Quantitative Methods 2 Flashcards
(36 cards)
Discrete random variable
Number of possible outcomes can be counted
Continuous random variable
Cannot describe the possible outcomes, as there are an infinite number of possibilities
Binomial distribution - Bernoulli experiment

Bernoulli and binomial variances

Multivariate distribution
Specifies probabilities for a group of related random variables. If returns are modelled as a group, need to take into account statistical interrelationships
Standard normal random variable, Z (descriptive)
- Subtract mean of population from random variable.
- Divide the result by the standard deviation
Standard normal variable formula
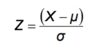
Z table example

Confidence interval

How to use z table for confidence intervals
Use normal distribution and z tables in reverse
Roy’s safety-first criterion
Risk portfolio value will fall bellow a minimum acceptable level
SFRatio

Lognormal distribution
Distribution of the natural log of a normally distributed variable. Bounded below by zero, skewed to the right. Asset prices bounded by zero
Normal/Lognormal distribution

Continuously compounded rate of return

Value at risk
Estimates how much a set of investments might lose given normal market conditions
Sampling issues
When your sample size is 30 or above, you have enough to count as statistically ‘large’
Central limit theorem
Distribution of sample means (DOSM) is approximately normal if the sample size chosen has to least 30 observations
Standard error (s.d. of sampling distribution of the statistics)

Confidence interval

T distribution
Used if population’s standard devision is not known. DOSM is t-distributed not normally disributed
T distribution graphical representation

Sample selection bias
Data availability leads to certain assets being excluded from the analysis
Look-ahead bias
Using information not available on the test date









