Respiratory Pathogens: Bacteria and Mycobacteria Flashcards
A 30-year-old female presents with high fever, sore throat, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly and fatigue. Infectious mononucleosis is suspected. Which of the is the most common lab testing method for diagnosing this condition?
A test for heterophile antibody, which cross reacts with antigens found on a variety of animal red blood cells
An unvaccinated 60-year-old man develops a sore throat and difficulties in swallowing while on 2 weeks long trip to rural India. Two days after his arrival in Mannitoba, he visited a local hospital. A tough, adherent gray fibrinous exudate in oropharynx along with bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy was noted on physical examination. Which organism is most likely responsible for patient’s symptoms?
Diptheria
Gram positive rods with granules
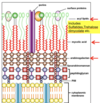
What is an important characterisitic of the streptococcus bacteria?
Gram Positive
Catalase NEGATIVE- Used to differentiate from (see panopto 9/10 42min)
What are syndromes that affect the upper respiratory tract?
- Common Cold
- Pharyngitis
- Influenza
- Diphtheria
- Sinusitis & Otitis media
- Rhinocerebral mucormycosis
- Epiglottitis
- Croup /Laryngitis
What are the syndromes that afect the lower respiratory tract?
- Whooping Cough
- Bronchitis/ Bronchiolitis
- Influenza
- Pneumonias –
- Typical and Atypical
- Community, Nosocomial, Occupational, Regional, Opportunistic
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
What are the physical defenses of the respiratory tract?
- Nose: hair, cilia, turbinates and mucus- filter dust and particles; Sneezing
- Change in direction of the airway
- Lymphoid tissue: Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring
- Normal flora
- Mucus and ciliated cells – coughing
- Respiratory secretions: lysozyme, sIgA, lactoferrin, mucus
- Alveolar macrophages
How do pathogens avoid immune defense?
- Bacterial adherence - surface structures
- (Avoid being caught up in the mucus and expelled out)
- Extracellular toxins – cytotoxins,
- Growth in host tissue – intracellular
- Evasion of host defense mechanism
- Capsules (avoid phagocytosis), existence in multiple types, production of IgA proteases
What are the gram postive bacterial respiratory pathogens?
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Staphylococcus aureus *
Bacillus anthracis
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
What are the gram negative bacterial respiratory pathogens?
Legionella pneumophila
Bordetella pertussis
Moraxella catarrhalis
Burkholderia cepacia
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Acinetobacter baumannii
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Francisella tularensis *
What are the bacterial repiratory pathogens (acid fast and non staining)?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (acid fast)
Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Chlamydophila psittaci
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Coxiella burnetti*
What are the fungal respiratory pathogens?
- Aspergillus spp.
- Blastomyces dermatitidis
- Coccidioides immitis
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Rhizopus spp.
- Mucor spp.
- Pneumocystis jiroveci
what are the parasitic respiratory pathogens?
Ascaris lumbricoides
Strongyloides stercoralis
Hookworms
Paragonimus westermani
Patient presents with sinusitis and otitis media. What pathogens can be at fault?
•Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Patient presents with sore throat, dysphagia, fever and swollen lymph glands in the neck in the middle of december. What pathogens could be the cause of these symptoms?
Pharyngitis
Adenovirus
Coxsackie virus
Epstein-Barr virus
Herpes Simplex virus
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Streptococcus pyogenes
A pateint with rhinocerebral mucorycosis could be infected with
Rhizopus spp.
Mucor spp.
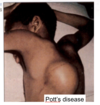
Patient presents with the symptoms shown. Diagnosis of Diptheria is made. What is the culprit of this disease?

Corynebacterium diphtheriae
A baby comes to the clinic with a cough and a high pitched air intake before each cough. What bacterial infection is causing this baby’s symptoms?
The baby has whooping cough. Bordetalla pertussis
What is the cause of tuberculosis?
mycobacterium tuberculosis
Causes of typical pneumonia
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Burkholderia cepacia
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Acinetobacter baumannii
Causes of atypical pneumonia
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae
- Legionella pneumophila
Causes of regional/ occupational/ opportunistic pneumonias
- Regional/Geographic Pneumonias
- Blastomyces dermatitidis
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Coccidioides immitis
- Occupational Pneumonias
- Bacillus anthracis
- Chlamydophila psittaci
- Opportunistic Pneumonias
- Aspergillus spp.
- Pneumocystis jiroveci
What are the characterisitics of the streptococcus genus?
Gram positive cocci
Catalase negative
In chains or pairs
Hemolytic patterns: α, β and γ
Catalase Test
Catalase producing organism + H2O2= O2 (bubble)+water
Classification of Streptococcus based on hemolytic properties
- Antigenic grouping – cell wall carbohydrate
- Lancefield groups: A-H, K-V (Group A is S. pyogens)
- Serotyping , Group A (GAS)- M protein – M1, M2 etc