currencies depreciate.
- Transaction exposure is the risk that exchange rate fluctuations will make contracted future cash flows from a foreign trade partners decrease in domestic currency value or make planned purchases of foreign goods more expensive.
Explain the limitations to hedging the exchange rate risk of a foreign market portfolio and discuss two feasible strategies for managing such risk.
Derivatives are used most often to hedge transaction exposure. Being long the currency (in this context) means you have contracted to receive the foreign currency. Being short the currency means you have contracted to pay the foreign currency, and the concern is that the currency will appreciate.
Risk of future FX receipt = sell a forward contract
Risk of future FX payment = buy a forward contract
Limitation: Not possible to precisely hedge currency risk only (without locking in the equity return).


