Lab Exam Flashcards
Primates

Entamoeba histolytica
Ameoba pathogenic to primates
Infection in liver and brain can be fatal
Four (4) nuclei is diagnostic
Human

Entamoeba coli
Eight nuclei
Larger size than E. histolytica
NON-pathogenic
All animals + humans

Naegleria fowleri
Large dark nuclear endosome is diagnostic
Brain infection from swimming in hot water
Infects all animals + humans
Animals + humans

Giardia sp.
Trophozoite stage (rare in feces)
Tear drop shap and two nuclei
Remember zinc sulfate soolution
Animals + humans

Giardia sp.
Cyst stage
Four nuclei (only 3 may be visible)
More common in feces
Cattle

Trichomonas foetus
Undulating membrane is diagnostic
Direct smear of preputial wash from bull
Causes abortions in cattle
Chickens & turkeys
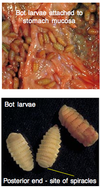
Histomonas meleagridis
Round parasite with central nuclei
Large space between parasite and host = diagnostic
Infects turkeys
Heterakis is a transport host (nematode)
Swine and humans

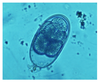
Balantidium coli
Trophozoite stage
Harmelss commensal of swine intestine
Pathogenic in humans (primates)
Pear shaped
Macro and micro nulcei plus cilia
Swine and humans
Balantidium coli
Cyst stage
Fish

Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
Trophozoite stage
Horse-shoe macromucleus
“White spot” in fish
T. stage lives in galleries in the epithelium
Fish

Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
Infective stage = tomite or swarmer
Red stained both macro and micro nucleui
Rabbits
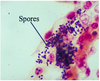
Nosema cuniculi
Dark stainging spores!
Gram positive staining
Infects rabbits
Chickens
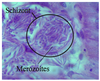
Eimeria tenella
Major coccida of chickens
Infection of cecum
Note: Schizonts containing merozoites (bananas)
Chickens

Eimeria tenella
Chicken cecum
Note: bloody casts
Cattle

Eimeria bovis
Left: unsporulated oocyst
Right: sporulated oocyst
4 sporocysts with 2 sporozoites each
Highly pathogenic bovine coccidia
Goose kidney
Coccida

Eimeria truncata
Infects goose kidney
Ocysts in urine!
Rabbits

Eimeria stiedai
Infects rabbits
Swine
Coccidia
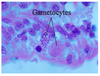
Isospora suis
Most pathogenic coccida of swine
2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites each!
Eimeria versus Isospora
Eimeria: cattle and poultry
4/2
4 sporocysts with 2 sporozoites each
Isospora: dogs and cats
2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites each
Swine and humans = both are infective
Mouse abdominal fluid

Toxoplasma gondii
Motile tachyzoites
DH: cat
Mouse brain

Toxoplasma gondii
Cyst with bradyzoites
Duck muscle

Sarcocystis sp.
Rice grains in muscle = sarcocysts
Duck is IH
DH are carnivores
Thin walled sporulated sporocyst in fecal float
All mammals
DMSO carbol fuschin stain
Cryptosporidium parvum
Pink stained oocysts
Small oocysts
4-8 naked sporozoites in fresh feces = NO sporocyst
Does not need to sporulated to be infective
All mammals

Cryptosporidium parvum
Oocysts on villi of small intestine
Humans
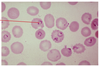
Plasmodium vivax
Human malaria
Ring stage in RBC with jewel and ring
Birds

Haemoproteus columbae
Pigeon
Blue staining on one side of RBC
Turkey
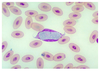
Leucocytozoon smithi
Parastized WBCs
Transmitted by black flies (fast water)
Turkey

Leucocytozoon sp.
Cracked appearance of cytomeres in the schizont
= Megaloschizonts
Black fly (Simulium sp.) in the vector
Dogs

