Q2-FUN11/Transcription and regulation of gene expression Flashcards
At what steps of transcription does regulation occur at?
- chromatin structure
- transciption initiation
- mRNA stability
- transcript processing
What are the 3 major functions of RNA within the cell?
copying genetic info from DNA, helps make ribosomes, help build new polypeptides
The structure of DNA is _____ while the structure of RNA is _________

DNA is located in the _______ while RNA is located in the _________

What types of RNAs are involved in transcription and translation?
mRNA, rRNA, tRNA

What are snRNAs?
small nuclear RNAs, they function in a lot of nuclear processes, inc. splicing pre-mRNA
What are ncRNAs?
they are non-coding RNAs. They function is a lot of different cellular processes, including
-regulation of gene expression.
- X-chromosome inactivation
- protein transport.
What distinct signals are encoded within the DNA sequence of a gene?
start and stop
Where does transcription start and end at?
it starts at the transcription start site (TSS, located at the end of the promoter region) and ends at the terminator site.
Each gene has a _________ promoter
unique
What are the two types of promoters?
basal promoter element and enhancer element
What is an enhancer?
Enhancers are regulatory DNA sequences that, when bound by proteins called transcription factors, enhance the transcription of a gene.
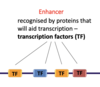
What is a basal promoter?
it is bound by RNA poly II and basal transcription factors

What is an example of a basal promoter?
TATA box - most common
2-30 base pairs from transcriptional site
can bind basal TFs and RNA poly II
What typically catalyses transcription?
RNA poly II
How does RNA poly II work?
it transcribes one of the 2 DNA strands of the gene. it reads its template from 3’ to 5’ and makes an RNA copy of 5’ to 3’.
It incorportates AGCU when making the mRNA copy of the DNA
What are the 3 stages of transcription?
initiation, elongation, termination
What happens in initiation of transcription?
RNA poly II binds to DNA and unwinds a 17-18 bp segment of the promoter. This segment is called the open complex.
Explain what happens during elongation of transcription.
RNA Pol II moves along the template until it reaches the terminator region. During this phase, an area of DNA under the RNA pol II stays unwounded. This unwounded part is called the transcription bubble and it moved along the DNA.
What 2 things happen during temination?
- transcription continues beyond the protein coding region (3’ UTR)
- endonuclease (enzyme that cleaves mRNA) cleaves abt 20 base pairs beyond the sequence
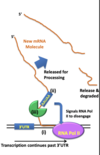
What is the primary transcript?
What are hnRNAs?
heterogenous nuclear RNA. bulk of transcribed RNAs that hasnt been processed
(processed means hasnt been 5’ capped and no poly A tail)
What are the 2 types of post translational mRNA processing?
5’ capping and 3’ poly A tail
explain 5’ capping.
add a 7-methyl-guanosine residue to the 5’ end of the mRNA.
the mRNA is catalysed by guanylyltransferase (capping enzyme) and then methylated by a methyltransferase enzyme
the 1st and 2nd nucleotides are also methylated





