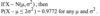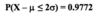Reasons for Incorrect Statements for the Midterm Flashcards

0, 1, 2, 3, 4

0, 1, 2, 3, …, +∞

If X is discrete quantitative

The equality of the two probabilities hold only if the population mean is equal to 0

then P(X=1)+P(X=2)+P(X=3) = 1.0–P(X=0)

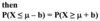
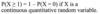
P(X ≥ 1) = 1 – P(X ≤ 1)
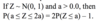
then 2P(Z ≤ a) – 1 = P( – a ≤ Z ≤ a)

then E(X) = np ≠ Var (X)

m is the population mean, but X ~ Po(m) is not symmetrical in general
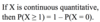
then P(X ≥ 1) = 1 – P(X ≤ 1)

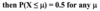
The distribution X ~ Bi(4, 0.5) is symmetrical with respect to 4.
is symmetrical with respect to 4 x 0.5 = 2
P(X≤4) = P(X<3)+P(X=4) if X ~ Bi(5, 0.5)
= P(X ≤ 3) + P(X = 4)
If X ~ Po(m), then Var(X) = m2
Var(X) = m
P(Z = 0) = 0.5 if Z ~ N(0, 1)
P(Z = 0) = 0


If X ~ Bi(4, p), then
P(X ≤ 2) = P(X ≥ 2) for any p.
Not for any p, only for p = 0.5.
If X ~ Po(5), then
P(X > 3) = P(X = 4) + P(X = 5).
then P(X > 3) = P(X = 4) + P(X = 5) + … + P(X = ∞).
If Z ~ N(0, 1) and a < 0, b > 0, then P(a≤Z≤b)=2P(Z≤b)–1.
P(a ≤ Z ≤ b) = P(Z ≤ b) – P(Z < a).
If X ~ Bi(n, p), then E(X) = np(1– p).
E(X) = np
If X is continuous quantitative, then
P(X ≥ 1) = 1 – P(X = 0).
P(X ≥ 1) = 1 – P(X < 1)