Red Eye Flashcards
What are causes of subconjunctival haemorrhage?
- Trauma
- Spontaneous
- Haemorrhagic disorders
- Valsalva pressure spikes
What investigation might you consider doing in somoene with a subconjunctival haemorrhage?
BP check
What is episcleritis?
A benign, self-limiting inflammatory disease affecting part of the eye called the episclera. The episclera is a thin layer of tissue that lies between the conjunctiva and the connective tissue layer that forms the white of the eye (sclera)

What causes episcleritis?
No cause in 70%, but can be:
- Rheumatic fever
- SLE
What are features of episcleritis?
- Pain
- Discomfort
- Sectoral redness

How would you manage someone with episcleritis?
- Systemic/topical NSAIDs
- Topical Steroids
- Lubricants
What is scleritis?
“Vasculitis of the Sclera”
A serious inflammatory disease that affects the white outer coating of the eye, known as the sclera

What are causes of scleritis?
- Autoimmune conditions (Wegener’s, polyangitis)
- Infections
What are symptoms of scleritis?
- Severe Pain
- Redness
- Photophobia
- Decreased vision
What are signs of scleritis?
- Generalised inflammation
- Conjunctival oedema
- Scleral thinning
- Decreased visual acuity
What tests might you consider doing in someone presenting with scleritis?
Check for autoimmune disorder
- ESR
- ANCA
How would you manage someone with scleritis?
Refer to a specialist
- Oral steroids
- Immunosuppression
What is the following?

Corneal foreign body
How would you manage a corneal foreign body?
- Remove foreign body under magnification - Cotton bud or needle
- Remove rust ring
- Treat corneal abrasion
What is the following?

Rust ring
What is a corneal abrasion?
Breach in the epithelium of the eye - occurs without keratitis
What is keratitis?
Inflammation of the cornea - marked by white area on the cornea, indicating a collection of white cells on the corneal tissue

What is important to do when examining someones eyes for a corneal foreign body?
Invert the upper lid to look for additional FBs
What clinical features would point towards a corneal abrasion?
- Pain
- Watering
- Photophobia
- Conjunctival injection
- Swollen lids
How would you investigate for a corneal abrasion?
Stain with flourescin and bright blue light (shone tangentially across the globe)
How would you manage a corneal abrasion?
- Look for conjunctival foreign bodies +Evert eye lid
- Topical antibiotics - chloramphenicol
- Cycloplegics
- Pressure pad and patch
When would you not use a pressure pad and patch in someone with a corneal abrasion?
If there is suspected infection
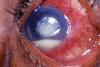
What is a corneal ulcer?
Also known as ulcerative keratitis - an inflammatory, or more seriously, infective condition of the cornea involving disruption of its epithelial layer with involvement of the corneal stroma.
Image - corneal ulcer with hypopyon
What organisms cause of corneal ulcers?
- Bacteria
- Herpes viruses
- Fungi - candidia, aspergillus
- Acanthoemeba
- Vasculitis - RA,
























