Respiratory Pathology Flashcards
Describe the normal lung anatomy.
- Right - 3 lobes
- Left - 2 lobes
- Airways - have cilia
- Bronchioles - pulls out into the alveolar spaces

What are the common non-neoplastic and neoplastic lung diseases?

Define asthma
A condition in which breathing is periodically rendered difficult by widespread narrowing of the airways that changes in severity over short period of time.
How has the prevalence of asthma changed?
Increased
What are the causes and association of astham?
- Allergens and atopy
- Pollution
- Drugs - NSAIDs
- Occupational - inhaled gases/fumes
- Diet
- Physical exertion - “cold”
- Intrinsic
Underlying genetic factors
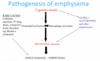
Describe the pathogenesis of asthma
- Pt exposed to allergen
- Antigens absorbed by APC
- Sit in respiratory epithelium presents to T cell
- Antibody response and recruits cells
- Reintroduction - magnified reaction
- IgE binds to mast cell
- Mast cells in airways activate and release mediators
- Secretion of mucus
- Leaky capillaries
- Acute spasm of bronchiole muscles
- Overtime:
- Tissue damage
- Increased mucous production
- Muscle hypertrophy

What does this image show?

- Mucus plug
- Overinflated lungs
- Mucus plug in-situ
Macroscopic features of asthma
Describe the histology in asthma.

Define COPD
- Chronic cough productive of sputum
- Most days for at least 3 months over at least 2 consecutive years
Casues of COPD
• Smoking • Air pollution • Occupational exposures
Describe histology of COPD

What do patients present with in COPD?

Define bronchiectasis
Permanent abnormal dilatation of bronchi
What are the common causes of bronchiectasis

What are the complications of bronchiectasis?

Define CF
- prevalence
- inheritance pattern
- mutation
- result
in lung - thick dense mucous

What organ systems do CF affect

What treatment is available for CF?

Define pulmonary oedema
What are the causes
Describe the pathology

Define diffuse alveolar damage
What is the pathogenesis (in adults and neonates)

Describe.

- Fluffy white infiltrates in all lung fields (“white out”)
- Lungs are expanded and firm, plum coloured, airless, often weigh >1kg
Diffuse alveolar damage
Describe the histology of diffuse alveolar damage.

What are the clinical outcomes of DAD

What are the infective agents causing pulmonary infections? What symptoms does it cause?