Nasal Cavity & Ear II Flashcards
What aspect of the provided images indicate a diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma

Left: keratin pearl
Right: Intercellular bridges
What are the major risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck?
- Chronic smoking / alcohol use
- Sunlight & pipe smoking
- HPV 16 (oropharyngeal cancer)
What is the difference in prognosis for squamous cell carcinoma that is HPV (+) vs. HPV (-)?
HPV 16 (+) have greater long-term survival
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
What features of the photos indicate this diagnosis?

Squamous cell carcinoma
L: ulceration & induration of the oral mucosa
R: malignant keratinocytes invading underlying connective tissue stroma & skeletal muscle
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Verrucous carcinoma
“wart-like” filiform appearance
don’t tend to metastasize but can cause problems where they are
What is a detigerous cyst?
Treatment?
Cyst originating around the crown of an unerupted tooth
Complete remoal of the lesion is curative

What pathology is shown in the provided image?
Describe how it was identified.

Unilocular lesion most often associated with impacted 3rd molar (wisdom) teeth
What is a periapical cyst?
Treatment?
Cyst inflammatory in origin found at the apex of the tooth
removal fo the offending material
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

periapical cyst
What is a keratocystic odontogenic tumor?
Most commonly affected demographic?
Treatment?
Radiographically present as well-defined unilocular/multilocular radiolucencies posterior to mandible most common
10-40, males
complete removal of the lesion
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
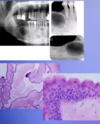
Keratocystic odontogenic tumor
locally aggressive
Multiple keratocystic odontogenic tumors is associated with what syndrome?
It is associated with what mutation?
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma
PTCH gene mutation
What is an odontoma composed of?
hamartoma
enamel, dentin, +/- cementum & varying number of tooth-like elements
What is shown in the provided image?

Odontoma
What are the features of an ameloblastoma?
benign, but locally aggressive with high recurrence rate
expansile, multiloculated “soap bubble” appearance
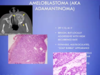
What patholgoy is shown in the provided images?
Describe the featues of each

Radiographically: “soap bubble”
Histologically : stellate reticulum, peripheral palisating (outside perpendicular to inside cells) with apical clear cytoplasm
What are the common causes of laryngitis?
allergic, viral, bacterial or chemical (tobacco smoke)
gastroesophageal reflux
systemic infections (tuberculosis & diptheria)
What is the cause of laryngotracheobronchitis?
Presentation?
“croup” in children - parainfluenzavirus
nonspecific respiratory symptoms & low grade fever
w/in 1-2 days hoarseness, barking cough & inspiratory stirdor
What are the common causes of laryngoepiglottis?
Presentation?
H. influenza, RSV, N. meningitidis, Strep
Medical Emergency in children
Cherry red epiglottis, drooling , tripod posture
What is reinke’s edema?
severe swelling of the vocal cords that occurs in heavy smokers
change in character of the voice & progressive hoarsness
What are singer’s nodules?
reactive nodules that occur in people who put great strain on their vocal cords
change in character of voice & progressive hoarsness
What can happen to individuals who put put great strain on their coval cords or have reflux irritation?
contact ulcers
change in character of the voice & progressive hoarsness
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Singer’s nodule
What patholoyg is shown in the provided image?

Reinke’s edema
What is often the cause of squamous papilloma & papillomatosis on the vocal cords?
Describe their appearance.
HPV 6 & 11
soft, rasperry-like proliferations
benign neoplasm
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
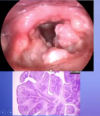
Squamous papilloma
multiple slender, finger-like projections supported by central fibrovascula core
covered in stratified squamous epithelium
What is the presentation of carcinoma of the larynx?
Most commonly affected demographics?
Treatment?
Persistent hoarseness, dysphgea & dysphonia
men, chronic smokers, 6th decade, alcohol use
Treatment: organ perservation early in disease (chemoradaition, w/ or w/o salvage laryngectomy later in disease)
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
check out keratin pearl on right side
What patholoyg is shown in the provided image?
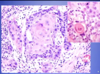
squamous cell carcinoma
keratin pearl
identify the different types of vocal cord nodules


