Reproduction 1 - Male Reproductive System Flashcards
What are the 4 categories the male reproductive system can be grouped into?
- The External Genitalia
- The Gonads – Where gametes or sex cells are produced and also the site for the production of male sex hormones
- The Tube System – For transporting the sperm from the gonads
- The Accessory Glands – These support the sperm and lubricate the copulatory organs.
What are some of the organs of the male reproductive system?
- Testis
- Vas Deferens or Ductus Deferens
- Seminal glands
- Prostate
- Epididymis
- Bulbourethral glands
What is A?
Urinary bladder

What is B?

Ureter
What is C?

Vas deferens
What is D?
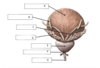
Seminal glands
What is E?

Prostate
What is F?

Bulbourethral glands
What is G?

Urethra
What is the name of the canal that the testis pass through during development?
Inguinal canal
What are the deep and superficial openings of this canal called?
Superficial and deep inguinal rings
What is A?

External spermatic fascia
What is B?

Cremaster muscle and fascia
What is C?

Internal spermatic fascia
What is D?

Deep inguinal opening
What are the 3 fascial layers of the inguinal canal from superficial to deep?
External spermatic fascia
Cremaster muscle and fascia
Internal spermatic fascia

What doing the inguinal canal carry?
This canal carries a group of structures known as the spermatic cord.
What are the 6 main structures of the spermatic cord?
1) Vas deferens
2) Testicular artery
3) Artery of the ductus deferens
4) Cremasteric artery
5) Pampiniform plexus
6) Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve
What are the ovoid testes suspended in the scrotum by?
Spermatic cord

What is the tough outer fibrous layer of the testis called?
Tunica albuginea
What are the 2 layers of the tunica vaginalis?
Visceral and parietal
What material is present between the 2 layers of the tunica vaginalis?
Cavum vaginale
What are 2 pathologies associated with the tunica vaginalis?
- Hydrocele
- Haematoceles
What is hydrocele?
Swelling in the scrotum that occurs when fluid collects in the thin sheath surrounding a testicle