Radiology Flashcards
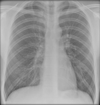
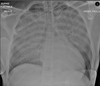
What does this CXR show? Where is the air bronchogram?

Right middle and lower lobe pneumonia. Air bronchogram circled.
Opacification in RLZ. Hemidiaphragm (lower lobe) and right heart border (middle lobe) are obscured.
What kind of pneumonia causes lobar opacification?
CAP
How can you differentiate consolidation from lung collapse?
Lung collapse will display volume loss- a shift in mediastinal structures, diaphragm, hila, fissures.
Consolidation may also have air bronchograms
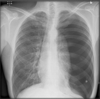
What does this CXR show? What is circled in red and green?

Shows left lower lobe pneumonia. Red: air bronchogram. Green: stomach and splenic flexure.
Increased opacification in left lower lobe, left diaphragmatic border reduced.
What is upper lobe diversion? What causes it?
Increased pulmonary vasculature in upper lobe, caused by heart failure.
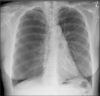
What does this CXR show? What is circled in green?

Bronchopneumonia with NG tube (green) in wrong position.
Multifocal opacification, more so in L than R. Air bronchograms present.
Where should a NG tube be positioned on CXR?
Should cross the carina and end below the diaphragm in the stomach
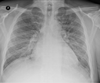
What does this CXR show?

Left lower lobe collapse
Triangular opacity that is obscuring the diaphragm and descending thoracic aorta. Depressed left hilar. Smaller left lung. Darker left lung.
What kind of pneumonia causes bronchopneumonia?
HAP
What does this CXR show?

Left upper lobe collapse.
Patient also has breast implant. Increased opacification in upper zone from collapsed lung. Left visible heart border and mediastinal shift. Left hilar point pulled up.
What does this CXR show?
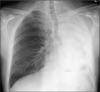
Complete left lung collapse. Entire hemithorax opacification.
Could also be due to pneumonectomy
How do you differentiate a white out due to lung collapse from pleural effusion?
There would be mediastinal shift in lung collapse.
What else should you look for if pleural effusion is present?
Lobulated pleural thickening due to malignant mesothelioma

What does this CXR show?

Multifocal well defined round opacifications. Cannonball mets due to pulmonary mets.
What are the common sources of pulmonary mets?
bronchus, breast, prostate, colon, kidney
Are nodules from infection ill defined or well defined?
Ill-defined e.g. miliary TB
What does this CXR show?

Lung cancer- ill defined, spiculated opacity in the LUL