Respiratory Images Flashcards
Identify

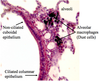
Respiratory epithelium (pseudostratified columnar epithelium)
- Thick basement membrane
- Prominent basal bodies under cilia
- Basal cells (dark) and goblet cells (clear) present

Identify

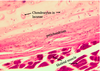
Trachea
- Tube lined with respiratory epithelium
- Regular rings of hyaline cartilage (connected dorsally by smooth muscle)

Identify

Tracheal mucosa closeup
- Lined with respiratory epithelium
- Thick basement membrane

Identify

Nasal fossa: two chambers in skull separated by bony septum
Arrow points to a sinus
Identify

Nasal fossa. Blank spot shows tooth germ
Identify

Nasal Fossa Details

Identify

Nasal fossa details

Identify


Identify

Nasal fossa detail

Identify

Nasal fossa, olfactory region

Identify

Nasal fossa, olfactory nerve detail

Identify

Nasal fossa, olfactory mucosa

Identify

Larynx
- Vestibular folds are the false vocal cords (respiratory epithelium)
- True vocal cords (stratified squamous epithelium
- Separated by vocal folds

Identify

Larynx details
- Skeletal muscle articulated cartilage (for talking)
- Hyaline cartilage for support

Identify

Identify

Larynx, vestibular fold

Identify

Larynx, vestibular fold epithelium
- Has serous glands in lamina propria to provide a moist environment for air before the true vocal cords

Identify

Larynx, vocal cord detail

Identify

Larynx, vocal cord mucosa detail

Identify

Larynx, detail of epithelial transition in vocal region

Identify

Lung (4x) with alveoli
Identify

Lung, detail of pleura
Alveolar septum: thin wall for gas exchange from air to blood

Identify

Lung, bronchus
- Cartilage is irregular rings or plates
- Smooth muscle in irregular bands - causes wavy (folded) mucosa

Identify

Lung, regular bronchiole
- No cartilage
- Prominent smooth muscle - causes folds
- Less cilia than in bronchi