Pulmonary Diseases of Vascular Origin Flashcards
What is the definition of an embolism?
A thrombus that has moved from its original location
can also refer to a foreign body
What is a clot?
blood that escapes in a space/potential space (ie.subdural region)
What pathology do you notice about the provided image?

thrombo emboli packed into the vessels

What is the “Lines of Zahn”?
layering of the thromboemboli within the vessel rather than homogeous
lighter: fibrin & platelets
darker: erythrocytes

What is usually the underlying reason a pulmonary embolism occurs?
usually predisposing condition that results in hypercoaguable state
What are primary conditions that lead to hypercoaguable state?
- factor V Leiden mutation
- prothrombin mutation
- antiphospholipid syndrome
What are secondary conditions that lead to hypercoaguable state?
- obesity
- recent surgery
- cancer
- oral contraceptive use
- pregnancy
- immobilization
- burns
- trauma
- fractures
What are the gross findings associated with pulmonary embolism leading to infarction?
- wedge-shaped & extend to periphery o lung
- initially red-blue
- the paler & red-brown after RBC lyse and hemosiderin is produced
- eventually a scar
What are 5 gross features that are indicative of a pulmonary embolism upon autopsy?
- distends vessel
- adherent to vessel
- rough surface
- Lines of Zahn
- may or may not take shape of vessel
What is shown in the provided image?
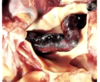
saddle clot pulmonary embolism
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

pulmonary infarct
What embolism feature is indicated by the arrows in the provided image?

Lines of Zahn
What are the small white areas shown in the provided thromboembolus & how are they formed?

fibroblasts come into the thrombus from the vessel wall, they will cluster together and make a lining (neovascularization), hopefully restoring blood flow
What is abnormal about the provided pulmonary tissue?
Infarct
very eosinophilic, no nuclei, only remnant of alveolar tissue
What are the 5 uncommon types of Pulmonary Embolisms?
- Fat and bone marrow
- Air embolism
- Septic embolism
- Tumor embolism
- Amniotic fluid embolism
What are the main causes of bat & bone marrow embolisms?
trauma
after chest compression
fat embolisms after long bone or pelvic fractures
What are the main causes of air pulmonary embolisms?
trauma
surgery
IV catheters
What are the causes of septic pulmonary embolism?
tricuspid valve vegetation
neutrophilic inflammatoyr reaction
What type of embolism is shown in the provided image?

fat/bone marrow embolism
What substance is the clear circle in the provided H&E stain?
This is suggestive of what pathology?

fat
fat embolism if it is in a vessel
What is the most common genetic muation seen in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension?
bone morphogenic proetin receptor type 2
BMPR2
autosomal dominance with incomplete penetrance
What are the common gross findings associated with pulmonary hypertension?
pulmonary artery atherosclerosis
right ventricular hypertrophy
What microscopic findings would you expect to see in someone with pulmonary hypertension?
- medial hypertrophy of arterioles & small arteries
- intimal fibrosis (pinpoint lumen)
- atheromatous deposits in pulmonary artery & major branches
- plexiform lesions

If you find many organized & recanalized thrombi, what was probalby the cause of the pulmonary hypertension?
What if it is present with emphysema & chronic bronchitis?
due to chronic thromboemboli
duet to COPD
What demographic is most commonly affected by idiopathic pulmonary hypertension?
Symptom progression?
Treatment?
- Demographic
- 20-40 yr
- women
- Symptoms
- initially
- dyspnea, fatigue, angina
- later
- severe respiratory distress
- right ventricular hypertrophy
- cor pulmonale
- initially
- Treatment
- therapy for driggers
- vasodilators
- lung transplant
What pathology is demonstrated by the provided histological slide?
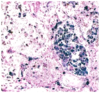
Diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage syndrome
lots of blue (positive for iron) macrophages that have been breaking down erythrocytes - indicates the process has happened over time or repetitively
What are the major pathological components of Goodpasture syndrome?
What is the most commonly affected demographic?
Treatment?
- Lung & kidney injury b/c autoantibodies against type IV collagen a3 chain
- inflammatory destruction of basement membranes in glomeruli & alveoli
- hemoptysis
- rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
- necrotizing hemorrhageic interestitial pneumonitis
- Demographics
- teens or 20s
- males
- smokers
- Treatment
- plasmapheresis - removes antibodies
- immunosupression
What are the gross findings from the lung of a person with Goodpasture synrome?
heavy lungs with red-brown consolidation
What are the microscopic findings from the lung of a person with Goodpasture synrome?
- necrosis alveolar walls
- alveolar hemorrhage
- hemosiderin-laden macrphages in alveoli (filled w/ iron)
- septal fibrosis, type II pneumocyte hypertophy
- immunofluorescent linear Ig deposits along septal wall basememtn membranes
What pathology is shown by the provided histological slide?
How do you know?
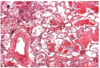
Goodpasture’s syndrome
thickened alveolar walls, prominent type Ii pneumocytes, many RBC & macrophages in alveoli
higher magnification provided

What feature of Goodpasture’s syndrome is beign depicted by the provided image?

linear immunoglobulin deposits along alveolar walls
What is the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis?
Clinical presentation?
Most commonly associated demographic?
Treatment?
- Pathogenesis
- intermittenet diffue alveolar hemorrhage
- pulmonary findings similar to Goodpasture
- Clinical presentation
- cough
- hemoptysis
- anemia
- Demographic
- young children
- Treatment
- immunosuppressive therapy
What is the pathogenesis of Polyangiitis with ganulomatosis?
Associated mutation?
Clnical presentation?
- Pathogenesis
- autoimmune disease of upper respiratory tract and/ or lungs
- T-cell mediated hypersensitivity to inhaled agents
- PR3-ANCA (C-ANCA)
- Necrotizing vasculitis
- granulomas of repiratory tract
- granulomas of small to medium vessels
- focal nectorizing glomerulonephritis
- Clinical presentation
- hemoptysis
- inflammatory sinusitis with mucosal granulomas
- ulcers of respiratory tract with associated granulomas
- alveolar hemorrhage
What pathology is shown in the provided images?

Polyangiitis with ganulomatosis
- Left:
- multinucleated histiocytes
- poorly formed granuloma on bottom left
- lots of inflammation in vessel wall (vasculitis)
- Right:
- large nodular centrally cavitating lesions
The geographic pattern shown in the provided slides is suggestive of what diagnosis?

Polyangiitis with ganulomatosis
necrosis (dark blue) & granulomas (circular)
lots of multinucleated cells


