Practice Lab Exam Flashcards
A goldfish presents to your office with small pustular lesions throught its epidermis and gills. What is the name (common or scientific genus) of the parasite causing the lesions?

Ich
Ichthyophthirius
Which life stage is found in the lesion?

Trophozoites
Live in galleries in the skin of fish
This protozoan is commonly found in the swine gut, but it can cause dysentery-like symtpoms in apes and humans. What is the genus of this parasite?

Balantidium (coli)
This is a life stage of a coccidian. What name is given to this stage?

Oocyst
Which of the following animals was the definative host… a cat or a llama?

You can see 2 sporocysts
= Isospora
= cat
(Remember Eimeria has 4 sporocysts)
(E = IIII) (I = II)
(Emieria = chickens & ruminants)
These parasites were found in ovine (sheep) bile ducts. Are these parasites tapeworms, flukes, nematodes, or acanthocephalans?

Flukes
(Fasciola hepatica)
Is the transmission the same for both parasites?

No!
Flukes: ingest snail while grazing
Tapeworms: ingest eggs or infected insects/animals
Nematodes: ingest eggs
Acanthocephalans: ingest eggs
This parasite was found in the gut of a duck. What is the genus of this parasite?

Echinostoma
After preforming a fecal floatation exam on a horse, you find many of these eggs. What is the genus of the parasite that produced these eggs?

Anoplocephala
(Tapeworm)
What is the intermediate host for the eggs in Q9? What is the larval stage of this parasite called in the IH?

Oribatid mites (pasture mite)
Cysticercoid (larval stage of tapeworms)
A client brings in their dog into the clinic after this parasite was seen protruding from the dog’s anus. The client, an avid fisherman, admits that he routinely gives his dog raw pieces of fish. What is the genus of this parasite?

Diphyllobothrium (latum)
DH: Bear, human, dog
IH: Copepod & pike
What is the intermediate host of this parasite from Q11?
Copepod & Fish (pike)
Two IHs!
You are called out to a small “mom and pop” range poultry operation because the owners report serious losses. The owners have noticed that the birds are having difficulty breathing. You nectropsy a few birds and see the following lesions in the trachea. What parasite is causing the disease?

Syngamus trachea
Gapewrom or Y-worm
How are these birds in Q13 becoming infected? Two ways.
- Ingestion of earthworms (paratenic host)
- Direct ingestion of eggs
You have been called out to a small farm. Your client’s chief complaint is that her old warmblood has had some serious coughing. You notice that the horse is in the same corral as a donkey. When you ask the client about the donkey, she responds that she bought the donkey several months ago to keep her horse company. What parasite may be causing the horse’s condition?
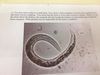
Dictyocaulus arnfieldi
(Donkey lungworn)
What diagnostic test would you run on the horse’s feces in order to verify the presence of the parasite in Q15?
Baermann examination of feces (larvae)
NO eggs in feces!
You visit a small pig operation where several pigs have been coughing. After running a fecal float (on fresh feces), you see the following. What parasite is infecting these pigs?

Metastrongylus apri
(Larvated egg in fresh swine feces)
How are the pigs becoming infeced in Q17?
Pigs eat earthworms
You see a few lesions by the mucocutaneous junction of the upper lip of a horse. The lesion is chronic granulomatus and has not healed. You examine some scrapings of the lesion and see what appear to be nematode worms. What parasite is likely causing the lesion?

Habronema
Where in the horse do the adult forms of the parasite in Q19 live?
Stomach
(Horse stomach worm)
You see the following on a cat fecal. What two species (not genus) do you see?

- Toxascaris leonina
(lighter, more space w/ smooth shell)
- Toxocara cati
(dark w/ rough shell)
What is the genus of this parasite?

Trichuris
Which egg would the female produce in Q22?

B
Bipolar plugs, thin wall, colorful
You see these eggs on a sheep fecal.
a) Name the two genra that could have produced the most commonly observed type of egg
b) Name the genra of the large egg
c) Name the genra of the egg in the bottom right corner

a) Haemonchus & Trichostrongylus (HOT)
b) Nematodirus
c) Trichuris








