Quantitative Genetics Flashcards
(115 cards)
Definition
the rate of probability that two people with shared genes will develop the same organic disease
Concordance rate
Define
Multigenic inheritance
characteristic that is specified by a combination of multiple genes
Definition
relating to or occurring in a family or its members
Familial
A risk figure or recurrent risk can be calculated from what?
- Diagnosis and mode of inheritance
- Analysis of family pedigree
- Results of rests - linkage studies etc.
Define
Conditional probability
the probability of an event ( A ), given that another ( B ) has already occurred
Define
Discordant
showing lack of agreement
If the recurrance risk of autism in siblings = 6%
Incidence of autism in general population = 0.1%
What is the relative risk ratio for siblings?
60
Definition
an increased likelihood of developing a particular disease based on a person’s genetic makeup
Inherited predisposition
Define
Narrow-sense heritability
the degree to which a trait is passed from parent to offspring expressed as the ratio of the additive genetic variance to the total phenotypic variance (VA/VP)
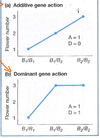
What does dominant genetic variance mean?
The animals/plants with the desired trait could be homozygous or heterozygous


Define
Index case
the first identified case in a group of related cases of a particular communicable or heritable disease
Definition
inheriting the same genetic characteristic
Concordant
How can you estimate narrow-sense heritability?
Comparing the offspring values against the averaged value for the two parents (mid-parent value)
What are the two common characteristics of quantitative traits?
- Many genes contribute to one trait = polygenic or multigenic inheritance
- The trait can be affected by the environment
What is heritability?
- The proportion of the total phenotypic variation (VP ) in a population that is due to genetic factors
- Different in different environments
Define
Monozygotic
Twins derived from a single ovum, and so identical


True or False:
Broad-sense heritability considers GxE interactions
False
Define
Empiric risks
The chance that a disease will occur in a family, based on experience with the diagnosis, past history, and medical records rather than theory


Define
Quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping
a statistical method that links two types of information—phenotypic data (trait measurements) and genotypic data (usually molecular markers)—in an attempt to explain the genetic basis of variation in complex trait
How can you calculate phenotypic variance (VP) from genotypic (VG ), environmental (VE) and genotype-by-environment interaction (VGxE ) variance?
VP = VG + VE + VGxE
Definition
when two different genotypes respond to environmental variation in different ways
Gene-environment (GxE) interactions