Restrictive (Can't get air IN) Lung Dysfunction: Exam 2 Flashcards
Lobular Consolidation
Think Lobe==Large
Lobes are LARGE
Consolidation IN lobes
Lg. amount bc lobes are LRG
*something in lungs that SHOULD NOT be…
Segmental Consolidation
Segments are SMALL
think SMALL amt bc segments are SMALL
Small amt of consolidation
INCd attenuation
**More white in chest x-ray instead of black (Air)
Atelectasis
- Inside lungs
- Collapsed alveoli
- Cond or status lung is in
- inability to fully expand alveoli
- collapsed lung @ alveolar lvl
Pleural Effusions
“fire in the wall”
“Water ON lung”
- Fluid b/w layers of pleura
- IN lining of lungs
- ***remember the fire IN the wall analogy!!!
Pulmonary Edema
“fire in the Room”
fluid IN lungs
- remember the “fire in the ROOM” analogy!!
- Think
- CHF
- Infections
Ventilation
AIR in and out of lungs
Alllllll of these things go along w/ Ventilation
- lung compliance
- elastic recoil
- surface tension
- surfactant
- Inspiratory mm contraction
- intrapleural pressure
- diaphragmatic excursion
Ventilation:
Lung compliance
allows tissue to stretch aka dispensibility of the lungs
Ventilation:
Elastic Recoil
INWARD PULL of lungs back to orig. size
*like when you exhale
Ventilation
Surface Tension
WHY we blow harder into balloon initially
- INWARD pull
- determinant of lung recoil
Ventilation:
Surfactant
Type II Alveolar cells
DECs surface tension
keeps the alveoli from collapsing after exhalation and makes breathing easy.
Ventilation:
Inspiratory muscle contractions create:
OUTWARD pull
Ventilation:
Intrapleural Pressure
when BELOW ATM pressures==> air comes IN
Normally slightly LESS than ATM pressure
Ventilation:
Diaphragmatic excursion
- Diaphragm descends —> sucks air IN
- diaphragm ascends –> pushes air OUT
Remember the elevator analogy as you breathe IN thru nose—-goes DOWN
Diffusion of lungs
tollbooths opening for air to get into lungs
*all of these are tools to get O2 to blood*
- Surface area of the capillary membrane
- Diffusion capacity
- thick capillary-alveolar memb’s
- ability of air to diffuse
- V/Q ratio
- zones of west
-
LOWER LUNGS
- BEST potential to expand BUT last recruited when one breathes
Perfusion of lungs
think BLOOD
- Gravity dependent
- Cardiac output
- CO==HR*SV
**Optimized V/Q is @ MIDZONE in healthy individuals== 0.8
Etiology:
Restrictive Lung Disease
Everything smaller, BUT ratios are the SAME

Pathophysiological aspects of Restrictive Disease
Normal vs. Abnormal Alveolus
Cant get air IN
alveoli cannot Expand

Actual Restrictive Diseases
We will cover the following Subtopics:
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Cancers
- MSK
- NMSK
- Pulmonary Edema
- Connective Tissue
- PNA
- Traumatic
- Alteration in Thoracic/Abdominal Pressure Balance
- Others:
S/S Restrictive Lung Disease
- Tachypnea OR dyspnea
- Dry, nonproductive cough
- Cachectic
- mm wasting/atrophy
- Hypoxemia
- DECd breath sounds
- DECd PFT
- DECd diffusing capacity
- R. sided HF or cor pulmonale
- DEC TLC
- INCd work breathing
More S/S Restrictive Lung Disease
See chart

Changes in Lung Volumes and Capacities
Restrictive vs. Normal vs. Obstructive
see chart

PFT
see chart
NOTE: SAME but smaller ratios
NOTE: FEV1/FVC for Restrictive will be HIGHER

