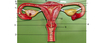
Reproductive System Anatomy Flashcards
Identify the Structure
Scrotum
Identify the structure

Glans penis
Identify the structure

Prepuce (foreskin)
Identify the structure

External urethral orifice
Identify the structure

Inguinal canal
Identify the structure

Corpus cavernosum
Identify the structure

Corpus spongiosum
Identify the structure

Testes
Identify the structure

Seminiferous tubules
Identify the structure

Rete testes
Identify the structure

Epididymis
Identify the structure

Vas deferens
Identify the structure

Vas deferens ampulla
Identify the structure

Seminal vesicle
Identify the structure

Ejaculatory duct
Identify the structure

Prostate gland
Identify the structure

Bulbourethral gland
Identify the structure

Urinary bladder
Identify the structure

Prostatic urethra
Identify the structure

Membranous urethra
Identify the structure

Penile urethra
List the major components of seminal fluid and their functions.
- Fructose - ATP production
- Prostoglandins - Sperm motility and viability
- Clotting Proteins - Coagulation of semen
List the major components of prostatic fluid and their functions.
- Calcium, Citrate, and Phosphate ions
- Enzymes - Clotting & Protein hydrolyzing
What is secreted by the bulbourethral gland and what is its function?
Mucus - Newtralizes urea and lubricates