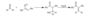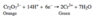Reactions Flashcards
Base-catalyzed addition of an Alcohol to an Aldehyde or Ketone
hemi-acetal or hemi ketal formation


B
Cyano groups are meta directors. Thus, attack of the sulfonate group would be directed towards the meta position, producing only compound [B].
Addition of Cl2 (or any halogen) to an alkene in aqueous solution results in the formation of a _______ or ______ (or halohydrin in general), with the halogen ending up on the cabron atom of the double bond with the _____number of hydrogen atoms.
chloro alcohol, chlorohydrin, greatest

C
SOCl2 converts alcohols into alkyl chlorides and carboxylic acids into acid chlorides.
Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O (aka the Jones reagent) is an oxidizing agent.
Finally, CH3MgBr is a Grignard reagent, which makes carbon-carbon bonds. Esters are not especially electrophilic, so they require a STRONG reducing agent.
LiAlH4 is a stronger reducing agent than NaBH4, so the best answer choice is C
The reagent used in this reaction is called ____

Jones reagent - used to oxidize primary alcohols to carboxylic acids

B
2-butene reacts with osmium tetroxide, OsO4 followed by workup with aqueous Na2SO3 to yield a cis-diol, 2,3-butanediol. Treatment of this vicinal cis-diol with periodic acid, HIO4 oxidizes the diol into aldehyde.


A
Adding a Grignard reagent to an ester results in a total of TWO additions of the reagent and a final product of a tertiary alcohol.
Addition of a Grignard Reagent to an Aldehyde

Ozonolysis using H2O2 of an internal vs. terminal alkyne

Describe thin layer chromatography.
What is the plate made out of? How will this effect molecules that are being used in the experiement?
Describe the RF for nonpolar and polar molecules in TLC.
In thin layer chromatography (TLC), the chromatography plate is made with polar silica gel.
Polar molecules will be attracted to the plate and travel less, while nonpolar will travel further
more polar = low RF
more nonpolar = high RF
Rank the following alkenes in order of DECREASING stability:
a. but-1-ene
b. (E)-but-2-ene
c. (Z)-but-2-ene
B > A > C
The greater the number of attached alkyl groups (i.e. the more substituted the carbon atoms on the double bond), the more stable the alkene it will be.
Further, it is more stable to have sterically hindered groups trans to each other, which is why (E)-but-2-ene is more stable than (Z)-but-2-ene.

Addition of water to an Aldehyde or Ketone forming a Hydrate


A
Resonance structures should only involve movement of electrons through p-orbitals.
In order for electrons to resonate through a carbon atom, it must be sp2-hybridized (aka have an available p-orbital). This means that any pi-bond, charge, or radical that only has sp3-hybridized carbon atoms adjacent to it will not be resonance stabilized.
Addition of a Grignard Reagent to a Ketone

Addition of a Grignard Reagent to an Epoxide
Adds to the less substituted side

A conjugate base will be destabilized by ____ _____ groups and will have a decreased acidity
A conjugate base will be stabilized by ____ _____ groups and will have an increased acidity
electron donating
electron withdrawing
Addition of a Grignard Reagent to an Ester
grignard reactions with esters MUST ADD TWICE

How to convert from an acyl chloride to an acid chloride?


A
This is an E2 reaction. Sodium ethoxide is a strong base which is reacting with a secondary halide, which means E2 will dominate.
Which will reduce an alkyne to a cis alkene? Which will reduce an alkyne to a trans alkene?
cis - H2 and Lindlar’s catalyst
Trans - Na or Li with NH3
Side-Chain Oxidation of Benzene to form Benzoic Acid

The strength of base is determined by the availability of the____ ____.
Electron-______ substituents ______ basicity while electron-withdrawing substituents ______ basicity.
In general, the basicity of amines follows the trend _______ > ______ > _____> ammonia.
electron pair, donating, increase, decrease
basicity of amines = secondary > primary > tertiary > ammonia
How many sigma (σ) and how many pi (π) bonds are present in pent-3-en-1-yne?
A. 3 σ and 3 π
B. 10 σ and 3 π
C. 7 σ and 4 π
D. 4 σ and 3 π
E. 5 σ and 5 π
B
DRAW THIS OUT

A
The first step is a standard oxidation using the Jones reagent. This oxidizes the secondary alcohol to a ketone and the primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid (shown below). The resulting β-ketoacid undergoes a decarboxylation reaction in acid and heat. This decarboxylation produces a ketone (answer A) and carbon dioxide.