Tx Measures for Restrictive Diseases
- Supplemental O2
- Exercise
- CORTICOSTEROIDS—-control Inflammation!!! (you will see this OFTEN)
- Smoking cessation
- avoid exposure to irritating stimulus/noxious stim.
- Pulm hygiene tech’s ===secretion mgmt
- diaphragm strenghtening
- IMT
- good nutrition
- cytotoxic drugs
- lung transplant for IPF
Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Babies
old name== Hyaline Membrane Syndrome
What is it???
- dis. of prematurity OR lack of complete lung maturation
- lack of surfactant (allows alveoli to open/close) and inadequate surfactant production
- Diffuse micro-atelectasis
Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Tx
- Mom’s Milk!!!
- surfactant replacement therapy
- Extracorpeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
- blood O2’d outside of body
- Corticosteroids to mother BEFORE birth
Normal ventilation
vs.
Ventilators
Normally==> Neg. pressure—suction
Ventilators==> Pos. pressure–PUSH air in–barotrauma–this irritates lungs
What do we WANT to see on Chest X-ray for babies??
Sail Sign
+ Respiratory Distress Syndrome
*babies
see pics

Clinical Manifestation of Respiratory Distress Syndrome
See chart

Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Dysplasia==altered growth/production
what is it and what is the cycle?
- Chronic respiratory distress syndrome > 1month
-
Cycle:
- Scarring of lung tissue –> fibrosis–> thick alveolar walls–> segmental atelectasis (collapsing of alveoli)
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic== do not know where came from
Fibrosis==scar tissue, difficulty O2 diffusion
What is it and Etiology??
- Inflammatory process of alveolar wall
-
Etiology:
- patchy focal lesions scattered, chronic inflamm. changes –> epithelial damage–> scarring –> become fibrotic
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Tx
- Corticosteroids
- you will see this w/ anything INFLAMMATORY
- Cytotoxic drugs
- smoking cessation
- maint. adequate oxygenation/ventilation
- good nutrition
-
for EVERY lung disease
-
supports extra mm contracts.
- extra breathing tools!
-
supports extra mm contracts.
- w/ Restrictive disease, pts are using a LOT of fuel so NEED TO EAT but they do not WANT to eat
-
for EVERY lung disease
- Tx infection
- lung transplant
Idiopathic Pulm Fibrosis
Normal lungs vs. Lungs w/ Pulm Fibrosis
see pics

Chronic Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis
*starts w/ irritant*
- interstitial lung dis. caused by inhalation of coal dust==fibrotic changes in lungs
-
Tx
- cessation of exposure
- nutrition
- intervents to ensure adeq. oxygenation/vent.
- progress. ex.
Asbestosis
*macrophages try to eat asbestos===MORE inflammation
asbestos is indestructible
- Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrotic disease due to inflammation from asbestos exposure
- long latency pd. after exposure of 15-20yrs
-
Tx: no cure
- symptomatic support
- dis. progresses even when exposure ceases
Bronchiolitis Obliterans
Popcorn lung disease
*attacks DISTAL airways—-> terminal bronchioles
- fibrotic lung dis. affects small airways
- Pediatrics: assoc’d w/ viral infection
- Adults: assoc’d w/ toxic fume inhalation, viral, bacterial, mycobacterial and connect. tissue dis.
- Necrosis of resp. epithel
- inner lining lungs
-
Tx:
-
Children
- supportive–> hydration, O2, postural drainage
- Adults
- O2, fluid balance, corticosteroids
-
Children
Atelectasis
What is it and types?
- Incomplete expansion of lung OR loss of volume
- Types:
- Primary
- Obstructive
- Post-op
- Compression/Collapse
- Chest radiograph shows opacification (whiteness) OR collapsed lung and elevated hemidiaphragm
Atelectasis
Prevention:
Tx:
- Deep breathing
- incentie spirometry
- coughing
- early mobility
- DEC sedation
Tx: chest tube
Mechanisms of Atelectasis
- Something pushing on lungs —cannot expand
- ==Atelectasis
- tracheal deviations
See pics
- Pneumothorax
- Air
- collapsed lung
- Hydrothorax
- Fluid
- Compression
- Tumor
- Obstruction

