Risk Flashcards
1
Q
What is risk
A
- Probability that a hazard will give rise to harm
2
Q
Risk versus benefits: Finasteride
A
- = Prevents further hair loss
- Decrease in urgency
- Decrease in frequency
- Decrease in episodes of urinary incontinence
- = Impotence
- Loss of libido
- Decrease semen
- Pain in testicles
- Breast tenderness
- Breast cancer
- Decrease in episodes of urinary incompetence
3
Q
Risk reduction
A
- Relative risk reduction (RRR)
- The reduction of risk in the intervention group relative to the risk in the control group
- Absolute risk reduction (ARR)
- The difference in risk between intervention and control
4
Q
Number needed to treat (NNT)
A
- The number needed to treat (NNT)
- The number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one additional adverse outcome
- The lower the NNT the more effective the treatment
- Ideal NNT = 1
- Everyone improves with treatment, nobody improves with control
5
Q
NNT
A
- NNTs for treatment should be small
- Expect to see large effects in a small number of people
- Between 2 and 4
- NNTs for prophylaxis
- Expect to see small effect in large numbers of people
- Around 50 not common
- BUT
- Depends entirely on clinical context and needs to be weighed against potential harm
6
Q
RRR, ARR and NNT- an example
A

7
Q
Presentation of risk reduction
A
- Anglo-Scandinavian cardiac outcomes trial- lipid lowering arm
- Lasted 3.3 years
- RRR (heart attack)
- ARR
- NNT
8
Q
The effect of event frequency on risk reduction
A

9
Q
NNT
A
- Converse of NNT
- The average number of patients who need to be treated with the intervention for one extra patient to experience harm (e.g. ADR)
- The lower the NNH, the more likely the treat os to cause harm
- NNH of 1= everybody who is treated suffers the harm in question
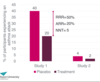
10
Q
NNH- An example
A
11
Q
NNT v NNH in acute bipolar disorder
A

12
Q
Understanding of RRR, ARR and NNT
A
- RRR makes reductions in risk appear larger than they are (overstates benefits of treatments)
- Cochrane review
- RRR and ARR are equally well-understood by both patients and clinicians and both are better understood than NNT
- When the same information is expressed as ARR and NNT, ARR is perceived to indicate a larger effect
13
Q
Framing of risk
A

14
Q
Mean rating of the effectiveness of ChE lowering drugs
A

15
Q
Contraceptive pill scare
A
- Oct 1995: UK committee on safety of medicines dispatches 190,000 letters to doctors and pharmacists
- Warns VTE risk 100% more in 3rd gen to 2nd gen OCP
16
Q
Shared decision making
A
- A process in which patients, when they reach a decision crossroads in their health care, can review all the treatment options available to them and participate actively with their healthcare professional in making that decisions
17
Q
Adherence
A
- The extent to which the patient’s behaviour matches agreed recommendations from the prescriber
18
Q
Decision aids
A
- Help patients to participate in healthcare decisions by providing clear, evidence-based information on the available choices
- Use of decision aids
- Improves patient knowledge and risk perception
- Increases patients’ participation in decision making
- However, they have not been shown to improve patient outcomes
19
Q
Decision aids- statins
A

20
Q
Decision aids- diabetes management

A