What are the features of a branchial cyst?
Most commonly affected demographics?
On lateral neck from remnants of second brachial arch
20-40 yr olds
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Branchial cyst
both inside & outside is smooth
squamous-lined cysts
What are the features of a thyroglossal duct cyst?
midline cyst
remnant of the developmental tract
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
Histology: respiratory or squamous lined; pink round structures are thyroid follicles
What is the name of paragangliomas in the head & neck?
Most commonly affected demographics?
Mutation?
Carotid Body Tumor
painless masses 5th & 6th decade, men, high altitude living
Loss of function mutation SDH gene
What tumor is histologically identical to the paraganglioma?
Where does it arise?
Pheochromocytoma
arises in adrenal medulla
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Paraganglioma (carotid body tumor)
not brachial cyst b/c imaging shows a solid mass rather than a cystic mass
mass right at bifurcation of the carotids
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Paraganglioma
little nests of cells (“cell balling”) with delicate connective tissue stroma surrounding them
clusters separated by septa
Right: dense-core secretory bodies (black dots)
bottom: stain positive for chromogranin
What is xerostomia?
Causes?
dry mouth
old age, Sjogren syndrome, radiation therapy, lots of medications
What is Sjogren syndrome?
autoimmune disorder that causes dry mouth & is often accompanied by dry eyes due to lacrimal gland involement
Dry mouth can lead to what problems?
fissures, ulcers, dental carries, candidia infection ,dysphasia
What is sialadentitis & what are the 4 major causes?
Inflammation of the salivary gland
- trauma
- viral infection (mumps)
- bacterial infection
- autoimmune disease
What is sialolithiasis & what problem is it associated with?
Obstruction produced by a stone
bacterial sialadentitis (infection of major salivary gland)
Bacterial sialadentitis is often secondary to what 3 conditions?
Most common etiological causes?
- Ductal obstruction produced by stones
- Decreased secretory function
- decreased salivary secretions due to dehydration
S. aureus & Streptococcus viridans
What is the most common lesion of the salivary glands?
What do they look like?
Mucocele
flucuant blue hued nodole on lower lip
What is the cause of a salivary mucocele?
blockage or rupture of salivary gland duct w/ leakage of saliva in tissue
What is a ranula?
epithelial-lined cysts that arise when the duct of the sublingual gland has been damaged
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
What features helped you to identify the structure?
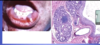
mucocele
Left: fluctuant fluid-filled lesion on the lower lip
Right: cyst-like cavity filled with mucinous material & lined by histocytes adn organizing granular tissue
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

ranula
If you find a squamous cell carcinoma in the salivary gland, what should you do next?
look for primary in oral cavity, nasopharynx, skin etc.
it is uncommon for primary squamous cell carcinoma to occur in the salivary glands
Where are the most common location of neoplasms of the salivary glands?
What is the relationship between rate of malignancy & gland sise?
Most commonly affected demographics?
- Location
- Parotid (65-80%)
- Submandubular (10%)
- Sublingual & minor glands
- rate of malignancy is inversely proportional to gland size
- sublingual 70-90%
- minor 50%
- submandibular 40%
- parodid 15-30%
- Demographics
- adults >> children
- higher rater malignancy in childrren
- females >> males
- adults >> children
Primary neoplasms of the salivary glands are more common in females than males, except what kind?
Wharthin tumor
Most primary tumors of the salivary glands are bilateral, what are the exceptions?
Warthin tumor
pleomorphic adenoma
acinic cell carcinoma
What type of tumor is a pleomorphic adenoma?
Where do they most likely occur?
Presentation?
benign tumor - grossly well demarcated & encapsulated
epithelial elements dispersed throughout in a matrix of myoid, hyaline, chondroid & osseous tissue
usually occur in the parotid
painless & slow growing
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

pleomorphic adenoma
notice it is kind of a lateral neck mass, but it is higher up - will move but is firm
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary gland
left: well demarcated w/ adjacent normal salivary gland tissue
right: (myo)epithelial cells within a chrondromyxoid matrix
Where are wharthin tumors located?
Most commonly affected demographics?
- Location
- parotid (restricted basically)
- 10% multifocal
- 10% bilateral
- Demographics
- smokers 8x more risk
- males > females
- 5-7th decade
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
Explain how you came to this conclusion.

Wharthin Tumor
big cystic spaces w/ solid stuff poking into them (looking finger-like) w/ viscous black gook
microscopically: well circumscribed neoplasm, centrally cystic, finger-like projections poking into the cyst
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Wharthin tumor
Left: Epithelial & lymphoid elements surroundign cystic space
Right: doule layer of eosinophilic (due to mitochondria) epithelial cells w/ underlying lymphocytes
Where do mucoepdermoid carcinomas mosly often occur?
What is the 5 yr survival rate of low grade? High grade?
60-70% in parotids
low grade- 5 yrs= 90%
high grade- 5 yrs= 50%
What is the most common form of primary malignant tumor of the salivary glands?
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
How can you tell?

mucoepidermoid carcinoma
nests of composed squamous cells, mucus secreting cells (eccentrically placed nuclei) & intermediate cells
Where do adenoic cystic carcinomas most commonly occur?
minor salivary glands (palatine)
infiltrative
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
How can you tell?

adenoid cystic carcinoma
cribiform pattern enclosing secretions
duct-like structures sharing epithelial walls
Where are acinic cell carcinomas most likely to occur?
Unique characteristics?
parotid > submandibular >>>>> other
second most common malignant salivary gland tumor in children
may be bilateral
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Acinic cell carcinoma
individual cells have zymogen granules, no salivary gland structure
Where are salivary duct carcinomas most commonly found?
Most commonly affected demographic?
They often contain what type of receptors & contain what muation?
- Location
- parotid > submandibular
- highly aggressive
- look very similar to breast cancer
- Demographic
- elderly males
- androgen receptors
- HER/NEU positive
Where is polymorphous adenocarcinoma found?
How common is it?
minor salivary glands, typically palate
2nd most common tumor of palate
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

polymorphous adenocarcinoma
ulcerating lesion of the oral cavity
histologically: looks like inocuous ducts (overrunning the tissue), but can be aggressive