Open Pneumothorax
vs.
Tension Pneumothorax
- Open:
- Air can still get in and out
- Tension
- Life-threatening emergency
- One-way door
- Continue to inhale only bc no way for air out

Pneumonia
PNA
What is it and types
- inflamm process of lung parenchyma (site of gas exchange)
- Begins as infection in the lower resp. tract
-
2 types:
-
Community acquired
- CAP
- Hospital acquired
-
Community acquired
Pneumonia
Can be ____ and _____
Most common routes?
Can be bacteria and virus
-
Most common routes of infection:
- inhalation—breathe something in
- aspiration–choke–something down wrong tube==infection
Pneumonia
Tx
*we need the underlying patho.
- drug therapy
- antibiotics if bacterial
- O2
- Mech. vent OR noninvasive vent.
- Postural drainage
- Airway clearance tech’s
- must get fluid OUT
Bacterial Pneumonias
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Legionella pneumophila
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Staphylococcus aureus:
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- == MRSA ****
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Viral Pneumonias
- Cytomegalovirus
- CMV
- Influenza virus
- Flu
-
COVID-19
- Corona Virus
Fungal Pneumonias
- Pneumocystis carinii
- PCP
Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome
ARDS
**Diffuse—all alveoli filled w/ fluid
2 Characteristics:

- SEVERE hypoxemia
- acute respiratory failure
- INCd permeability of alveolar-cap membrane
- MORE permeable to fluid==hypoxia
***O2 Sats DEC!!!***
2 Types of Adult Resp Distress Syndrome
- Direct:
- injury TO lungs
- ex. ventilator
- injury TO lungs
- Indirect:
- outside lungs
- fluid from something other than lungs
- ex. burn victim—systemic
ARDS
Causes:
- trauma
- lung contusion
- drowning w/ aspiration
- aspiration
- drugs
- heroin, narcotics, amiodarone
- inhaled toxins
- smoke, high O2 conc’s on mech. vents, PNA’s
***lungs change from air-filled to fluid-filled organ
ARDS
Progression:
- Acute phase:
- resolves completely
- Acute phase:
- fibrotic subacute phase
ARDS and Refractory Hypoxemia
- No matter amount of O2 pt is on—> will NOT raise O2 lvls bc O2 cannot get thru
ARDS
S/S
see chart

ARDS
Tx
- Treat precipitating cause + underlying trigger
- flu, toxins, etc..
- Support adeq. gas exchange and tissue oxygenation
-
mech. vents
- forces fluid out thru (+) pressure==opens lungs up
- ECMO
- O2 blood outside body
-
Prone positioning
- Tummy Time—improves V/Q matching
-
mech. vents
- manage nutritional status and fluid bal.
- prevent OR treat comps
Cancer
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
What is it and Causes?
-
Malignant growth of abnorm epithelial cells
- proliferate unchecked
-
Primary Causitive factor is cigarette smoking
-
Other causes:
- occupational agents
-
Other causes:
Cancer:
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Types:
- Small Cell
- Non-Small Cell:
-
Adenocarcinoma
- non-smokers, females
-
Squamous Cell
- smokers, men
-
Adenocarcinoma
Cancer
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
TNM:
- Primary tumor, nodal involvement, metastatic presence
Lung Cancers often metastasize to other organs
- bc lungs are filled w/ everything cancer wants
- Cx in lungs can go anywhere
-
Iatrogenic fx’s
- can be Cx

Cancer
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
TONS S/S
ex’s: pain @ night, pain doesn’t go away w/ anything
see chart
just have a relative idea

