Practical 3- Staphylococcus, Micrococcus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Lactococcus, Anaerobic cocci, Lactobacillus, Erysipelothrix, Listeria. Flashcards
STAPHYLOCOCCUS:
- Habitat
- Morphology
- Staining
- Habitat:
- skin, mucous membrane, food, feed, plant, soil, water - Morphology:
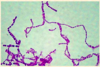
- coccus, clusters, bunches of grape - Staining:
- Gram-positive
S.Aureus
Staphylococcus:
-Culture:
Culture:
- simple: nutrient agar, nutrient broth
- pigment production: golden yellow, white, carotenoid
- haemolysis: β haemolysis (in some species double haemolysis), no haemolysis
Selective culture: 10% NaCl – mannitol – phenol red agar,
Na-tellurite – glycine – pyruvic acid – egg (Baird-Parker agar)

S.Aureus

Staphylococcus

Staphylococcus haemolysis

S.Aureus (salt-mannitol agar)

S.aureus (Baird-Parker agar)
Biochemistry of Staphylococcus:
Biochemistry:
-catalase: +, oxidase: -, fermentative
Extracellular enzymes: coagulase, fibrinolysin, hyaluronidase…
toxins: haemolysins, leucocidins ,enterotoxins, dermotoxin (exfoliative toxin) toxic shock syndrome toxins (TSST)
Staphylococcus :
- Antigens
- Resistance
- Pathogenecity
- Antigens:
- complex (surface proteins, polysaccharides)
- protein-A 7.
2.Resistance:
good
- Pathogenicity:
local suppuration, abscesses, arthritis, mastitis, metritis, dermatitis, septicaemia
Staphylococcus:
- Species, pathogenicity
- Virulence factors

Staphylococcus: Coagulase positive species:
S. aureus susp. aureus:
- biotypes, different hosts
- cattle, swine, horse, sheep, dog, poultry etc.
- MRSA: methicillin resistant S. aureus: human, dog, horse, pig
S. aureus subsp. anaerobius:
-sheep: Morel-disease
S. pseudointermedius:
-dog, cat: dermatitis, otitis externa
S. intermedius:
- dog, horse, birds: mucous membranes
- saprophyte
Staphylococcus: coagulase negatíve species:
S. epidermidis:
-wound infection (horse, dog)
S. haemolyticus:
- milk
- S. hyicus:
- a part of the strains is coagulase positive
- porcine exudative epidermitis
S. gallinarum :
-dermatitis
S. equorum:
-dermatitis
S. felis
- dermatitis

S.hyicus
MICROCOCCUS
- Habitat
- Morphology
- Biochemistry
- Pathogenicity
- Habitat:
- environment, mucous membrane, food, skin - Morphology:
- coccus, clusters (grape) - Biochemistry:
- decomposition of glucose is aerobic or missing - Pathogenicity:
- saprophyte
- to be differentiated from Staphylococci

M.Luteus
STREPTOCOCCUS
- Habitat
- Morphology
- Staining
- Habitat:
- skin, mucous membrane, food, milk - Morphology:
- spherical (coccus), chain, diplococci
- capsule: only on some species ,hyaluronic acid or polysaccharide - Staining:
Gram-positive

S. equi subsp. zooepidemicus

S.Pneumonia

S.Mutans
Streptococcus, Culture:
Culture:
fastidious:
-blood agar, serum agar
-some strains need CO2
selective culture:
-crystal violet, thallium-SO4 , esculin, blood (Edwards-agar)
haemolysis:
- α −haemolysis
- β −haemolysis
- no haemolysis (γ−haemolysis)

S. equi subsp. equi (Edwards agar)

Streptococcus haemolysis
Streptococcus: Biochemistry
Catalase -, oxidase -, fermentative
Utilisation of glycosides:
- esculin
- salicin
Extra cellular enzymes:
- fibrinolysin,
- hyaluronidase,
- nucleases,
- proteases
Toxins:
-some strains produce bacteriocins (probiotics)