Quiz 1: Lectures 2 to 5 Flashcards
(51 cards)
What does SLR camera stand for?
Single Lens Reflex camera
Name a few elements that form a digital camera
- lenses
- mirrors
- sensors
Explain the Pinhole Camera Model
imagine there is a point out in the scene at 3D position (x,y,z). That point projects through a small aperture (pinhole). The 3D point then projects uniquely to a 2D position (x,y) on the sensor.
The colour that the 3D point has on the 3D space, will also appear in the 2D point.
What is a pixel?
A pixel is a picture element.
It is formed by 3 8bits. Each 8bit value ranges from 0 to 255 and is associated with the RGB values.
In total, a pixel is 24 bits or 3 bytes.
What is a megapixel?
1 million pixels
Sometimes we talk about the definition of the pictures taken by a camera, what does 720p mean?
The size of an image 720p is more or less 1 megapixel. This image is a grid with 720 rows and 1280 columns.
p stands for “progressive scan”. (Compared to the “interlaced” method that was used at the beginning.)
Sometimes we talk about the definition of the pictures taken by a camera, what does 1080p mean?
The size of an image 1080p is more or less 2 megapixel. This image is a grid with 1080 rows and 2000 columns. It is considered HD (high definition).
p stands for “progressive scan”. (Compared to the “interlaced” method that was used at the beginning.)
RGB values
An RGB value ranges from 0 to 255.
It is a way of ordering “intensities” where 0 is the darkest and 255 the brightest.
Observe the image below, can you find the RGB values for the colours black, white, red, green, blue, cyan, magenta and yellow?
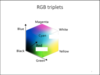
- Black (0,0,0)
- White (255,255,255)
- Red (255, 0, 0)
- Green (0, 255, 0)
- Blue (0, 0, 255)
- Cyan (0, 255, 255)
- Magenta (255, 0, 255)
- Yellow (255, 255, 0)
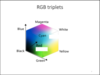
What does it mean for an image to be saturated?
Images whose colours are very close to the colours in the corners of the following cube.
(Colors are close to black, white, red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, yellow)
Light
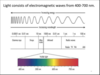
A beam of white light consists of superimposed beams of “coloured” light.
Light consists of electromagnetic waves from 400 to 700 nm.
Spectrum
How much light is emitted/absorbed/transmitted/reflected at each wave length.
Emission Spectrum
Distribution of the power of the light emitted by a light source at each wavelength
Absorption Spectrum
indicates fraction of the light that arrives at a surface or volume and is absorbed as a function of wavelength.
Transmission Spectrum
Indicated the fraction of the light that is reflected back in function of wavelength
Sensors in a camera
- The sensors in a camera form a 2D array
- Every grey square is basically colour blind
- To detect colour, there is a colour filter before the sensor.

Bayer Pattern
The pattern of the filters placed before the sensors is called Bayer pattern. Noticed that in this pattern, every 2x2 sensor filter there is twice as many green than red and blue filters.

How do we call the filter array for the sensors?
CFA: colour filter array
It is responsible for the colour sensitivity of the sensors.
Each coloured filter allows certain wavelengths to pass which is then transmitted to the sensor.
Exposure time
Modifies the amount of light absorbed by the sensor.
The longer the exposure, more light is absorbed and so the higher the intensity.
Can we modify the sensitivity of the sensor in a camera?
When the sensitivity of a sensor is modified, this is called gain or ISO.
This could help when you are shooting in dim conditions for example. A higher gain will allow you to get better intensity of the colours.
Aperture
The aperture is the space through which light passes to reach the sensor.
It is through this space that the image is projected into the sensor.
The aperture size can be modified. The bigger it is, the better the colour intensity.
What affect the RGB values of an image?
- exposure time
- aperture
- gain
What creates noise in the pictures?
Noise in the pictures might come from random photons emitted by the light source. Notice, this variation can be significant when the light levels are low.
Another possible source of noise is the sensor.
Analog-to-Digital Conversion
The signal (including noise) is digitized, namely quantized and then coded in binary.
A single sensor (which corresponds to a pixel) measures some amount of light energy and maps it to a real number intensity. This real number is then digitized (a number between 0 and 255) and stored as a 12-bit number.