Cancer
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Risk Factors:
- Environment:
- smoking
- 2nd hand smoke
- occupation, air pollution
- Nutrition
- free radicals
- Genetics
- Age
- Pulmonary Lung Dis.
Pleural Effusions
remember fire in the WALL example
- accumulation of fluid w/in pleural space/lining
- fire in the WALL
- disruption in balance of pleural fluid reabsorption
Pleural Effusions:
2 types of Fluids/Effusions
- Transudative Effusions– fluid in/out
- assoc’d w/ hydrostatic pressure in pleural caps
- more CHF
- assoc’d w/ hydrostatic pressure in pleural caps
- Exudative Effusions–comes from inflamm.
- assoc’d w/ INC in permeability of pleural surfaces
Pleural Effusions
Tx
- Target underlying cause
-
Dx thoracocentesis
- see pics
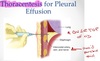
*NOTE: Quicker accumulation of fluid===worse/poorer outcomes
Pleural Effusion
Where exactly is the fluid accumulating???
see pics

Sarcoidosis
You should immediately think…
Specific—-GRANULOMAS ===focal points of inflammation
Sarcoidosis
- Autoimmune multisystem disease characterized by presence of Granulomas in many organs
- Affects: YOUNG 20-40 yo and women
- 90% pts have lung involvement
3 Distinct Stages of Sarcoidosis
- Alveolitis
- Formation of well-defined granulomas
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
Sarcoidosis
Tx
- Corticosteroids
- remember granulomas are focal pts of inflammation—–corticosteroids for inflamm!!!
Vaping-Induced Lung Disease
Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems
ENDS
what specifically should you remember???
Solid vitamin E in lungs!!!
Vaping-Induced Lung Disease
Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems
ENDS
Vit. E Acetate Theory
- Vit. E cuts well w/ nicotine or weed
- theory is Vit. E converts BACK to solid IN lungs
Vaping-Induced Lung Disease
Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems
ENDS
Pt present/CT
- Pt. Presentation
- wheezing/dyspnea
- CT scan shows:
- acute eosinophilic pneumonia
- diffuse alveolar damage
- groud-glass opacity
Vaping-Induced Lung Disease
Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems
ENDS
Patho. Findings
- Giant-cell interstitial PNA
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage
Pulmonary Edema
Fire in the ROOM
Inc in amt of fluid w/in the lung
Pulmonary Edema
2 Primary Causes:
- INC pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure
- L. sided CHF
- Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
- INC in alveolar capillary membrane permeability
- ARDS
- Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary Edema
Tx
- aimed @ DECing cardiac Preload and maint. oxygenation
what sounds will you hear w/ pulmonary edema?
Crackles
INC voice sounds
LOTS of consolidation
S/S Pulmonary Edema
see chart

Cervical Spinal Cord Injury
C3, C4, C5 keeps
Keeps the Diaphragm Alive!!!!!!!
NMSK cause of Restrictive Lung Disease
C/S Injury
SCI
- damage to OR interruption of neuro. pathways contained in SC
-
Cervial Injuries:
- lead to expiratory mm paralysis/weakness
- results in poor cough
- inspiratory mm paralysis/weakness
- inability to completely inflate lungs/hypoventilatin
- prone to atelectasis
- bc lose mm’s that open up lungs–diaphragm
- V/Q mismatching
C/S SCI
Tx
- strengthen + INC endurance of any remaining ventilatory mm’s
- active/passive chest wall stretch
- PNF
- Clear secretions
Cervical SCI and Paradoxical Breathing
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8TnrNrrEjuE
- OPP breathing pattern
- INHALE—stomach IN
- EXHALE—stomach OUT
Diaphragmatic Paralysis
NMSK cause of Restrictive Lung Disease
*lose Phrenic N. C3, C4, C5
- Loss or impairment of motor function of diaphragm due to lesion in the neuro or MSK system
- Cause commonly injury to phrenic N
Diaphragmatic paralysis leads to diaphragm pulled ______ and ant. ribs pulled_______
THIS RESULTS IN???
leads to diaphragm pulled UPWARD and Ant. ribs pulled INWARD
This results in alveolar hypOventilation
Diaphragmatic Paralysis
Tx:
- If unilateral involve…
- usually NO Tx
-
B/L involve…
- req’s lvl of mech. vent.
Kyphoscoliosis
MSK cause of Restrictive Lung Dis.
- Combo of:
- excess A/P and Lat. curvature of T-spine
- skeletal abnorms DEC lung compliance
-
**MOST ventilation occurs in upper lobes
- so now V/Q mismatch
Kyphoscoliosis
Over life-time
- Develop Atelectasis and R.side HF
Kyphoscoliosis
Sig. spinal curvature must be present before Pulm. sx’s develop
- Angles <70degs
- no pulmonary dysf.
- Angles 70-120degs
- some pulm dysf
- Angles >120degs
- SEVERE RLD and resp. failure
Kyphoscoliosis
Tx:
- Conservative
- orthotics + exercise
- Sx
- Harrington distraction strut bars
- Preventative + Supportive measures for pulm. compromise
Pectus Excavatum
MSK cause of RLD

