Red Cells, Haemoglobin, and Introduction to Anaemia Flashcards
(10 cards)
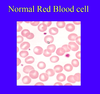
Describe the shape of the Normal Red Blood cell
- Discoid
- 7 micrometre diameter
- Big pink circles with central pallor (due to thinness)
- No nucleus or RNA: nucleus extruded during processing
- Big Blue Cells: polychromatic as they still have RNA in them
What does the shape of the RBC allow and what is the RBC function?
Unique shape and deformability Allows:
- Flexibility + movement (to squeeze through capillaries 3.5 micrometres)
- Increased areas for gas exchange
Function:
- Haemaglobin carriage (Haem repsonsible for most of Gas exchange)
- O2 transport: from lungs to tissues
- CO2 tissues to lungs
What determines the shape of Red blood cells and what happens if there are abnormalities in this?
RBC shape is determined by
- Membrane (bipolar lipid layer)
- Cytoskeleton proteins (spectrin, actin, ankyrin)
Abnormalities of these:
- Inherited rigid membrane → shortened life span of red cell
- Hereditary spherocytosis: a sphere, no biconcave disc
RBCs keep haemaglobin in a _______ state for?
RBCs keep haemaglobin in a reduced state to maintain osmotic equilibrium
- Glycolytic pathways produce ATP; maintains osmotic equilibrium
- HexoseMonoPhosphate Shunt produces NADPH: keeps Hb reduced
Inherited defects in this pathways → haemolysis and Red cell turnover
Lots of people have without realising and it’s not till they have an insult that they’ll have a haemolytic crisis
eg; G6PD deficiency
Within the RBC you have aminoacids that drive Haem production (this is because the Iron element receptor is switched on) How does this work
- Iron Element Receptor grabs Fe3+ from Transferrin in the blood into RBC
- Aminoacid precursors are assembled (know these)
- AT the stage of Pyrotoporphyrin , iron (Fe3+) gets added to create Haem molecule
- Assembled with Globin chains
- Makes a four (2 alpha and 2beta) Haemaglobin molecule

Haemaglobin and RBC properties
Primarily for gas exchanfe
HbA principle haemaglobin in adults
- 2 alpha + 2 beta + haem group
- Small amounts of HbF (fetal) and HbA2 also included in adult
- excess HbF in sickle cell anaemia
- Thalassaemia: defective production of Globulin chains (usually inherited)*
- Deficiency of Iron: Reduced production of Haem → low Hb*
Embryology of Red cells
- Primitive Red Cells forming in the Blood
- Form blood islands in the Embryo in AGM and Liver
- By 3rd trimester babies blood in in the bone marrow
HSM are at a ____ frequency but _________
Further down there’s a ____ frequency of specific cells, but these __________
HSM are at a low frequency but can self renew
Further down there’s a high frequency of specific cells, but these can’t self renew
- Not until the more mature/recognisable proeurythroblasts /pronormoblasts that you get the huge number of them seen in the bone marrow
- before pronormoblast all controlled by eurythropoietin with a high rate of E receptors
- Pronormoblast → Mature RBC take ~7 days

What are these

Pronormoblasts: Big diffuse cells, fine chromatin
More mature Cells have : dense pignotic (dying) nucleus.
Prochromatic (later) cells: increased Glucoforrin A.
Transferrin Receptor : Increased earlier on in the Pronormoblast stage as this is where iron feeds in
What happens to your Red cell production if you are hypoxic
- When your hypoxic and need O2 you want to drive eurythropoiesis with HIF-1 and HIF-1B and these will upregulate the transferrin receptor to supply iron to the system. More iron
- Also angiogenesis is upregulated for increased blood capillary growth. More capillaries
- Glycolytic Enzymes switched on for ATP/energy to the cell More energy

If too much O2 this is just down regulated


