Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides Flashcards
2 components of nucleotide:
- nitrogen base
- sugar
- phosphate group
Compare numerations in purines and pyrimidines.
In pyrimidines, numeration is clockwise. In purines, numeration is counterclockwise
How are pyrimidines similar to purines?
Purines are essentially a pyrimidine plus an imidazole.
Adenine

Guanine

Hypoxanthine
oxidized adenine

xanthine
oxidized guanine

Is caffeine a purine or pyrimidine?
Purine
In what pathways are the purines xanthine and hypoxanthine involved?
Purine biosynthesis and degradation
Why is the concentration of free nitrogen bases in the cell normally low?
They are normally found as nucleosides (sugar plus base) or as nucleotides.
Uracil

Thymine
methyl uracil

Cytosine

Orotic acid
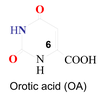
For what is orotic acid used?
An intermediate during pyrimidine biosynthesis
Hydrogen bonding between nitrogen bases contributes to their flatness. Why is this important?
It allows DNA to be more stable because flatness allows for base stacking.
Define nucleoside.
Nitrogen base + sugar
At which carbon do ribose and deoxyribose differ?
Deoxyribose does not have a hydroxyl group at carbon 2
In what configuration is the glycosidic linkage in nucleosides?
It is always beta, placing the nitrogen base above the sugar.
Describe the nucleoside nomenclature, and the exception for the rule.
uracil + ribose = uridine (pyrimidines end in -idine)
adenine + ribose = guanosine (purines end in -osine)
+ DNA = deoxyguanosine (dGMP)
exception: hypoxanthine + ribose = inosine
Nomenclature difference between nucleoside and nucleotide.
adenine base + sugar = adenosine
adenine + sugar + phosphate = adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
To which carbon of nucleosides do phosphate groups bind?
They can bind to the 3’ or 5’ carbon. In the case of cAMP, phosphate binds to both positions to cyclize the molecule. In DNA, phosphate binds to the 5’ carbon
Why are phosphates used to link nucleosides in DNA or RNA?
phosphoric acid can link two nucleotides and still ionize:
- the charge can stabilize the ester against hydrolysis
- the charge can retain the molecule within a lipid membrane, because the charge cannot pass the membrane
Phosphate monoesters are also very stable with a long half life, allowing for the formation of very long polynucleotides
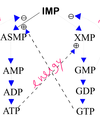
List the functions of purines and pyrimidines in the cell.
- storage of genetic information
- inhibitors of DNA synthesis
- universal source of energy
- activated intermediates of biosynthetic pathways
- components of coenzymes
- intracellular signaling molecules
- regulators of metabolism
- activated donors
Describe how nucleotides can act to treat HIV.
AZT and DDI both lack hydroxyl group at carbon 3’, so DNA synthesis cannot continue when they are present.

What nucleotide is a universal source of energy?
ATP
How do nucleotides act as activated intermediates of biosynthetic pathways, and what is an example?
Ex: UDP-glucose
- provides energy for glycosylation
- provides energy for storage of energy in glycogen

Describe nucleotides that are components of coenzymes.
NAD and FADH2 coenzyme cosubstrates contain nucleotides (adenine specifically)
Describe how nucleotides can act as intracellular signaling molecules.
cAMP – universal second messenger (regulates glycogen metabolism in response to glucagon, signals for degradation of glycogen)
Describe how nucleotides can be used as regulators of metabolism.
Allosteric effector AMP acts as a low energy signal to activate PFK in phosphorylation of F6P to F1,6DP
How do nucleotides act as activated donors?
- SAM acts as a methyl donor for histone methylation and DNA methylation
- PAPS acts as a sulfate donor
What are the sources of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides?
- de novo (major pathway)
- salvage pathway (minor pathway)
Describe abiotic synthesis of adenine.
Low efficiency, not used inside cells.
How was it determined that de novo synthesis of purines were made from small molecule precursors?
- pigeons and rats received radiolabelled bicarbonate, formate, and glycine
- excreted purines were isolated and chemically degraded, revealing labelled carbon and nitrogen in specific locations of the ring