*funnel chest
*connective tissue disorder
Pectus Excavatum
MSK cause RLD
- Funnel chest:
- congenital abnorm
- Sternal depression, DEC A/P diameter
- If SEVERE…
- DECd TLC, VC, MVV (max voluntary ventilation)
- MVV== tot. volume air exhaled during 12s of rapid deep breathing
Pectus Carinatum
- Pigeon breast
- Sternum protrudes ANT
- ***Assoc’d w/ prolonged childhood asthma***
Kyphoscoliosis/Pectus Excavatum
MSK causes RLD
PFT:
- in proportion to deformity….
- DECd volumes and capacities
- Diffusions usually normal
Kyphoscoliosis/Pectus Excavatum
Chest X-ray
- GROSSLY impaired due to severe spinal/chest deformity
- Compressed side visible w/ incd vasculature
Kyphoscoliosis/Pectus Excavatum
ABG:
- Hypoxemia
Kyphoscoliosis/Pectus Excavatum
Auscultation:
- DECd breath sounds over restricted side
- no air going in!
Kyphoscoliosis/Pectus Excavatum
Cardio:
- Potential for pulm HTN and R.sided HF
Scleroderma
Connect. Tissue cause of RLD
What is it?
- Progressive systemic sclerosis
- Progressive fibrosing disorder causes degen changes in:
- skin
- sm. blood vessels
- esophagus
- intestinal tract
- lung
- heart
- kidney
- articular structures
Scleroderma
In lungs?
- In lung appears as progressive diffuse interstitial fibrosis
Scleroderma
Tx:
- No effective drug intervention
- specific symptoms treated
- supportive care
Pregnancy
NOT A DISEASE CONDITION
- Cannot descend diaphragm efficiently bc baby
- progesterone INCs RR
see chart

Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
explain Obesity
- BW > 20% or more over ideal BW
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
Affect on Lungs:
- Extra tissue req’s add. O2
- Excess adipose tissue around chest wall DECs compliance of thorax
- LESS diaphragmatic excursion
-
LESS chest wall expansion
- shallow breaths
- Extra adipose rests on lungs:
- == inad. diaphragm use
- == stresses access. resp. mm’s
- == inad. diaphragm use
Pharmaceutical causes of RLD
- more than 350 drugs pot. cause RLD
Pharmaceutical causes RLD
Adversely Affect:
- lung parenchyma directly
- drug induced interstitial lung disease
- ventilatory pump
- ventilatory drive
- suppressed
- chest wall compliance
Pharmaceutical causes RLD
Ex’s
- O2
- >21%==Drug
- antibiotics
- anti-inflamm’s
- CV drugs
- Amyoteran
- Chemotherapeutic
- poisons
- anesthetics
- mm relaxers
- ilicit drugs
- vapes/Vit E
- nicotine/THC
- radiation to chest
****Remember- Inflamm==scar tissue==RLD
Comparing Obstructive (cant get air OUT) vs. Restrictive (cant get air IN)
- Obstructive
- cannot get air OUT
- vol’s/ratios DIFFERENT
- BIG/INC TLC
- INC RV
- Restrictive
- cannot get air IN
- vol’s REDUCED but ratios/vol’s compared to Normal are the SAME



