Regional Final Flashcards
Indications for Intercostal Block
- thoracic or upper abdominal surgery
- rib fractures
- breast surgery
Overview of Intercostal nerve blocks
- need to perform blockade of two dermatomes above incision and two levels below
- does not block visceral pain
- does not provide adequate coverage for intraoperative anesthesia
Landmarks for Intercostal block
angle of rib
(6-8 cm lateral to the spinous process)
Risks of Intercostal block
- Pneumothorax
- local anesthetic toxicity
- hematoma
- nerve damage
- epidural anesthesia
Technique for Paravertebral
2.5 cm lateral to midline
longest lumbar transverse process
L3
Trigeminal Nerve
[overview]
5th CN providing sensory innervation to face
- preganglionic fibers exit brainstem and synapse with trigemincal (gasserian) ganglion
- post-ganglionic fibers exit to form:
- V1 - opthalmic
- V2 - maxillary
- V3 - Mandibular
most common trigeminal nerves to have pain
V2 (maxillary) and V3 (mandibular)
carbamezapine
treats seizures and nerve pain
(especially trigeminal neuralgia)
Complications of Trigeminal Nerve Block
- intravascular injection (carotid)
- persistent paresthesias
- total spinal
- profound facial numbness
indications for Supraorbital block
lower forehead or upper eyelid
(blepheroplasty)
amount of local anesthetic in Supraorbital block
2 - 3 mL
injection of LA inside the cone of the eye provides anesthesia and akinesia of ___ and ____
globe and extraocular muscles
Oculocardiac Reflex
[afferent]
trigeminal
oculocardiac reflex
[efferent]
vagus nerve
increase in parasympathetic tone
steps in oculocardiac reflex
pressure on eyeball
ciliary nerves and ciliary ganglion
gasserian ganglion
trigeminal sensory nucleus in 4th ventricle
vagus nerve
increase parasympathetic tone and bradycardia
highest incidence of oculocardiac reflex
children
Treatment of oculocardiac reflex
removal of stimulus
anti-cholinergics
check depth of anesthesia
sensory anterior 2/3 of tongue
trigeminal
sensory above vocal cords
internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve
(vagus)
sensory posterior 1/3 of tongue
glossopharyngeal
sensory below vocal cords
recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve innervates all muscles of the pharynx except _____
cricothyroid muscle
innervation of cricothyroid muscle
external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve
Transtracheal block indication
blunts gag reflex
nerves involved in gag reflex
afferent (CN IX) and efferent (CN X)
nerves in lumbar plexus
T-12 to L-4
nerves in femoral branch
L2 - L4

1= Femoral Artery
2= Femoral Nerve
3= Femoral Vein
4= Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
5= Inguinal Ligament
6=Sartorius


}In the PACU your patient complains of knee pain after a Total Knee Arthroplasty. A continuous femoral nerve block has already been placed. What do you do?
adductor canal block
Boundaries of Adductor canal block
sartorius
vastus medialis
adductur longus and magnus
Advantage of adductor canal block over femoral
sensory block only
no motor fibers involved; good for athletes that need to recover quickly

Adductor canal block

Indications for Saphenous nerve block
saphenous vein harvesting
or
supplementation for medial foot/ankle surgery in combination with sciatic nerve block

saphenous nerve block

nerves in sciatic branch
L4 - S3
largest nerve in the body
sciatic
landmarks for sciatic nerve block
ischial tuberosity and greater trochanter
sciatic nerve block needle insertion
4cm distal to midpoint between ischial tuberosity and greater trochanter
branches of sciatic nerve
tibial and common peroneal
which nerve causes dorsiflexion?
common peroneal
which nerve causes plantarflexion?
tibial nerve
boundaries of popiiteal fossa
bicep femoris
semi-tendenosis and semi-membranosus

Popliteal block
if two nerves are seen (common peroneal and tibial) move caudally

Which is most appropriate combination of nerve blocks for knee arthroscopy with a tourniquet:
transgluteal sciatic nerve block
and
lumbar plexus block
(5) nerves in ankle block
- deep peroneal
- posterior tibial
- saphenous
- superficial peroneal
- sural

- Saphenous
- Deep Peroneal
- Superficial Peroneal
- Medial plantar Branch of Tibial
- Lateral Plantar branch of tibial
- Tibial
- Sural
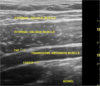
TAP
transversus abdominis plane
“triangle” in TAP block
latissimus dorsi
external oblique
iliac crest
indications for T.A.P.
large bowel resection
appendectomy or cholecystectomy
C-section
renal transplant
TAP ultrasound
indications for fascia iliaca block
anterior thigh and knee surgery


TEG
Thromboelastogram
R parameter on TEG
clotting time
(reaction time)
reasons for elongated R parameter
slow enzymatic reaction
factor deficiency or dysfunction
residual heparin
The R value represents which of the following
phases of hemostasis?
Activation of coagulation pathways and initial fibrin formation
alpha parameter
kinetics of clot formation
Which TEG parameters will best
demonstrate the need for coagulation factors?
R
Maximum amplitude in TEG
represents clot strength
what do you give for a low MA?
platelets
pain assessment in children
oucher
dose of oral acetaminophen
10 - 15 mg/kg
dose of oral ibuprofen
5 - 10 mg/kg
dose of naproxen
5 mg/kg
IV dose of fentanyl
0.5 - 1 mg/kg
IV dose of morphine
0.1 mg/kg
EMLA
lidocaine and prilocaine cream
- may cause methemoglobinemia in children < 3 months of age
most commonly used anesthetic
especially in children
bupivacaine
cardiotoxicity is ____ common than neurotoxicity in children
more
signs of cardiotoxicity
increased HR and NP
increased amplitude of T-waves on EKG
infants spinal cords end at ____
L3
neuropraxia
blunt injury to nerve
- myelin damage
- conduction slowing
axonotmesis
loss of axonal continuity
- endoneuriu intact
- no conduction
neurotmesis
complete interruption of the entire nerve
- loss of axonal and endoneurial continuity
delay between neuraxial block and heparin
1 hour
remove epidural 2 hours after last heparin dose
Lovenox
low-molecular weight heparin
- activates anti-thrombin accelerating interaction with factor Xa and thrombin
difference between Type I and II CRPS
type II has a defined nerve injury
TENS
transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
which nerve is spared in a 3-1 block?
obturator
nerves in obturator block
L2 - L4
Myasthenia Gravis
{overview}
resistant to Sux
- may be on pyridostigmine therapy
- destroy ACh receptors at neuromuscular junctions
Multiple Sclerosis
[overview]
demyelinating disease of the CNS
- do NOT perform spinal/epidural


