Portal HTN/Ascites Flashcards
Describe the classic bleeding pattern of perforated esophageal veins in a pt with portal HTN?

They bleed heavily and constantly (like a hose on medium flow- can die quickly) most commonly at night
It so high pressure that you dont even see pulsations
What is the blood supply to the liver?
70% portal vein
30% hepatic artery
Describe resistance in the normal liver
Normally, it is a very low resistance system due to the presence of sinusoids as the major blood conduits
How does resistance change in a pt. with cirrhosis?
It is drastically increased due to:
- extensive fibrotic induced scarring
- changing of sinusoids into high-resistance capillaries
- increased GI blood flow in these pts.
What are the consequences of collateral circulation arising following portal HTN?
- Hormones (e.g. glucagon) that normally goes through the liver are not re-routed into systemic circulation where they have a number of effects including:
- increased splanchnic blood flow
- changing arterial resistance
This is where blood goes in portal HTN pts.

How does the splenic vein react to portal HTN?
Its part of the splanchnic circulation (high pressure) so it will shunt to the renal vein which will have normal pressure
How common are varices in cirrhotic pts?
About 50% will develop them, with 32% bleeding within 2 yrs (massive hemorrhage usually- major cause of death)
What are the traid of findings with varices?
- high pressure bleeding
- thrombocytopenia
- coagulopathy (impaired clooting factor synthesis)
Why is thrombocytopenia seen in portal HTN?
splenic sequestration
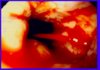
What is this?

Portal HTN gastropathy- the stomach will get congested in portal HTN

What are the major parts of treatment of portal HTN leading to variceal bleeds?
- endoscopic therapy to sclerose or band the varices
- splanchnic vasoconstriction to decrease blood flow to the stomach and intestine and decrease collateral BF via vasopression or somatostatin
- correction of coagulopathy
Why would somatostatin be used to constrict splanchnic blood flow?
it blocks glucagon, a potent vasodilator
How can portal HTN be addresses not in an acutely bleeding pt?
- beta blockers
- transjuglar portosystemic shunts
- liver transplant if needed




BP will be low!



What are the consequences of ascites?
- pressure develops on the stomach and diaphragm, leading to trouble breathing and eating
- hepatic hydrothorax (fluid upward through the diaphgram basically leading to pleural effusion)
- spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (often gram - rods from the GI)
How is ascites tx?
large volume paracentesis WITH IV albumin
-sodium restriction
- diuretics
- treat the liver disease/transplant
What is a common sequelae of ascites weakening the umilical area?
umbilical hernia


refractory ascites is a BAD prognosis