Babesia canis
Tear-drop shape in RBCs
Vector: brown dog tick
Bovids
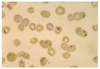
Theileria parva
Pleomorphic: varies in shape
Infects cattle (Africa)
DH: Ixodid (hard) ticks
Bovids

Theileria parva
Koch’s blue bodies = schizonts of Theileria
Inside macrophages
What characterizes flukes?
- Flat
- Suckers (acetabula)
- Blind gut = no anus
- Tegumant
- Hermaphroditic = monoecious
- No body cavity
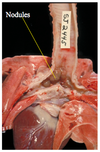
Cattle, sheep & humans

Fasciola hepatica
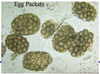
Common liver fluke of sheep adn cattle
Cepalic cone = diagnostic
Cattle, sheep & humans
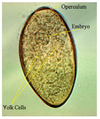
Fasciola hepatica
Large, amber colored eggs
Need fluke finder!
Cattle, sheep & humans
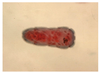
Fasciola hepatica
Miracidia
Penetrates snail (IH)
Cattle, sheep & humans

Fasciola hepatica
Lymnid snails
Intermediate hosts
Drainage ditches
Cattle, sheep & humans

Fasciola hepatica
Cercaria
Emerges from the snail
Encysts as metacercaria on vegetation
White tailed deer

Fasciola magna
NO cephalic cone!
Branched organs
DH: white tailed deer
Cattle & sheep

Dicrocoelium dendriticum
Lancet fluke
Parasitizes bile ducts esp. sheep
WIll NOT float
Not in MN
Cattle & sheep

Dicrocoelium dendriticum
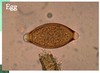
Egg
Mink, dog, cat + humans

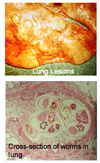
Paragonimus sp.
Lung fluke of mink, dog and cat
Mink, dog, cat + humans

Paragonimus sp.
Egg
Dark amber
Flattened on one side
Septum or feces!
Fish eating carnivores (dog)

Nanophyetus salmincola
Salmon poisoning fluke
Harbors Neorickettsia bacteria
Carnivores (dog)

Alaria sp.
Surface of small intestine
Carnivore eats frog or snake
Most common fluke seen in dog feces in MN!!!
Yellow large eggs
Chickens

Prosthogonimus sp.
Fluke of oviduct of fowl
Can show up in chicken eggs!
Birds

Echinostoma sp.
Flukes of birds and mammals
Spiny collar!!!
Birds and humans

Avian Schistosome
Swimmer itch
Cercaria
Fish

Black spot
Fluke metacercaria
Fish = IH
DH = belted kingfisher
No risk to humans
Insects

Horsehair worm
Freeliving stage of insect parasite
NOT nematodes
Pet may vomit after eating grasshopper
Tapeworm characteristics
- Flat
- Suckers
- Segmented!
- No gut
- Tegument
- Hermaphroditic
- No body cavity
Dog and cat

Tapeworms
Cyclophyllidean eggs
Hexicanth larvae are present in egg immediatly
Cats and dogs

Pseudophyllidean eggs
Tapeworms
Look just like fluke eggs when laid
Need time to develop hexacanth larvae
Which cestode life stage is most patogenic?
Larval stage
Humans, bears and dogs
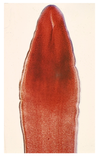
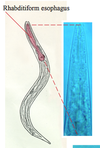
Diphyllobothrium latum
Pseudophyllideans (incubation)
LACKS suckers!
Infects humans, bears and dogs
Risk when eating raw fish
Predator-prey

Taenia sp.
Cyclophyllideans (larvated eggs)
Radially striated shell
Eggs in segments difficult to see on a fecal
Motile rice grains near anus!!!
Predator eats prey with muscle cysts
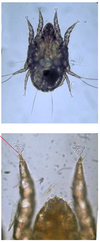
Predator-prey

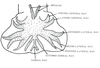
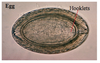
Taenia sp. scolex
4 sucker and 2 circles of hooklets = scolex