Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Other Non-fermenting Bacilli 9/4/15 Flashcards
What type of patients acquire Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections?
**Opportunisitic Pathogen
- Burn pts
- CF pts
- Hematologic malignancy pts
- Immunocompromised pts
- Infections typically occur at sites of moisture:
- Indwelling catheters
- Trach sites
- External ear
List major toxins produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and describe their principle effect on human cells.
- Exotoxin A:
- Blocks protein synthesis (like diphtheria toxin)
- Contributes to dermatonecrosis in wounds and tissue damage in lungs
- Exoenzyme S:
- ADP-ribosylating toxin
- Epithelial cell damage facilitates bacterial spread, tissue invasion and necrosis
***Elastase:
- Enzymes LasA and LasB act synergistically to degrade elastin
- Causes EG
- Degrades C’ and inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis/function
“The Three Es”
Describe morphology and habitat characteristics of P. aeruginosa.
Gram negative bacilli
NON-fermenter of glucose
Non-spore forming
Obligate aerobes
Motile with polar flagella
Mucoid polysaccharide slime layer
Good growth usually seen in 24hrs
Natural habitat: Water, soil, plants (unlike Enterobacteriaceae)
What are some common Pseudomonas Pulmonary Infections?
- Asymptomatic colonization
- Cystic fibrosis, chronic lung disease
- Severn necrotizing bronchopneumonia
-Most common cause of ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP)

What strain of bacteria is associated with the following infections:
- UTIs
- Ear infections: “swimmers ear”, malignant external otitis, chronic otitis media
- Eye infections: associated with eye cosmetics

Pseudomonas aeruginosa
List 3 disseminated P. aeruginosa infections.
- Bacteremia: Ecthyma gangrenosum
- Endocarditis: IVDA and tricuspid valve
- Osteomyelitis
Describe ecthyma gangrenosum associated with P. aeruginosa infection.
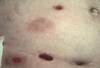
- Cutaneous lesions associated with bacteremia
- Hemorrhagic pustules/necrotic ulcers surrounded by erythema
- Usually in pts who are critically ill/immunocompromised
Discuss the association of Burkholderia cepacia and pulmonary infection in cystic fibrosis pts.
- Causes opportunisitic infections
- Pts with CF have abnormal mucus that adversely affects mucociliary clearance providing ideal niche for chronic lung infection
- Leads to intermittent pulmonary exacerbations: neutrophils and their elastases + cytokines = lung pathology
- Other pathogens that could cause chronic lung disease in CF pts: S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, Rhinovirus
Describe characteristics of P. aeruginosa that help with diagnosis.
- Culture:
- Metallic sheen in colonies
- Glucose non-fermenter
- Oxidase POSITIVE (unlike Enterobacteriaceae)
- Grape-like odor
-Produces pyocyanin
- Grows at 42 degrees Celsius
- Beta-hemolysis
What treatment options are available for P. aeruginosa infections?
- Combination therapy of cell wall active agent (i.e. penicillins) + aminoglycosides (for serious systemic infections)
- Resistant to many antibiotics due to changes in porins
- Lung transplants for CF pts with alginate formation
Which species of Burkholderia infects humans?
B. pseudomallei
Describe the gene defect and resultant pathology of cystic fibrosis.
- autosomal recessive
- mutations in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR): two non-working alleles
- regulates sweat, digestive juices, mucous
- thick, dry, sticky mucous = defects in mucociliary clearance = chronic lung infection
List diseases associated with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
- Opportunistic infection:
- Bacteremia
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
- Wound infections
- UTI
**Hallmark = life-threatening systemic infections in debilitated patients (usually malignancy)
The following symptoms are associated with what strain of bacteria:
- Chronic Lung Disease in CF pts
- UTIs
- Septicemia
- Other opportunistic infections
Burkholderia cepacia
What diseases are associated with B. pseudomallei?
- Melioidosis:
- Acute disease: septicemia with metastatic lesions (high mortality)
- Subacute disease: most common. TB-like pneumonia with cellulitis and lymphangitis
- Chronic disease: Localized chronic cellulitis.
The following symptoms are associated with what strain of bacteria:
- community acquired/nosocomial infections
- recovered from blood, urine, feces, vagina, sputum
- colonizes 45% of inpatient tracheostomy
Acinetobacter baumannii
-Most common gram-negative organism on skin of hospital personnel
What diseases are associated with Elizabethkingia meningoseptica?
-Pathogenic for premature babies
-Neonatal meningitis
- Nosocomial outbreaks traced to breast pumps used in hospital nurseries
- May cause pneumonia in adults (IC pts)
Name Non-fermenting bacteria that are listed as potential bioterrorist agents.
- Burkholderia pseudomallei: category B
- B. mallei??
Describe morphological characteristics of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
- BAP and MacConkey
- Oxidase NEGATIVE
- Some have yellow pigment
- Non-glucose fermenter
What treatment options are available for S. maltophilia infection?
***Very Resistant
-Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT) = Drug of Choice
What are the identification criteria for Acinetobacter baumanni?
- Coccobacilli
- Gram negative
- Good growth on BAP and MacConkey
- Oxidase NEGATIVE
- Non-motile
Name most common treatment options for A. baumannii.
- Resistance rates increasing
- Imipenem or meropenem
- Fluoroquinolone + amikacin or ceftazidime
Describe E. meningoseptica in colony plates.
- Oxidase POSITIVE
- Pale yellow pigment on BAP
- Poor growth on MacConkey agar
“The “queen” is too good for MacConkey”
What treatment options are available for Elizabethkingia meningoseptica infections?
- Very Resistant
- DOC = minocycline, rifampin, SXT, and quinolones


